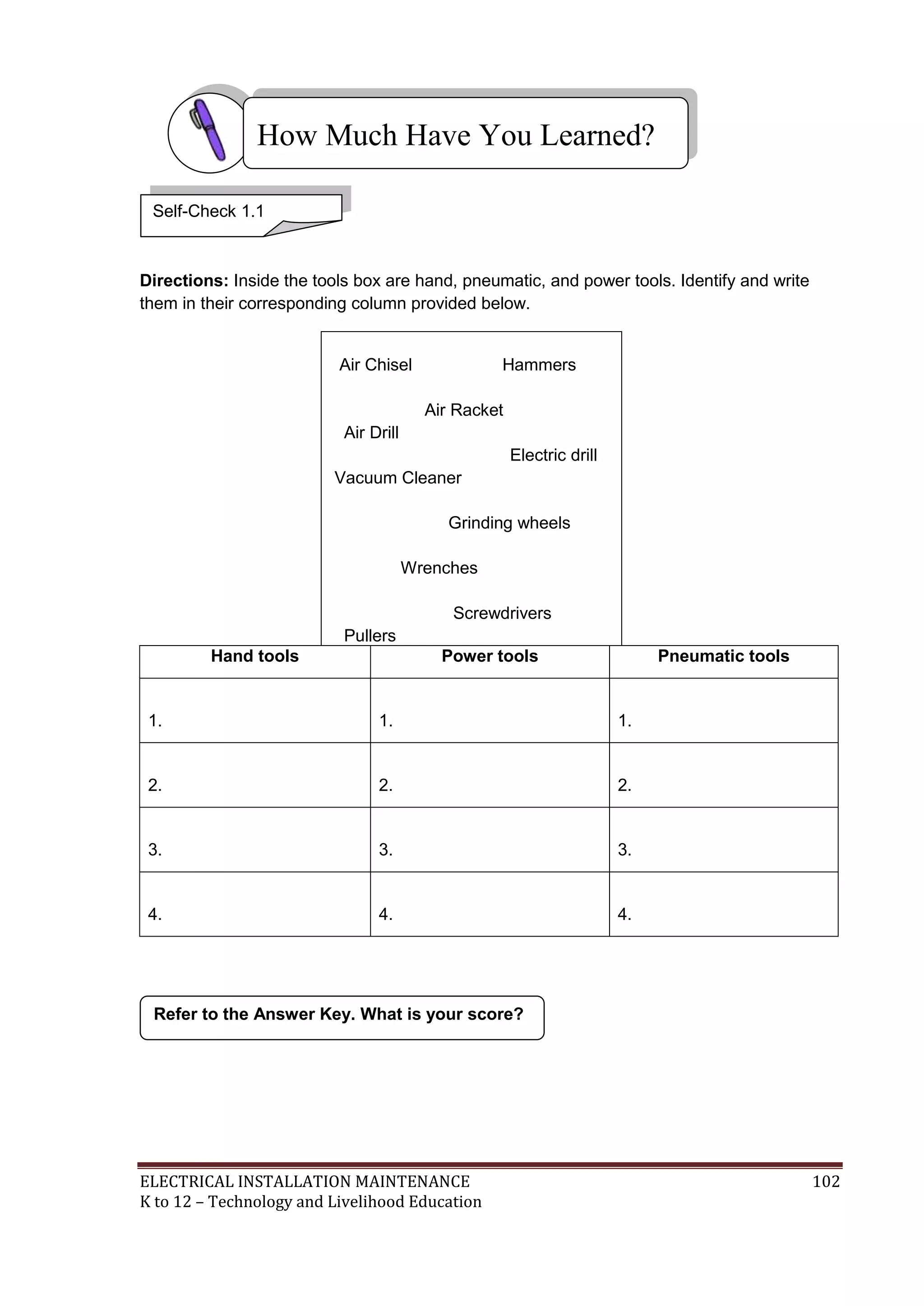
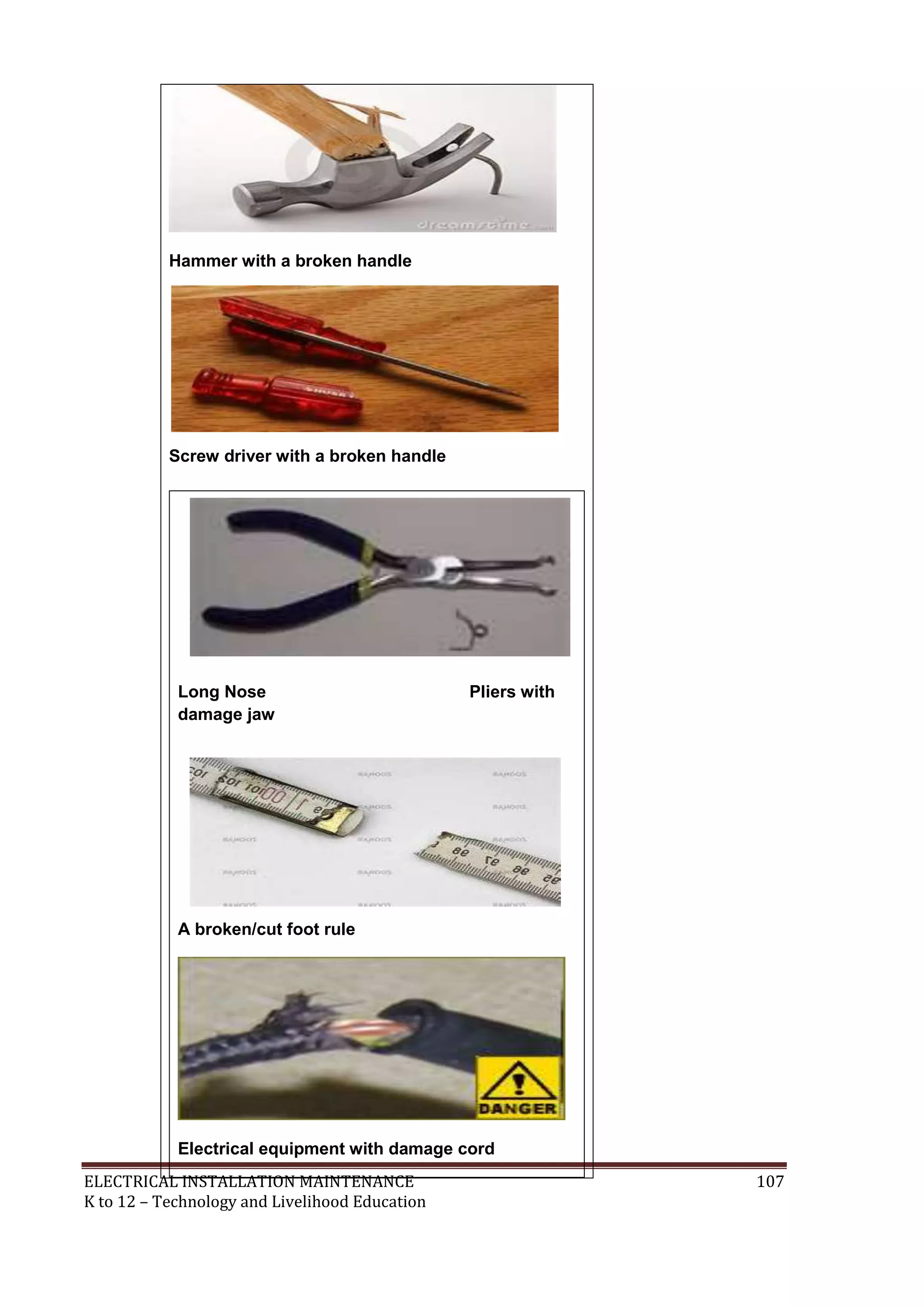
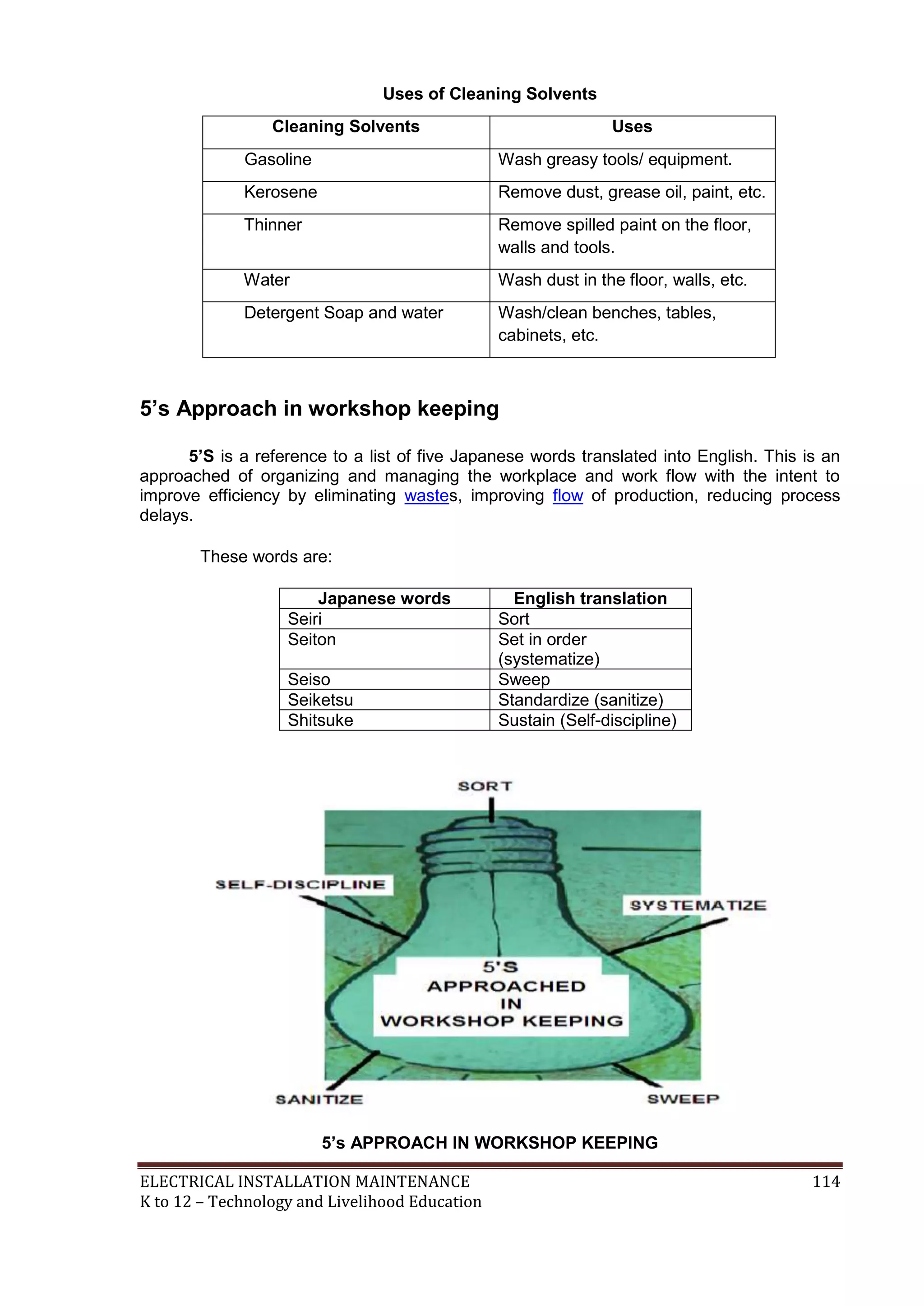
Here are the key points about electrical tools and materials from the information sheet:
- Screwdrivers come in various sizes and types like standard, Philips, stubby and Allen for different screw heads.
- Hammers are used for driving and removing nails. Common types are claw, mallet and ballpeen.
- Pliers are used for gripping, cutting and bending wires. Types include combination, side cutting and long nose pliers.
