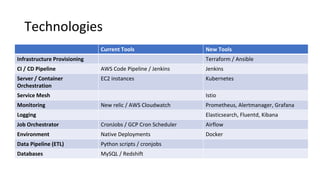
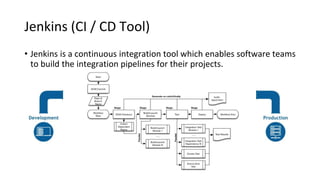
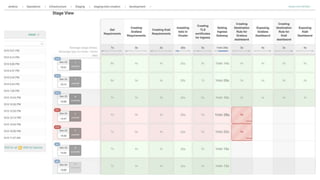
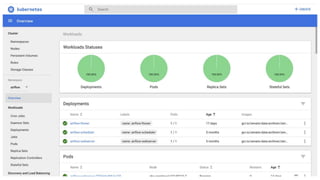
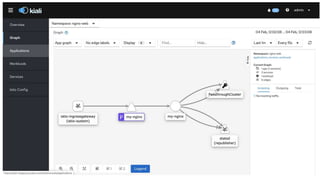
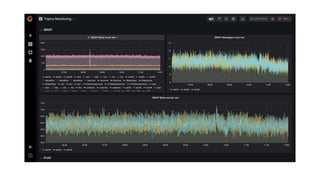
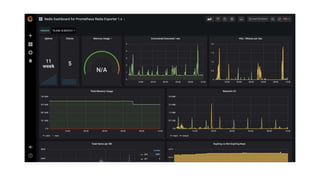
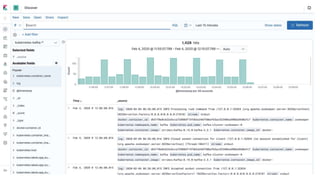
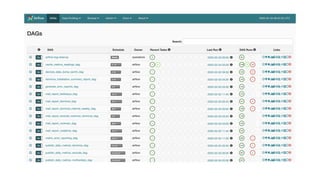
The document outlines an infrastructure 2.0 approach based on cloud native technologies. It advocates for infrastructure as code, test-driven deployments, open source tools, and seamless developer workflows. The approach uses microservices, containers, service meshes, and orchestration with Kubernetes. It recommends tools like Terraform, Jenkins, Kubernetes, Istio, Prometheus, Elasticsearch and Airflow for infrastructure provisioning, CI/CD, container management, service mesh, monitoring, logging, and job scheduling. It also discusses Docker, data pipelines, and processes for onboarding new applications.