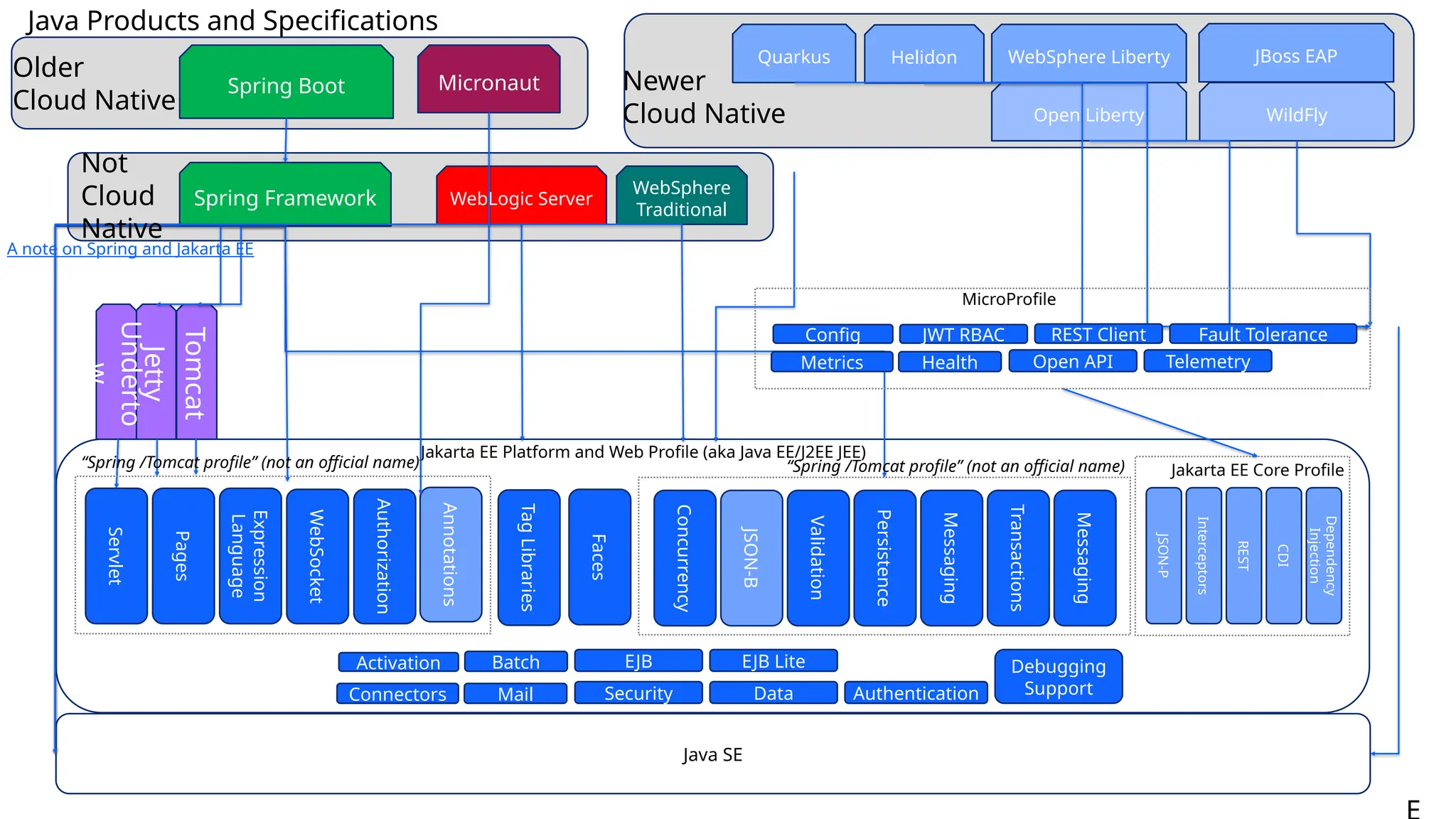
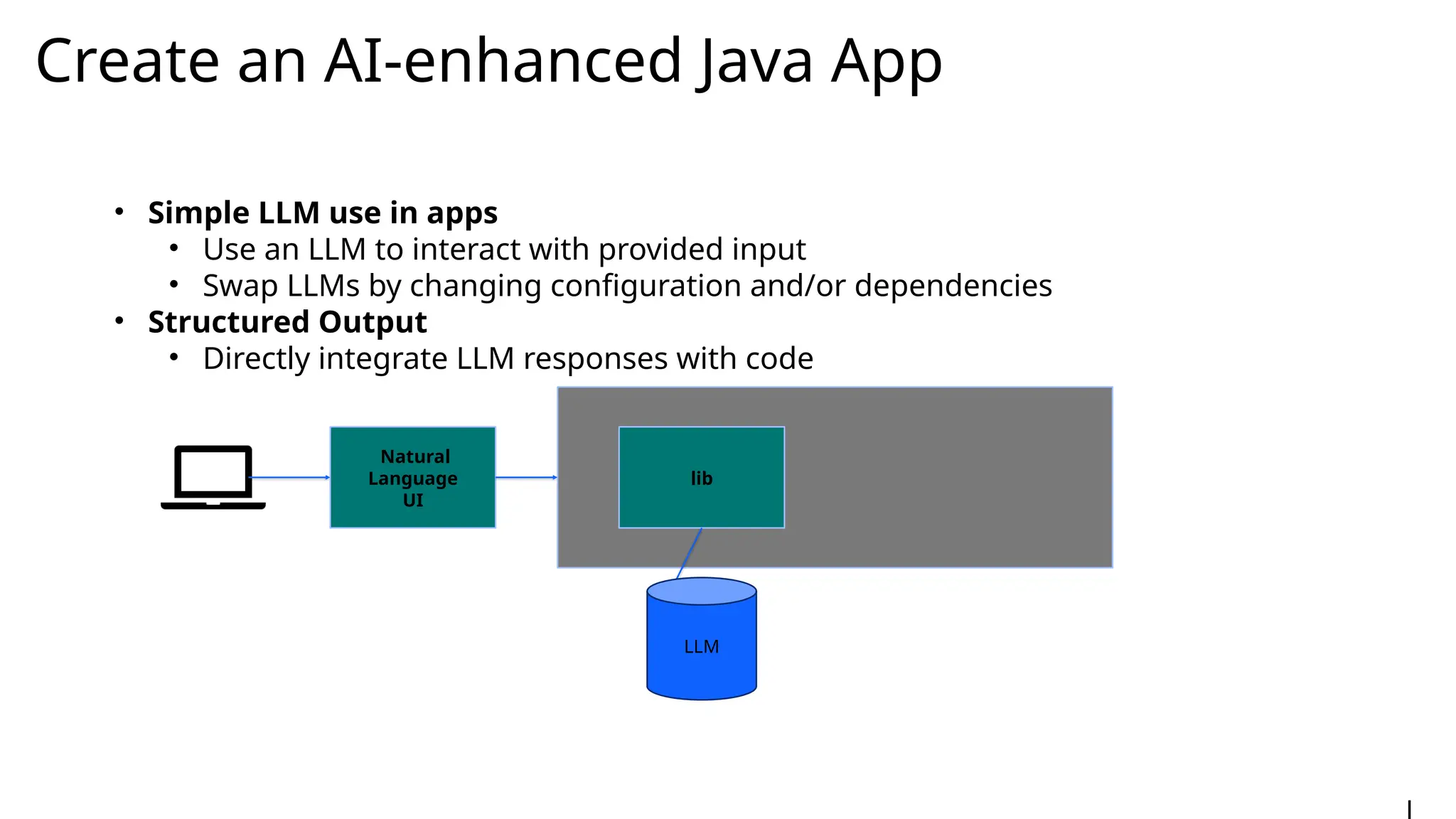
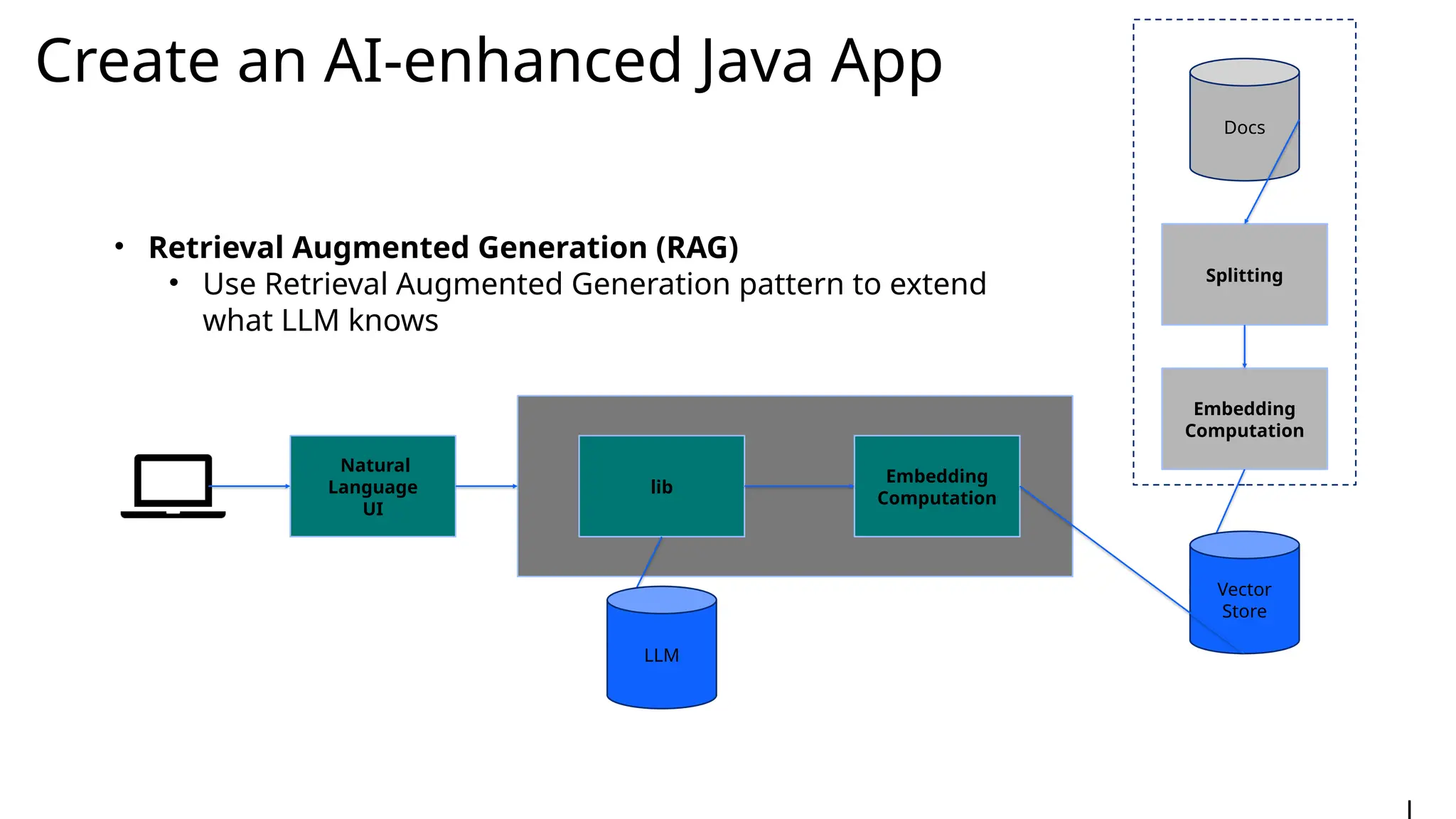
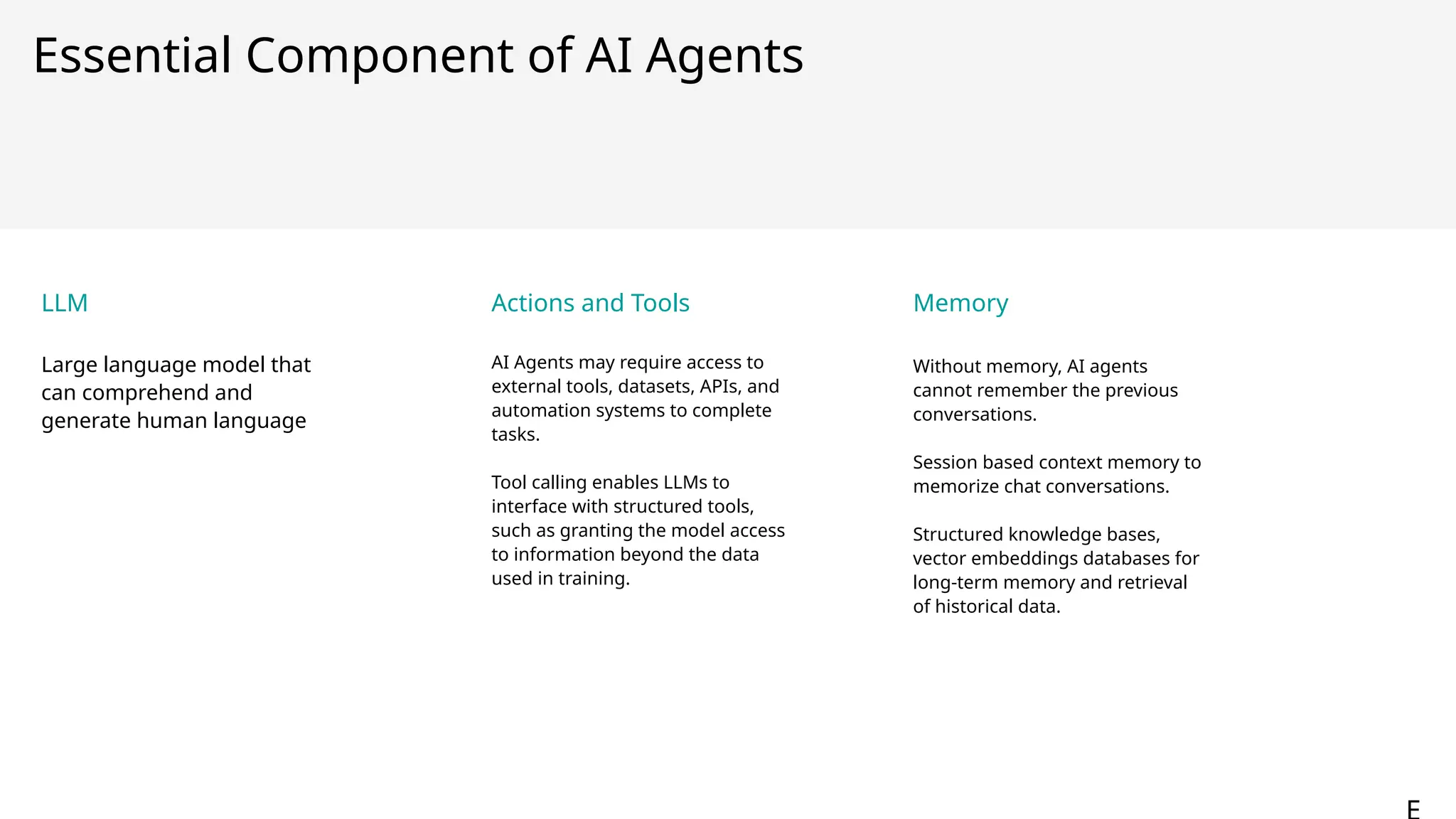
