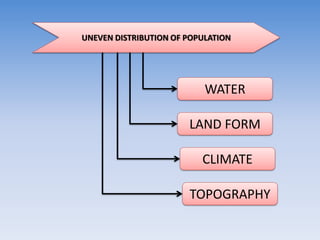
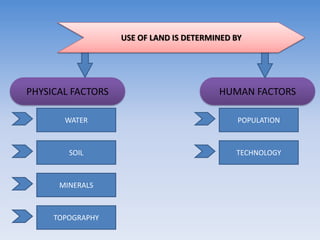
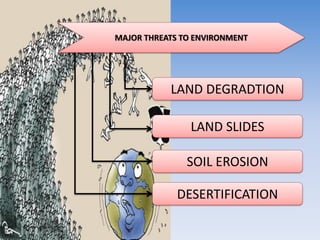
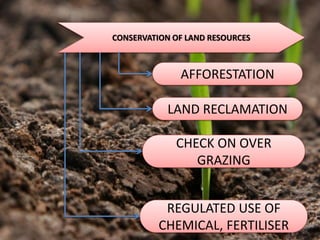
This document provides information about a social studies lesson plan for Class VIII on the topic of geography, land, soil, water, natural vegetation, and wildlife. It includes 4 learning periods that cover different objectives and activities. The objectives focus on understanding land use and distribution of population, causes of landslides and methods of soil conservation, availability and uses of water and methods of water conservation, and natural vegetation, wildlife, and their conservation.