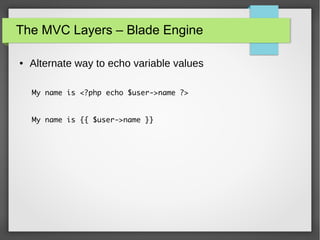
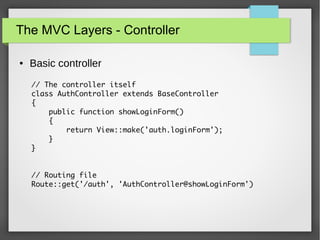
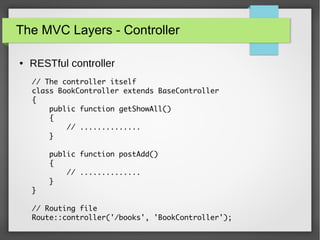
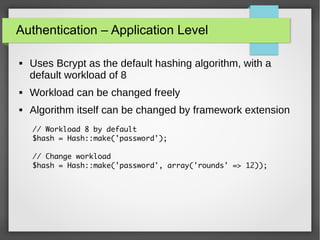
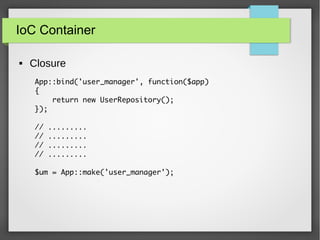
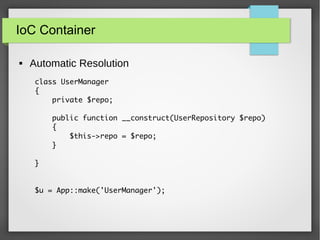
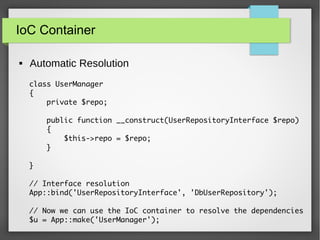
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to Laravel 4, covering topics such as installation, MVC layers, authentication, and the IoC container. It emphasizes the framework's objectives of rapid project development, adherence to SOLID design principles, and ease of use with features like Eloquent ORM and Blade templating engine. Additionally, it discusses advanced concepts like service providers and facades for dependency management and creating reusable components.








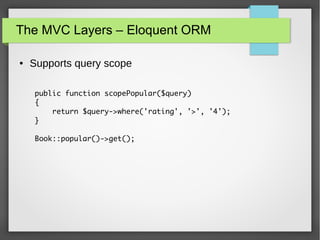
![The MVC Layers – Eloquent ORM
●
Supports accessors and mutators
// Accessor
public function getGenderAttribute($value)
{
return ($value == 'm') ? 'Male' : 'Female';
}
// Mutator
public function setNameAttribute($value)
{
$this->attributes['name'] = strtolower($value);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/laravelpresentation-131030215811-phpapp01/85/Intro-to-Laravel-4-16-320.jpg)