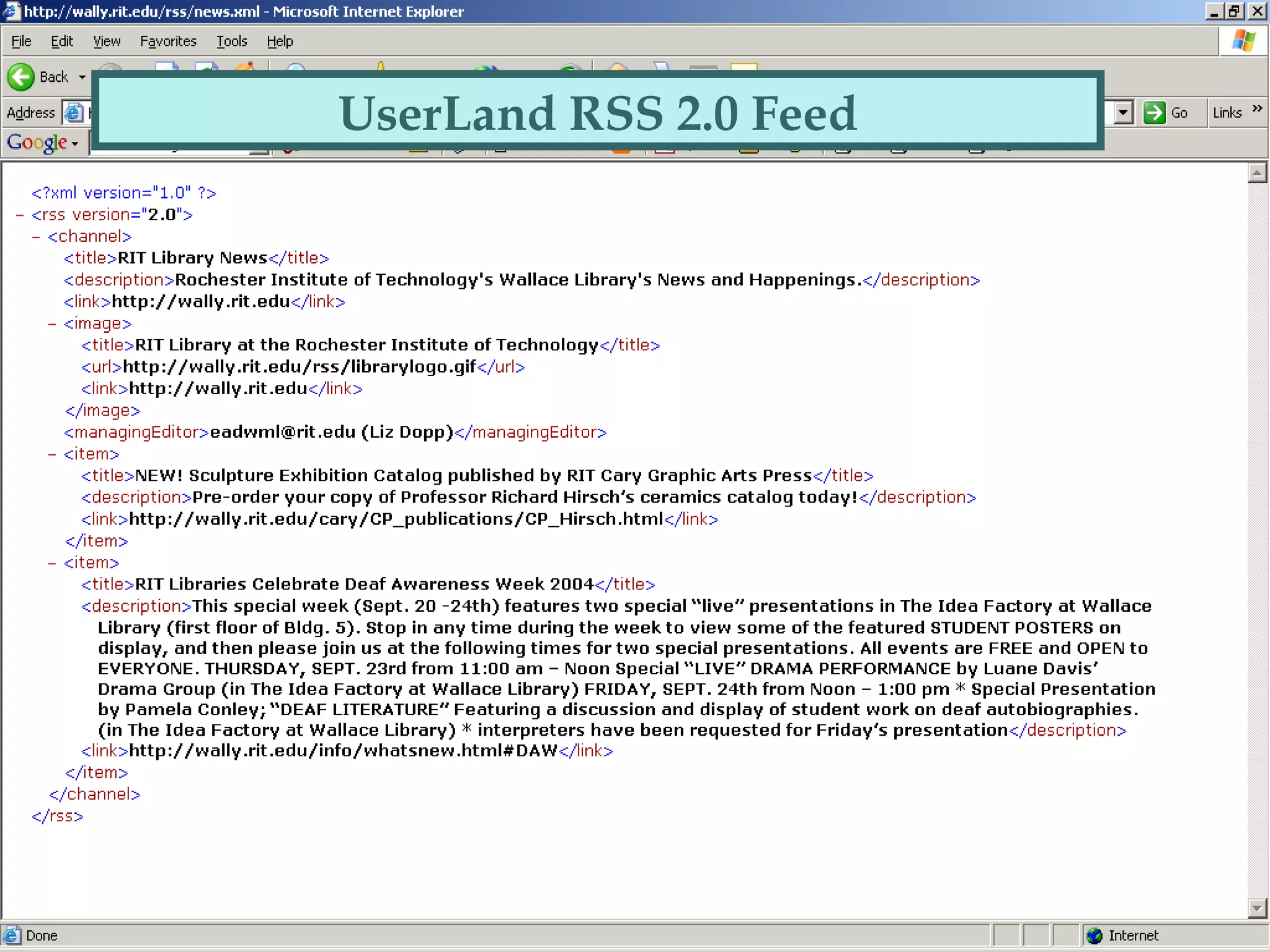
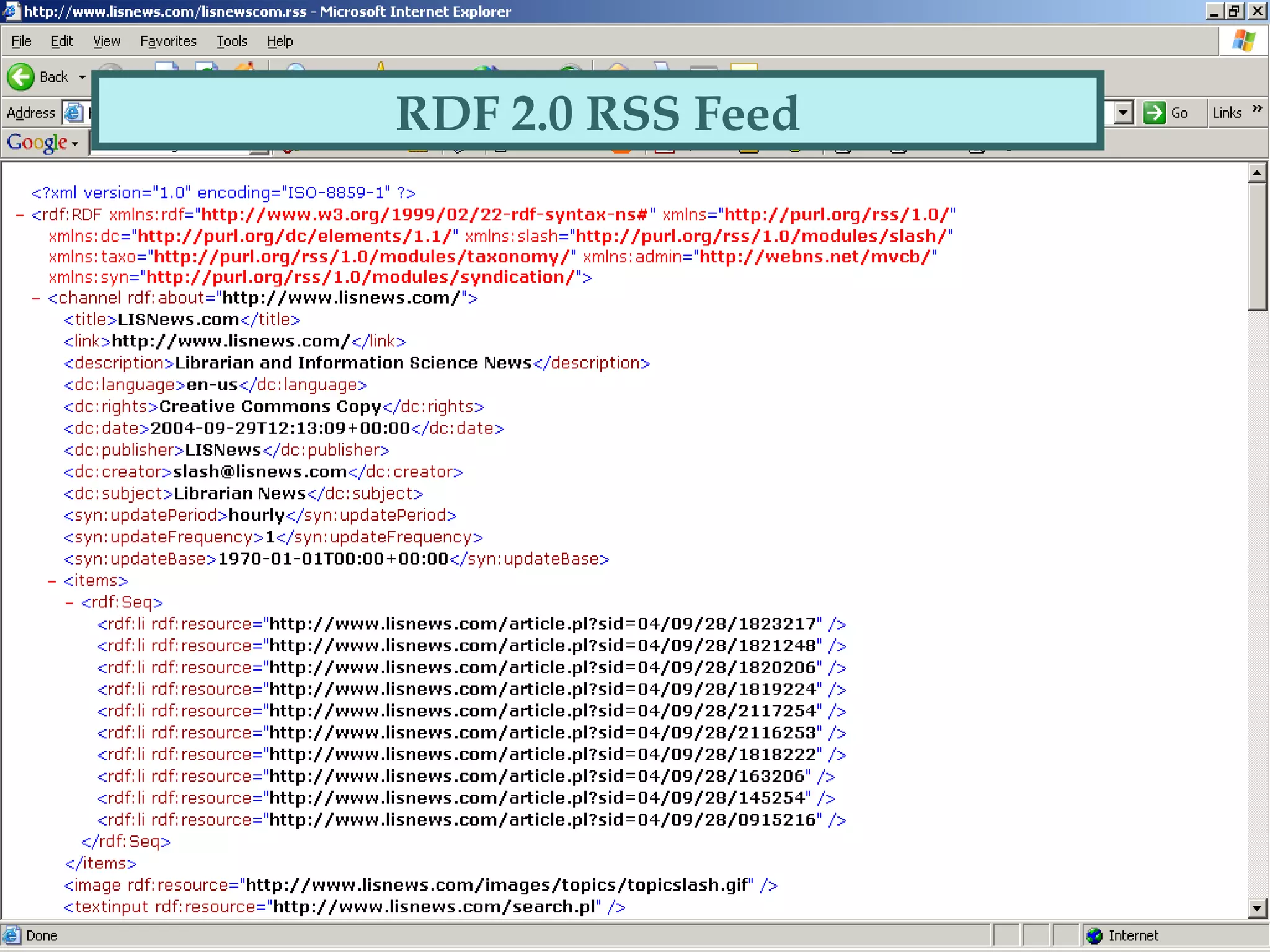
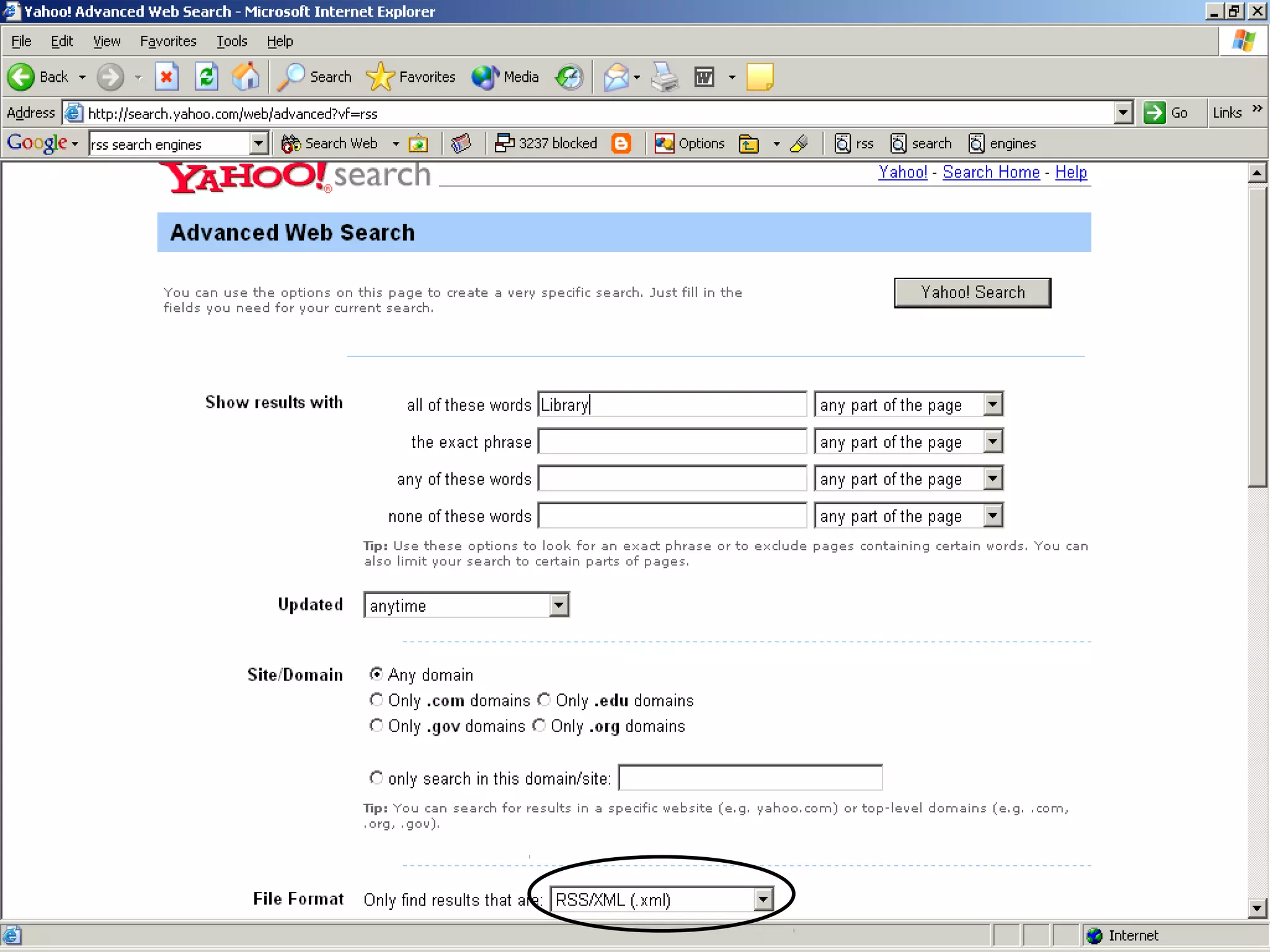
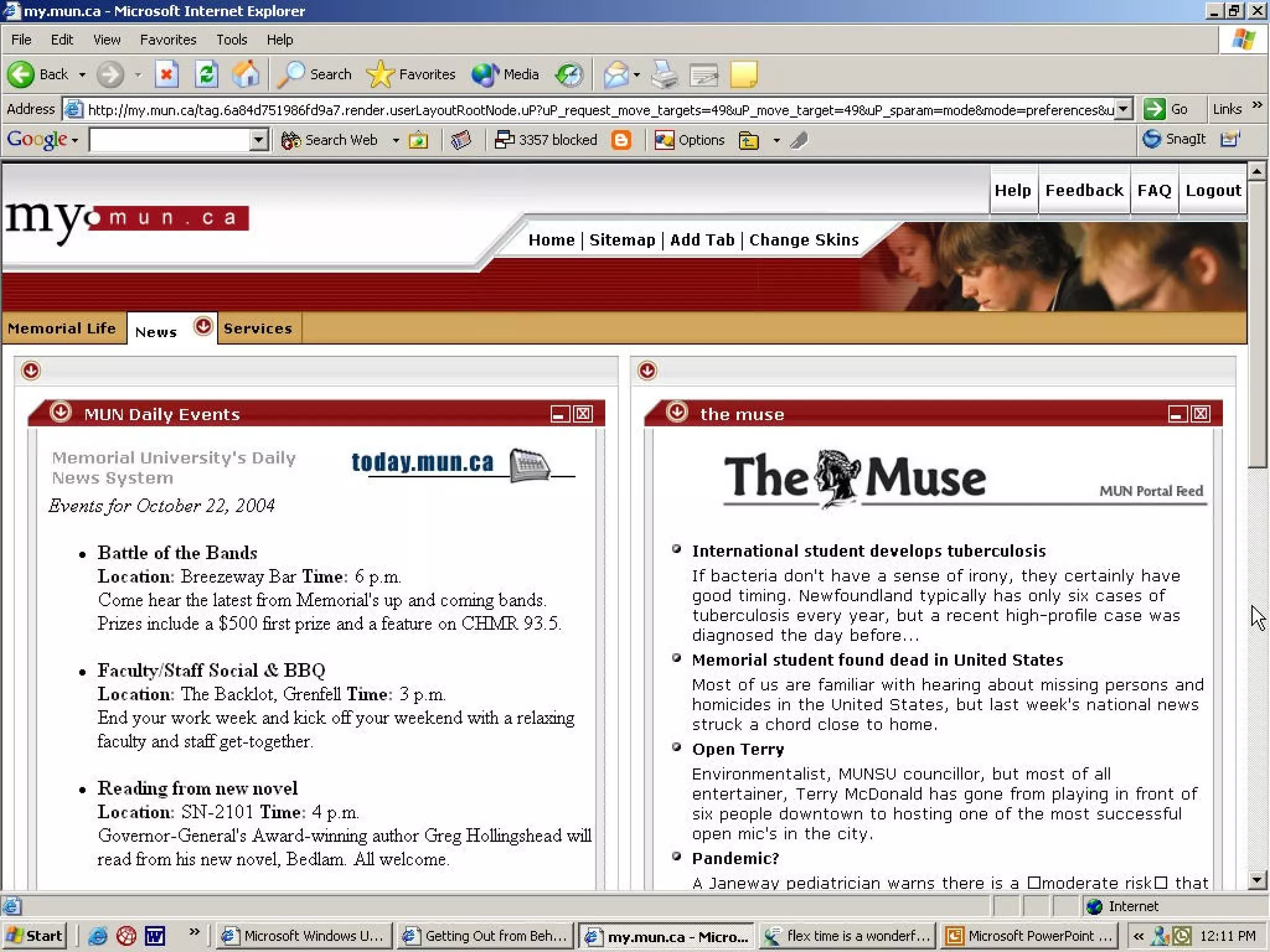
This document explains RSS (Really Simple Syndication), its definitions, versions, and applications within libraries. It highlights the advantages of using RSS for periodic web-based information and provides guidance on creating and finding RSS feeds. Additionally, it discusses various RSS aggregators for reading feeds and mentions potential future developments like Atom and portal integration.

![What is RSS?
Stands for:
“really simple syndication”
“rich site summary”
“RDF site summary”
Means:
“[XML] format for syndicating news and
the content of news-like sites”
Mark Pilgrim, Dive Into XML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/just-20the-20facts-2c-20maamrssrev-130812111202-phpapp01/75/Just-the-Facts-Ma-am-RSS-and-your-library-2-2048.jpg)