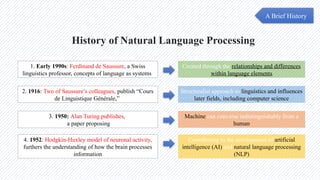
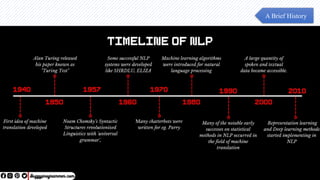
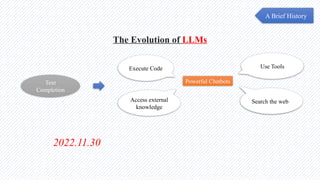
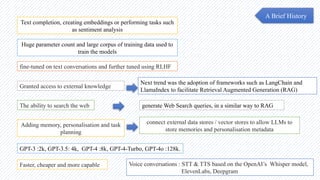
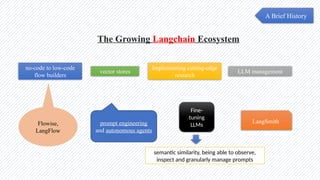
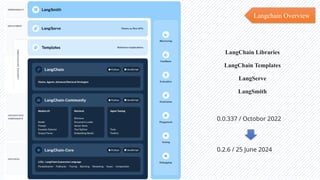
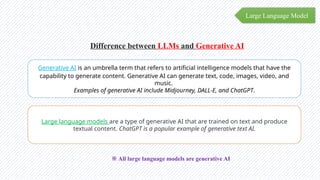
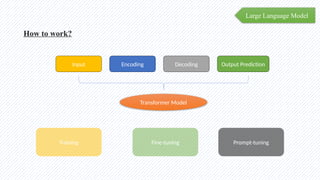
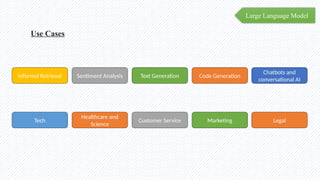
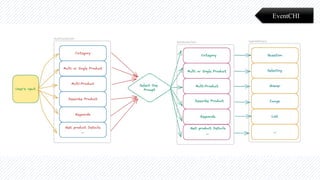
The document discusses the evolution of natural language processing (NLP), artificial intelligence (AI), and large language models (LLMs), tracing their development from early linguistic theories to modern applications of AI. It highlights LangChain as a framework for building applications powered by LLMs, emphasizing its tools and integration capabilities. The conclusion underscores the importance of understanding the synergy between LangChain and LLMs to enhance capabilities in various technological fields.