The document is a presentation by Irfan Maulana about CSS, highlighting its importance beyond mere cosmetics in web design, and detailing various aspects such as selectors, positioning, text formatting, and element display. It provides guidelines on how to use CSS effectively in HTML, including merging rules and using pseudo classes and elements. The document also includes references and contact information for further engagement.






![CSS Selector
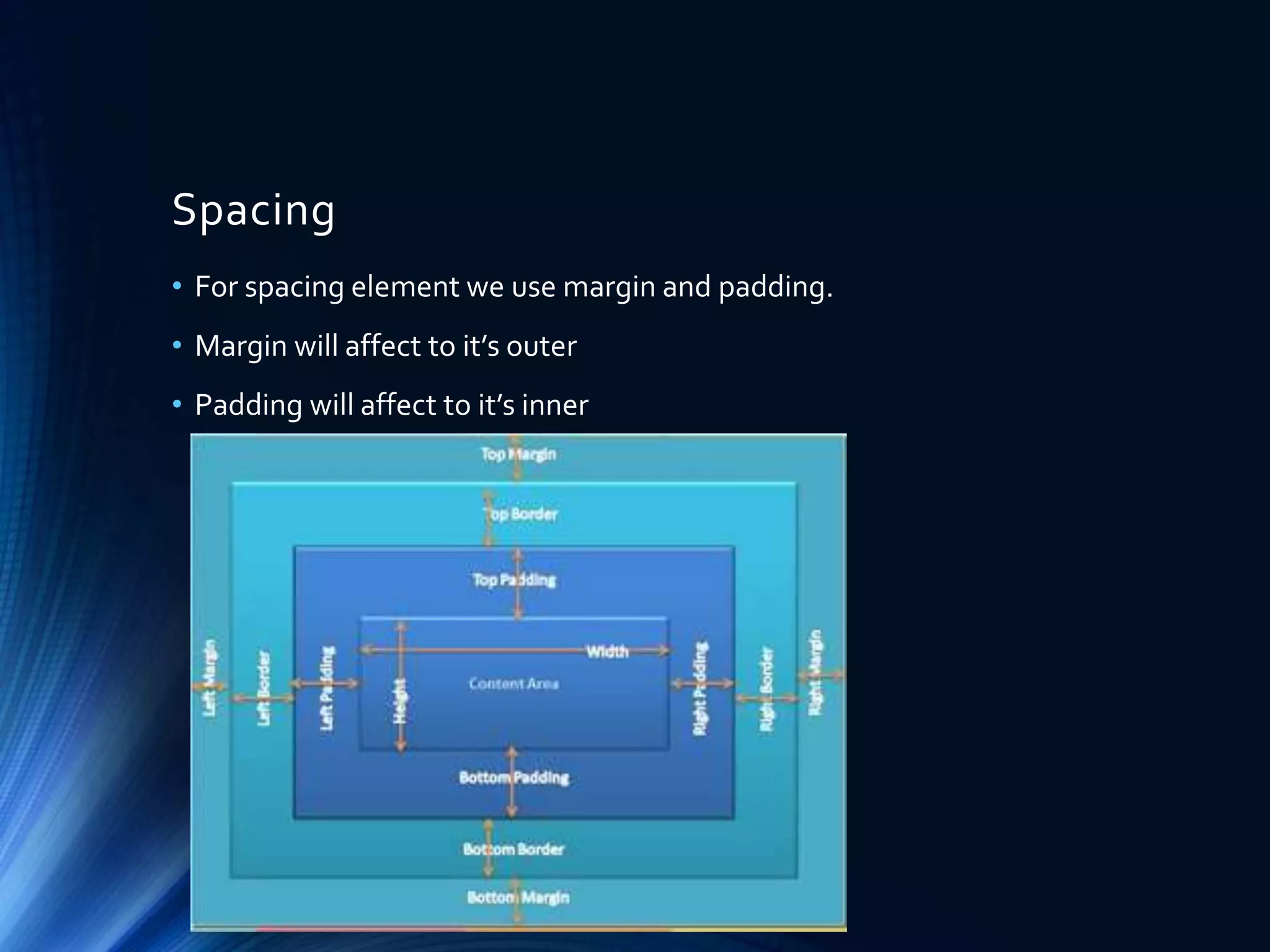
• CSS Selector used to find HTML element will be style-ed.
• CSS will styling element that select by selector that used like HTML
element, Id, or class, attribute, etc.
• HTML element will apply to all HTML element that given style.
Ex : input[type=“text”], a, ul li, etc.
• ID is unique in one web page, represented by attribute id=“” in
HTML element.
• Class is NOT unique, can be reuse to any HTML element in one web
page, represent in attribute class=“” in HTML element.
• Class can be multiple in one HTML element using space separator.
• CSS use hash (#) for select id, and dot (.) for select class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rpdcv8csqfymcppb72gs-signature-49f4ec28f49bd9684a1ed6adcb70488426d105e249ce63f4180cf47058370981-poli-161207102745/75/Journey-To-The-Front-End-World-Part2-The-Cosmetic-7-2048.jpg)

![Advance CSS Selector
• We can select all classes that contains string like :
Ex :
[class*=“bli-"] {
color: blue;
}
• Read more about selector :
http://www.w3schools.com/cssref/css_selectors.asp](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rpdcv8csqfymcppb72gs-signature-49f4ec28f49bd9684a1ed6adcb70488426d105e249ce63f4180cf47058370981-poli-161207102745/75/Journey-To-The-Front-End-World-Part2-The-Cosmetic-9-2048.jpg)