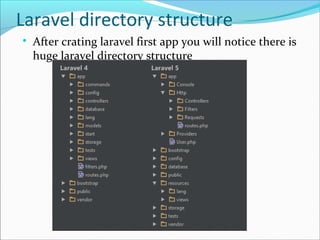
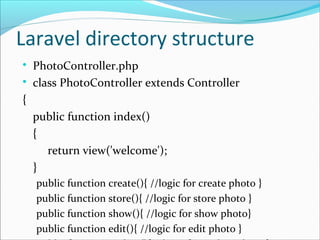
This document provides an overview of Laravel, an open source PHP framework, including its MVC architecture, requirements for installation, and directory structure. It explains that Laravel uses the MVC pattern with models for the backend logic, views for the frontend HTML/CSS, and controllers to connect models and views. It also outlines the steps to install Laravel and create a new Laravel project, and describes the main folders and files in the Laravel directory structure.