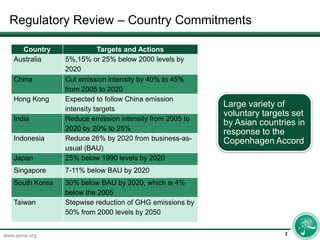
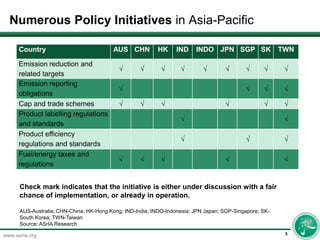
Regulatory developments are occurring across multiple countries in Asia. Several countries in the Asia-Pacific region like China, India, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, and others are either discussing or have implemented new policy initiatives. The document provides a table checking off which countries have certain regulatory initiatives either under discussion or already in operation.