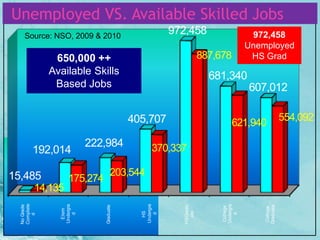
The document discusses the K-12 Basic Education Program introduced by the Department of Education in the Philippines. It aims to address issues with the previous 10-year basic education program such as low achievement scores, insufficient mastery of competencies, and graduates lacking basic skills. The K-12 program enhances the curriculum and extends basic education to 12 years, in line with international standards. It is expected to benefit students by improving education quality, preparing graduates for employment or higher education, and developing important skills for life and work.