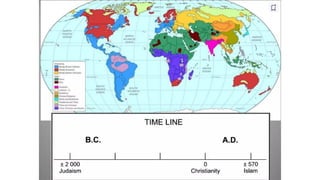
The document explores the intricate relationship between language and religion, highlighting how both serve as vital means of cultural expression and identity formation within communities. It discusses the characteristics of religion, the impact of language on religious practices, and the significance of specific languages in various faiths, such as Arabic in Islam and Sanskrit in Hinduism. Furthermore, the document notes the potential for misunderstanding and division caused by linguistic and religious differences, emphasizing the importance of respect for diverse religious languages.