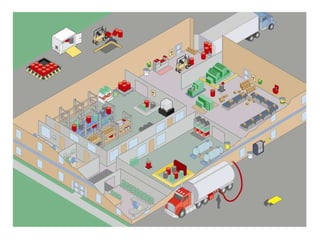
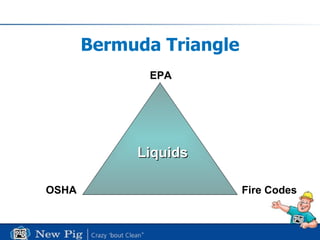
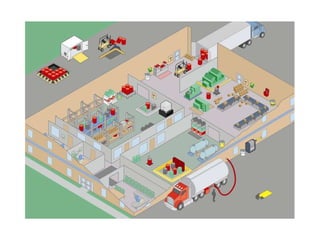
The document provides best practices for leak and spill control, covering regulations from OSHA, EPA, fire codes and more. It outlines regulatory requirements and offers tips for proper drainage covers, storage, spill cleanup, waste handling and containment to prevent violations under laws like NPDES, RCRA, SPCC and fire codes. Recommendations focus on prevention through good housekeeping, secondary containment, inspections and using absorbents tailored to fluid types.