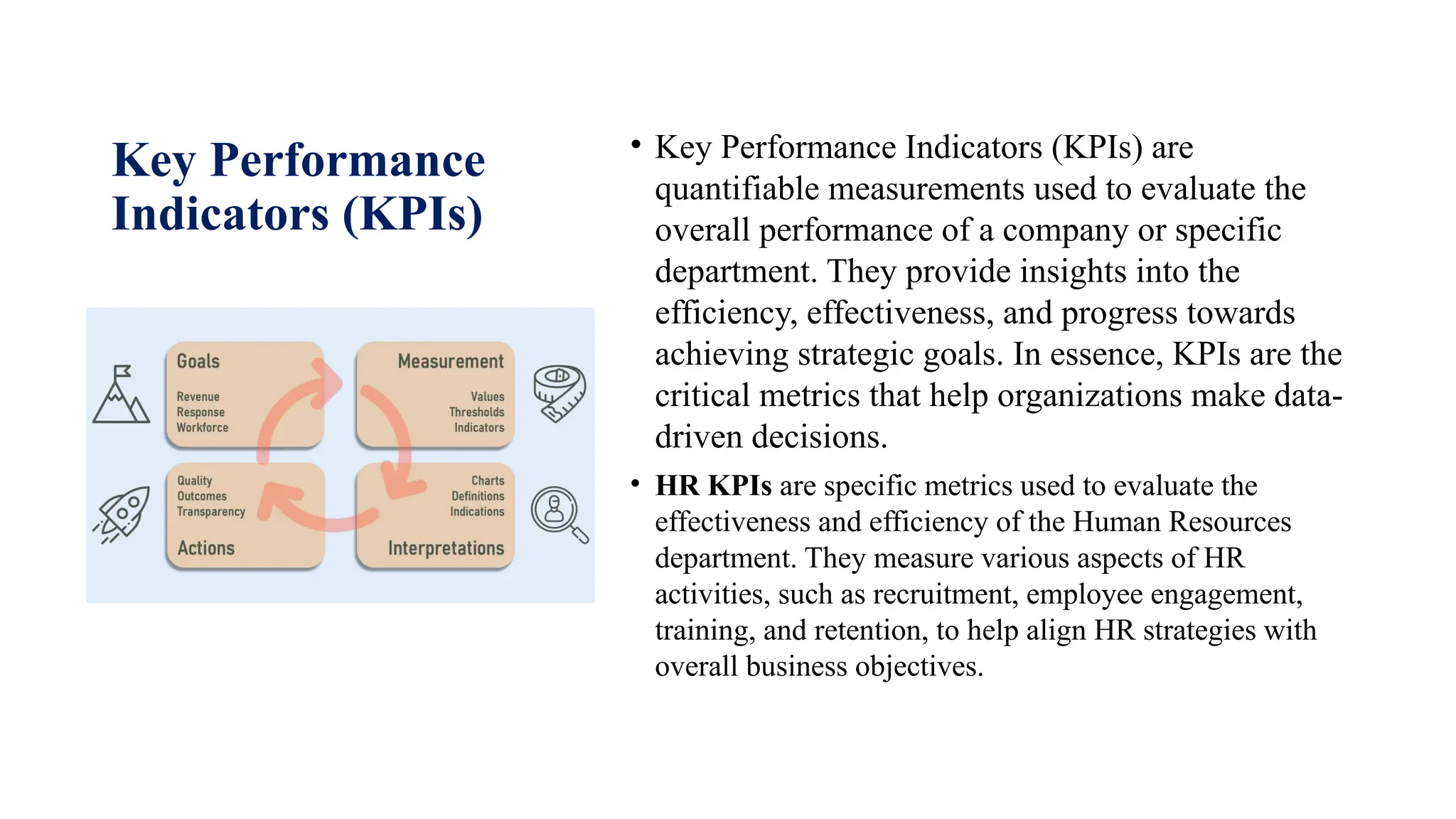
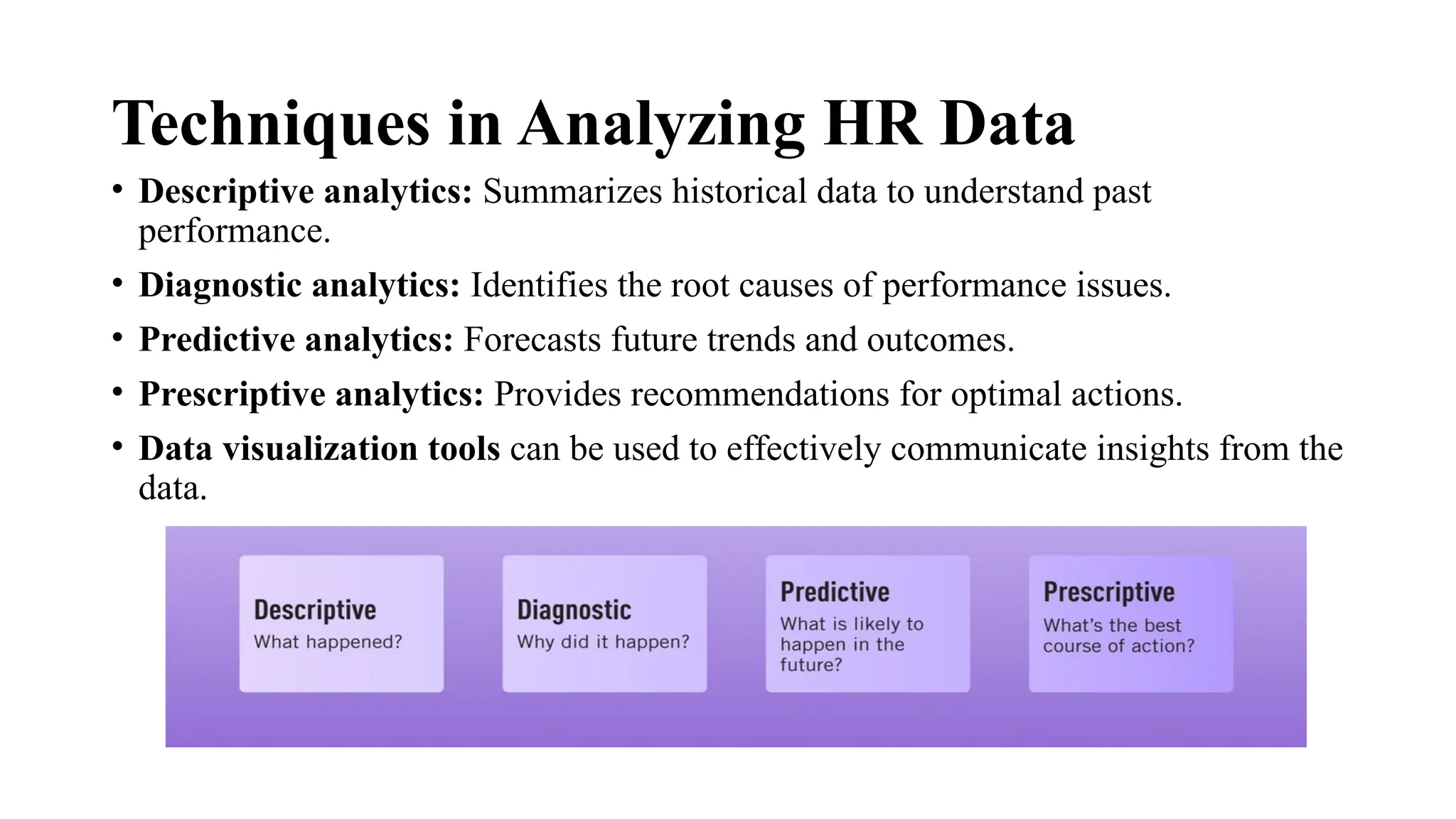
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable metrics that assess the performance of a company or department, aiding in data-driven decisions aligned with strategic goals. HR KPIs specifically evaluate the efficiency of HR activities, including recruitment and employee engagement, while HR analytics employs various methods to analyze data for improving HR functions. Effective reporting and interpretation of HR data are crucial for understanding trends and making informed decisions, with predictive analytics helping to forecast future needs and performance.