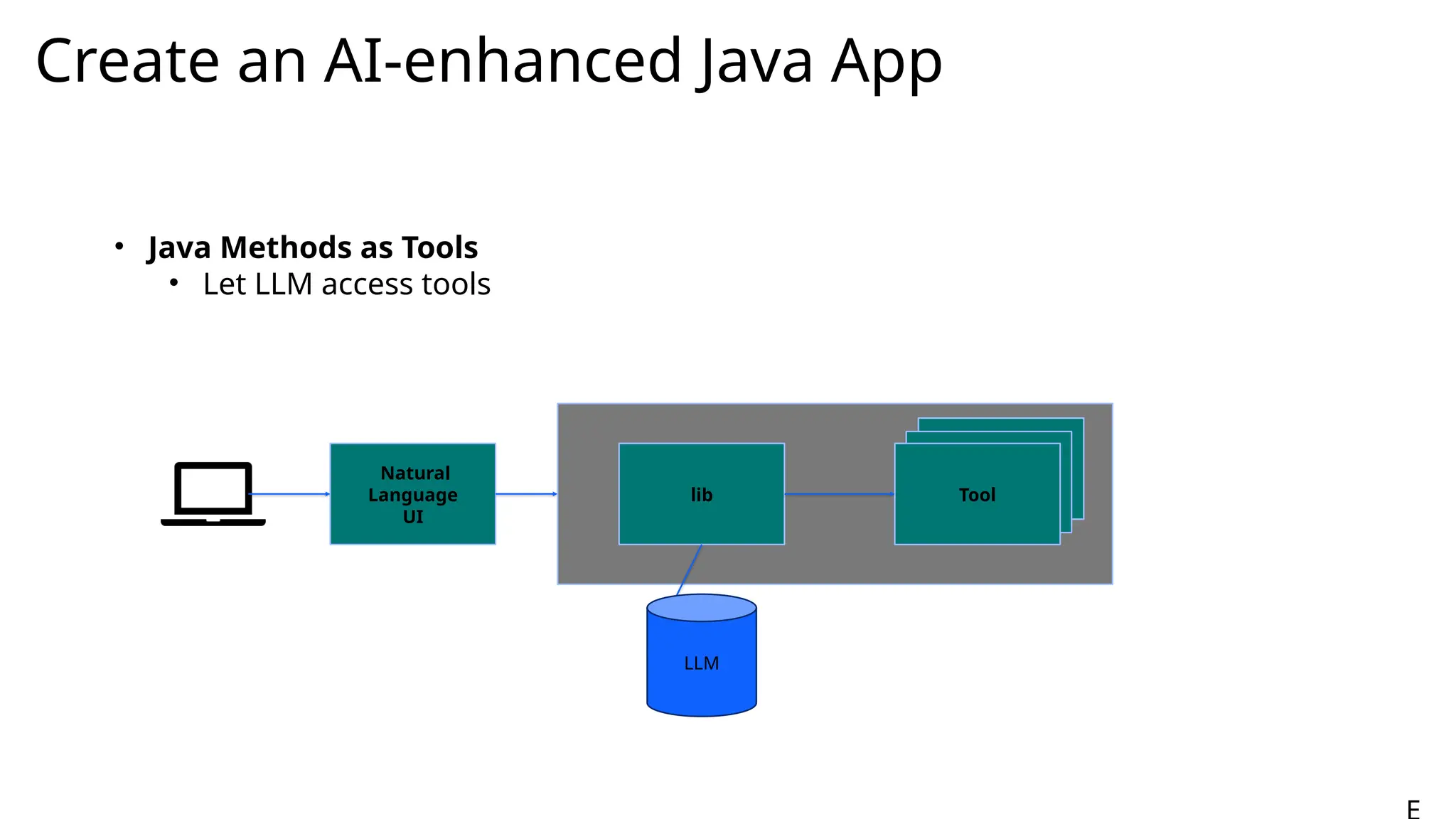
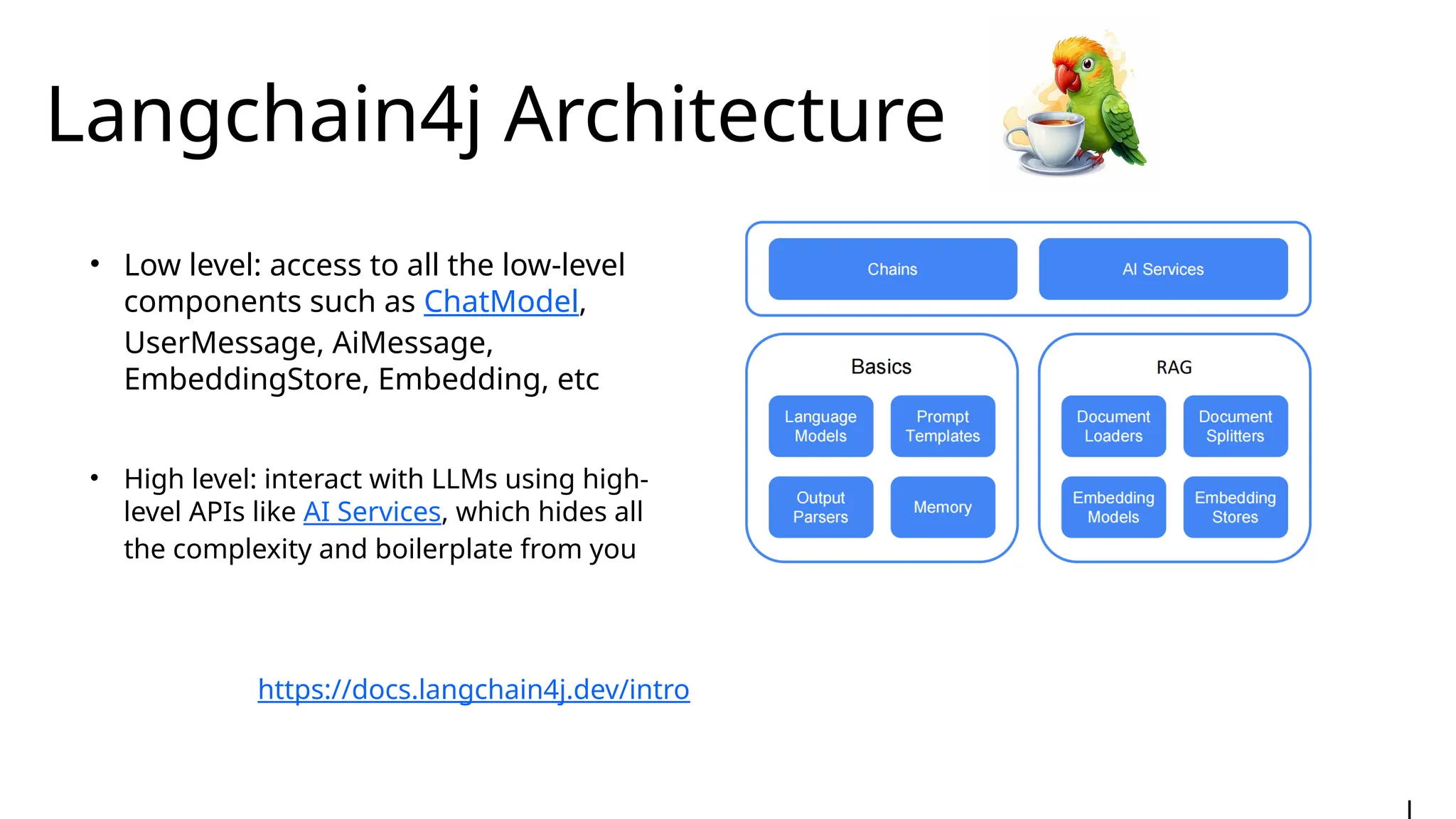
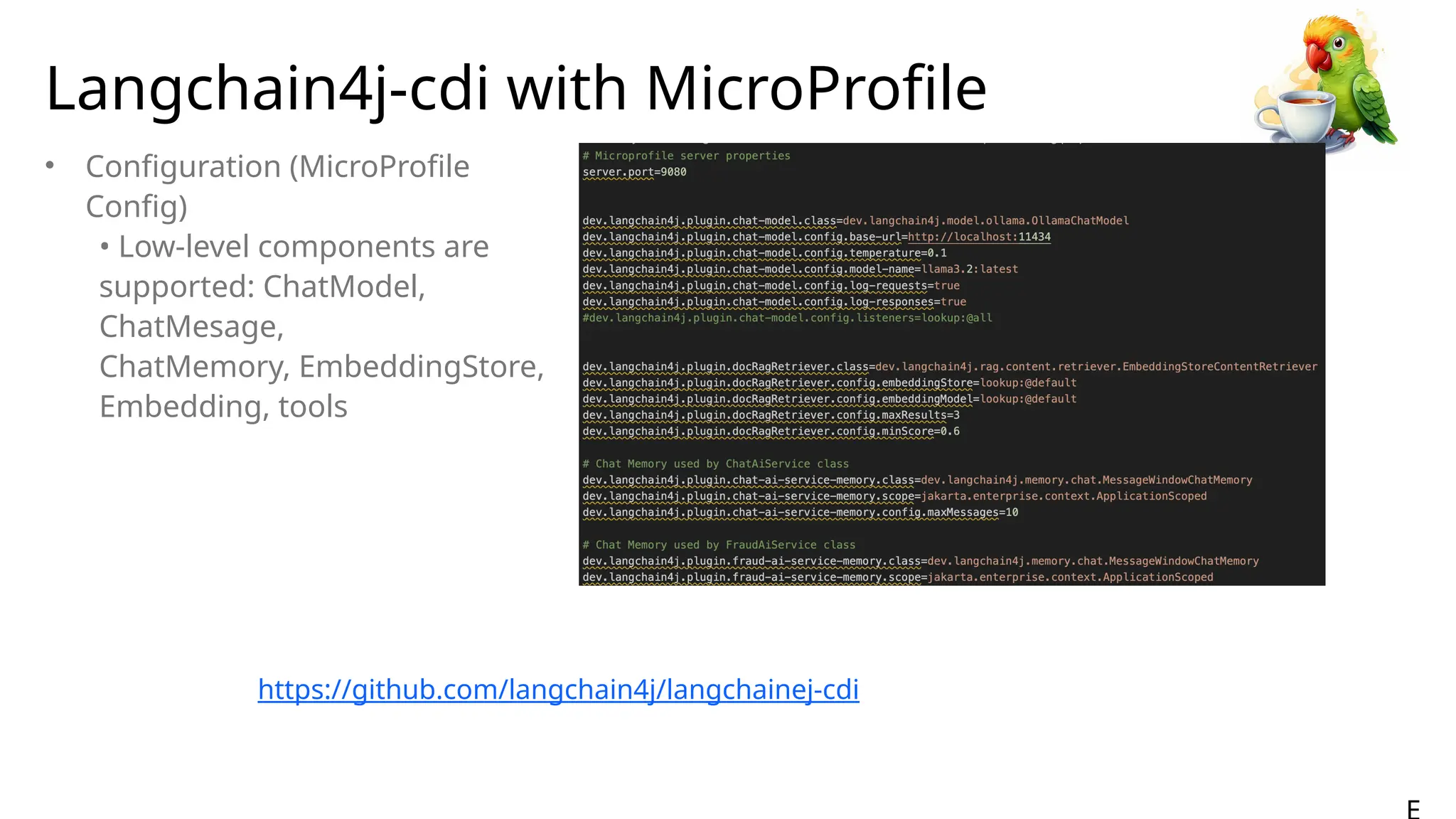