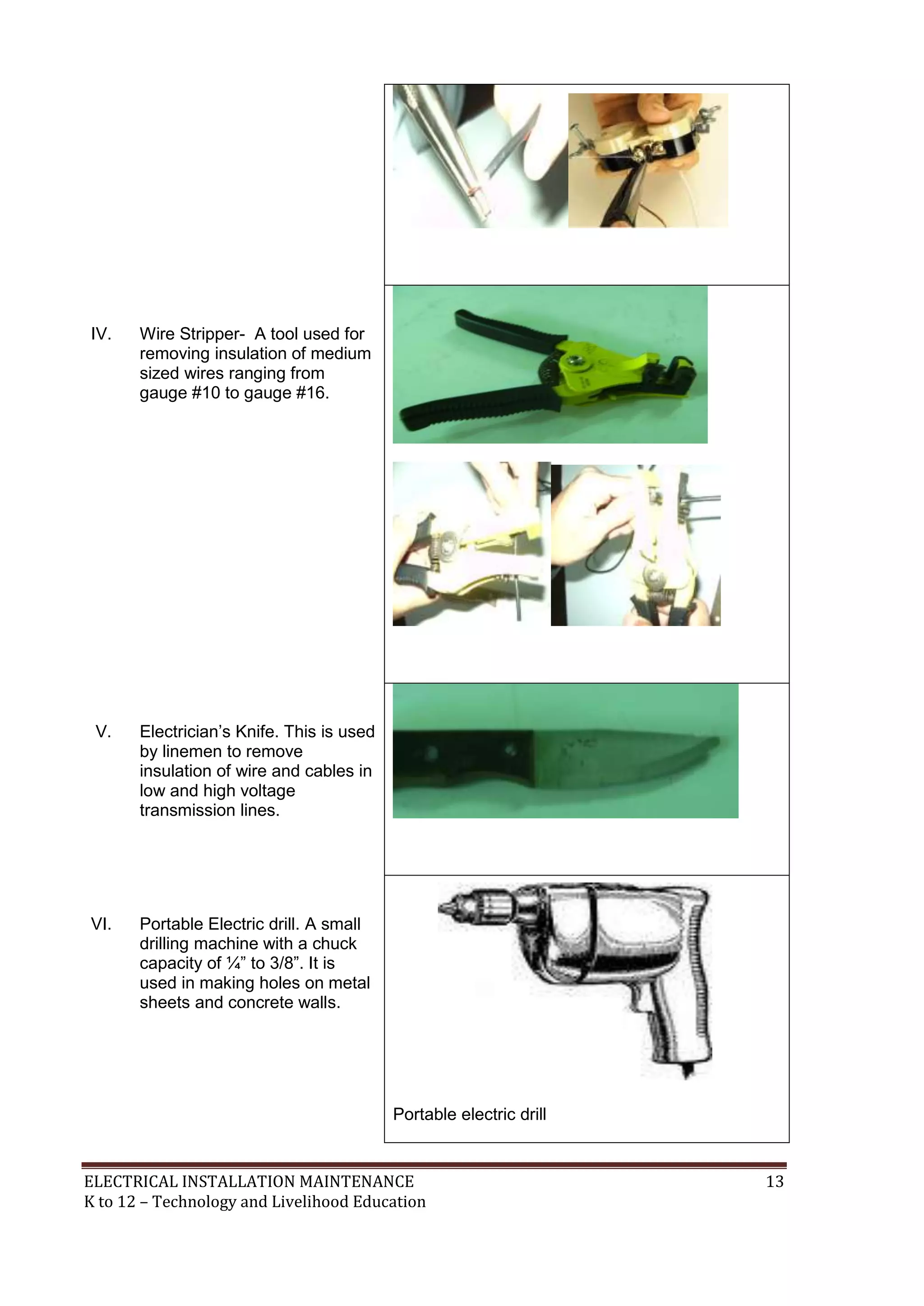
- Other tools are wire strippers, electrician's knife, portable electric drill and hacksaw for stripping insulation, cutting and drilling.
