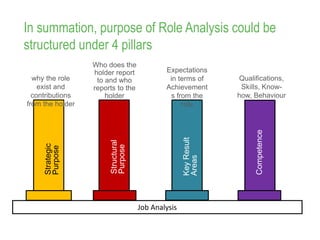
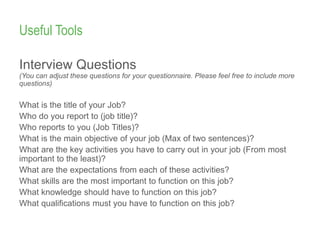
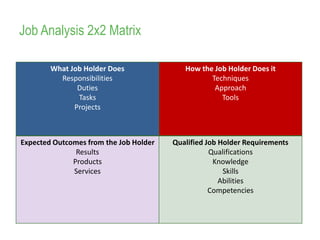
This document provides an overview of job analysis and how to conduct it. Job analysis aims to understand the expectations and requirements of a job through analyzing responsibilities, skills needed, and performance parameters. Information for job analysis comes from organizational data like strategies and structures, as well as gathering input from job holders, supervisors, and customers through tools like interviews, questionnaires, and observation. The output of job analysis is a job profile that describes the key details of the role like title, activities, requirements, and metrics for success. Conducting accurate job analysis requires buy-in, clear communication, focusing on job not holder, using appropriate tools, and implementing findings.