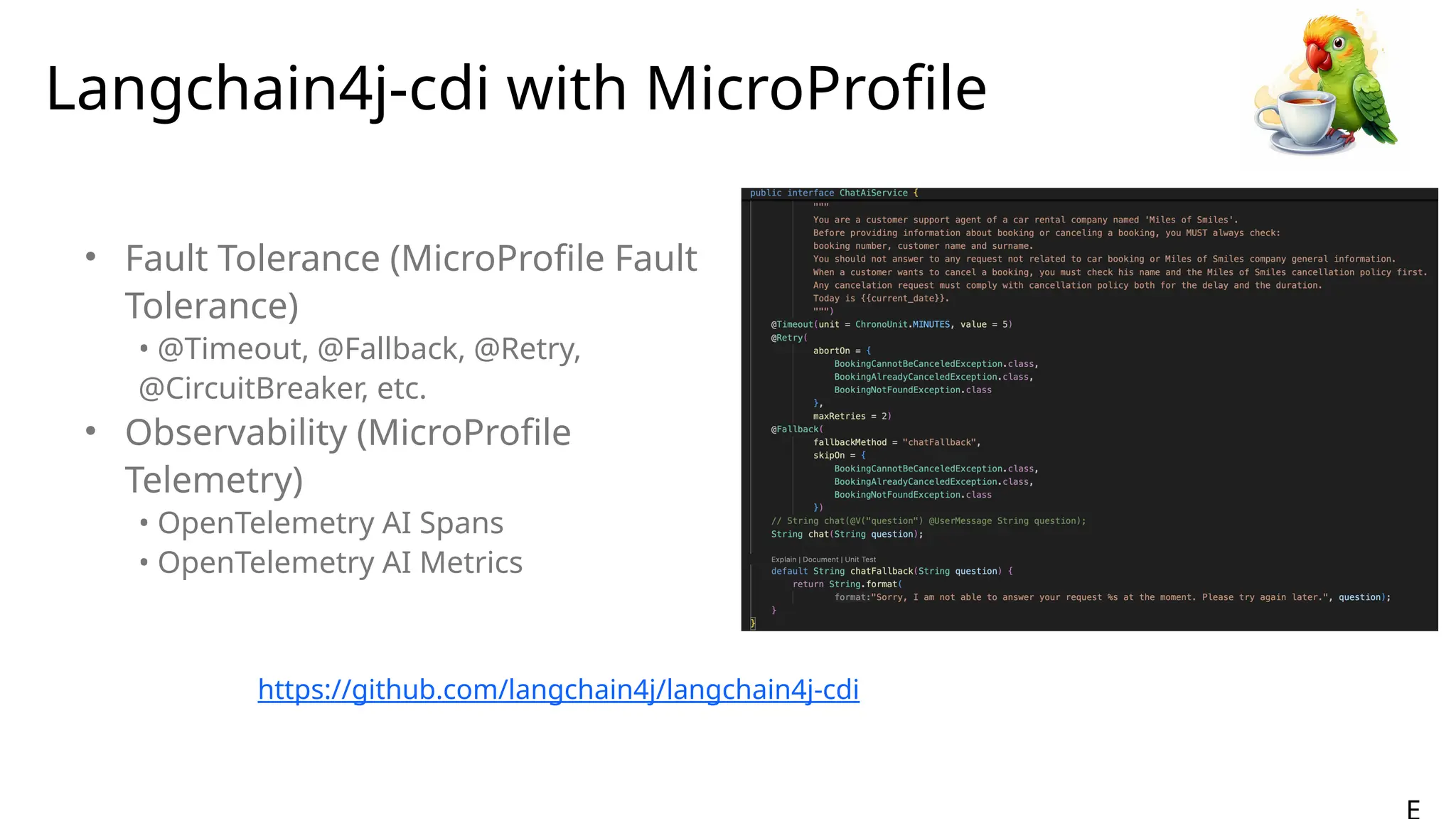
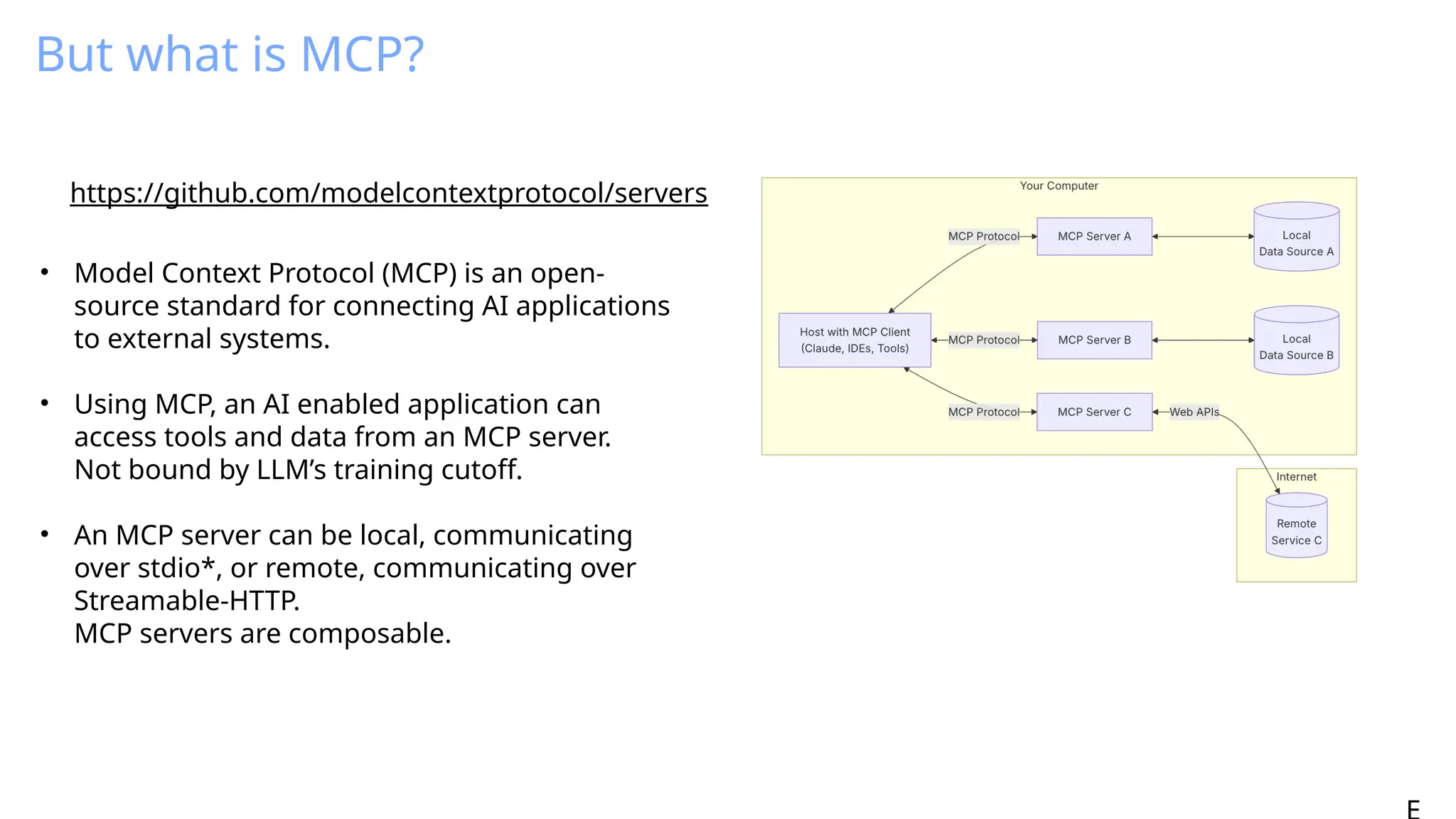
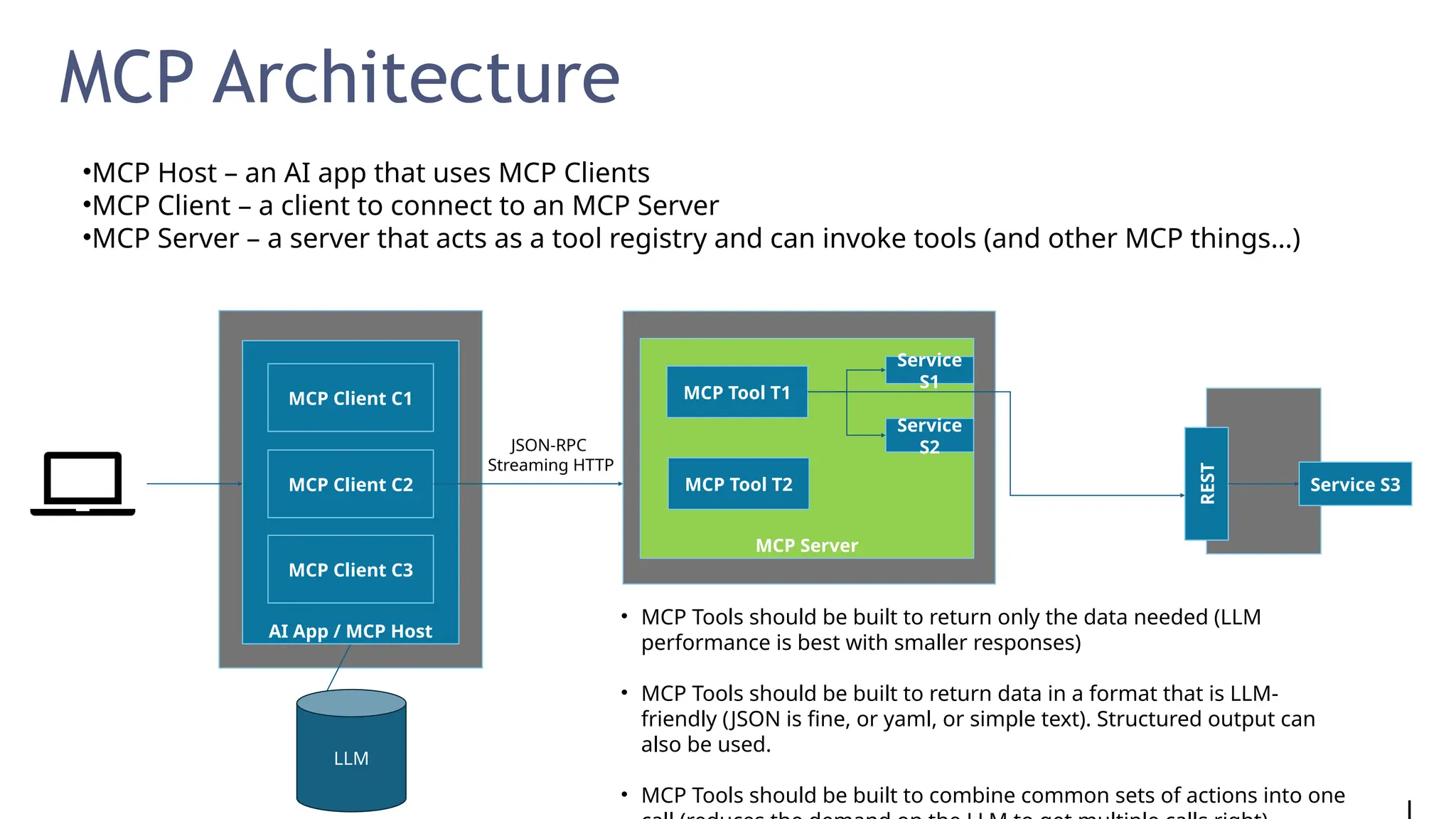
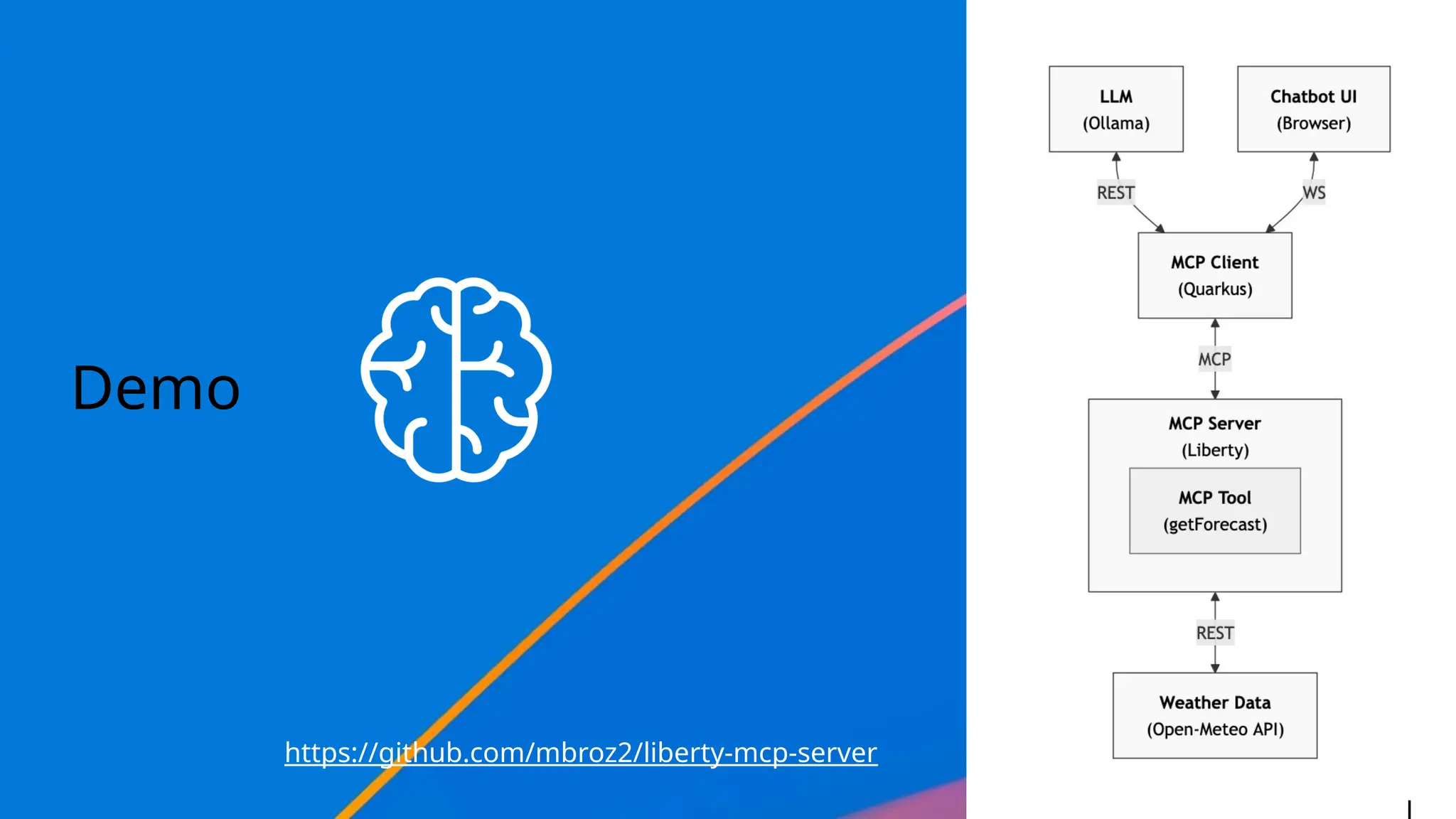
Generative AI burst on to the public scene in November 2022, over ten years after Andrew Ng’s Machine Learning premiered on Coursera. Java developers have long felt like second class citizens, compared to the cool Python kids. LangChain4J changes the game. Java is cool with AI now! This lecture from 30-year industry veteran Ed Burns explores why it took so long for Java developers to have access to easy-to-use AI libraries, compared to Python developers. This session introduces the new langchain4j-cdi repository within the LangChain4j GitHub organization. Combine the power of Jakarta EE with the reach of LangChain4j. All the idioms you know and love from Jakarta now work with all the AI exposed by LangChain4j: injection, validation, persistence, REST and more!