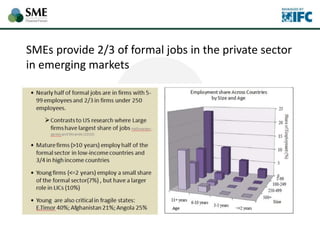
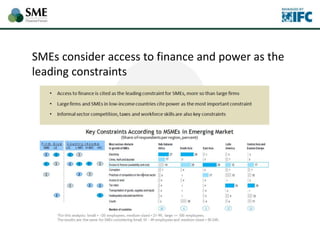
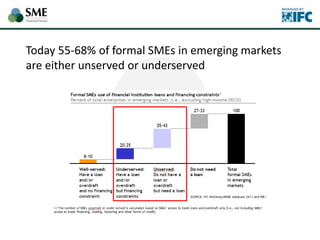
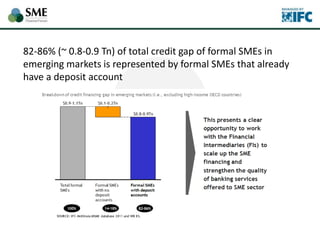
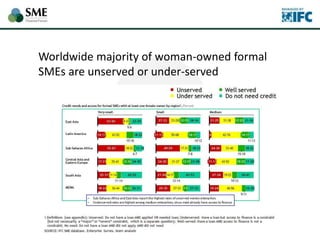
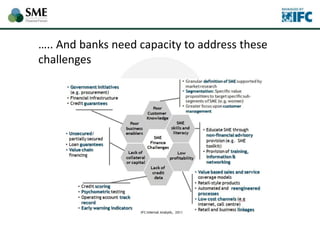
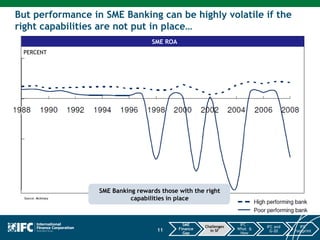
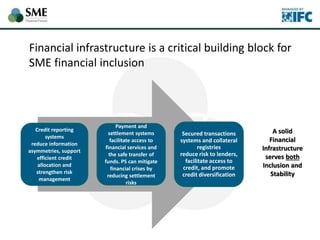
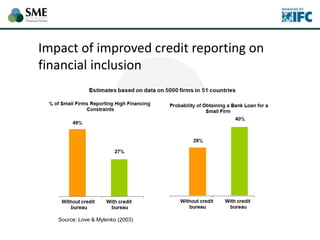
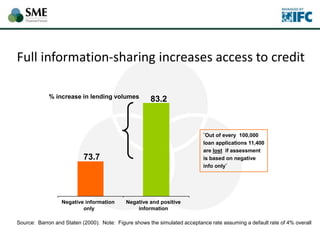
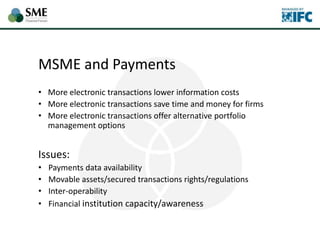
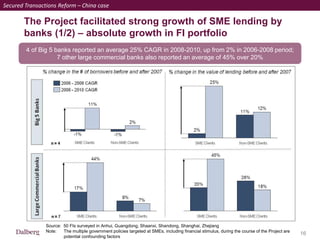
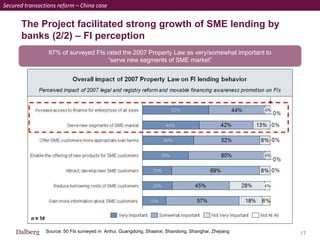
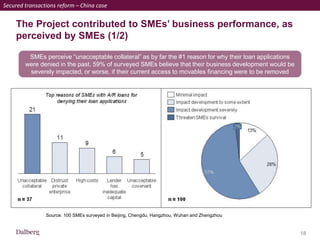
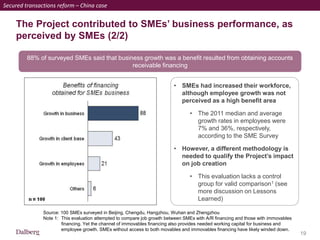
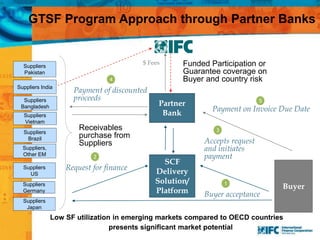
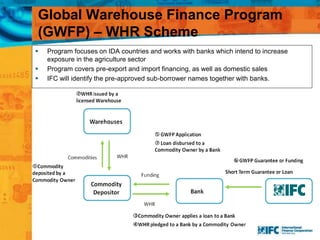
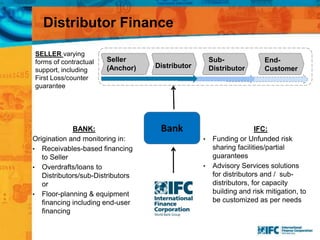
SMEs provide most formal private sector jobs in emerging markets. SMEs cite access to finance and power as key constraints. There remains a large credit gap of around $1 trillion for formal SMEs globally. Over half of formal SMEs in emerging markets are unserved or underserved. Most women-owned formal SMEs also lack access to finance. While SME banking can be very profitable, performance is volatile without the right capabilities. Financial infrastructure like credit reporting and payments systems are critical for SME inclusion and stability.