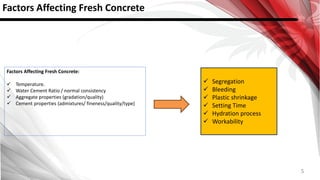
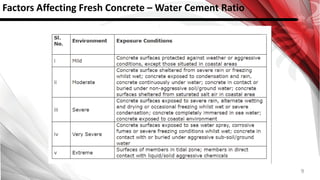
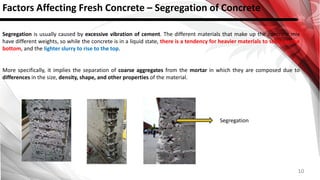
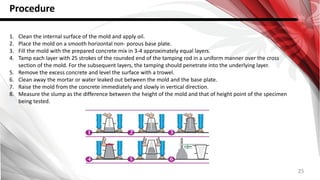
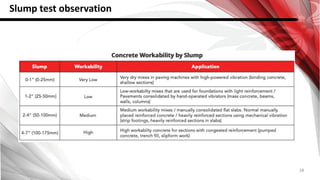
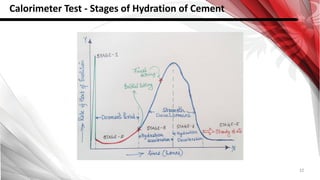
This document discusses factors that affect the workability of fresh concrete. It describes how water content, aggregate size, shape and grading, and use of admixtures can impact how easily concrete can be mixed, placed, compacted and finished. Maintaining an appropriate water-cement ratio is important for strength and to prevent issues like bleeding or segregation. Other factors discussed include temperature effects, cement properties, setting time, hydration processes, and plastic shrinkage. The document provides details on how each of these numerous factors influence the workability of fresh concrete.