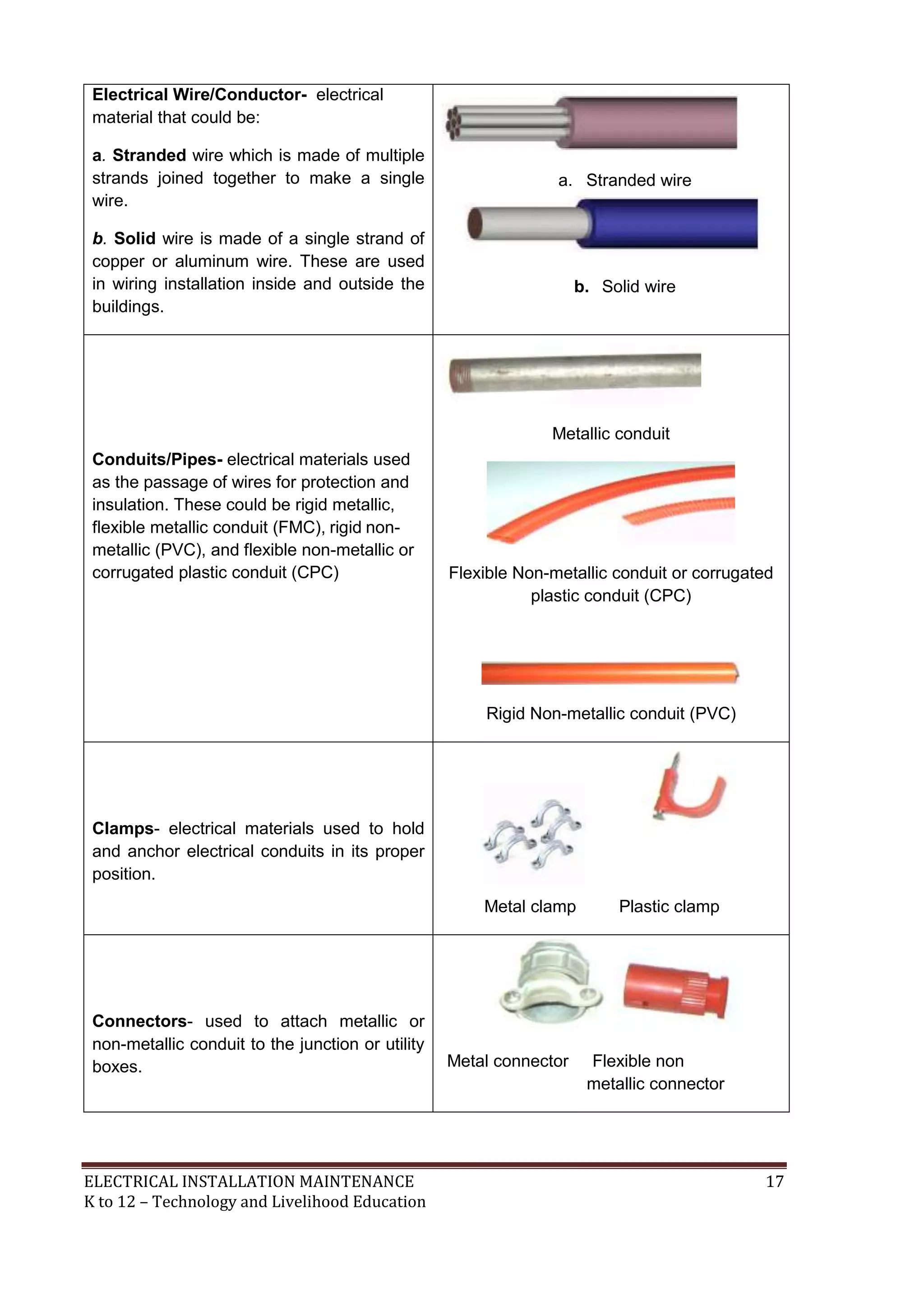
- Electrical materials include convenience outlets, male plugs and lamp holders for supplying power. Outlets can be surface or