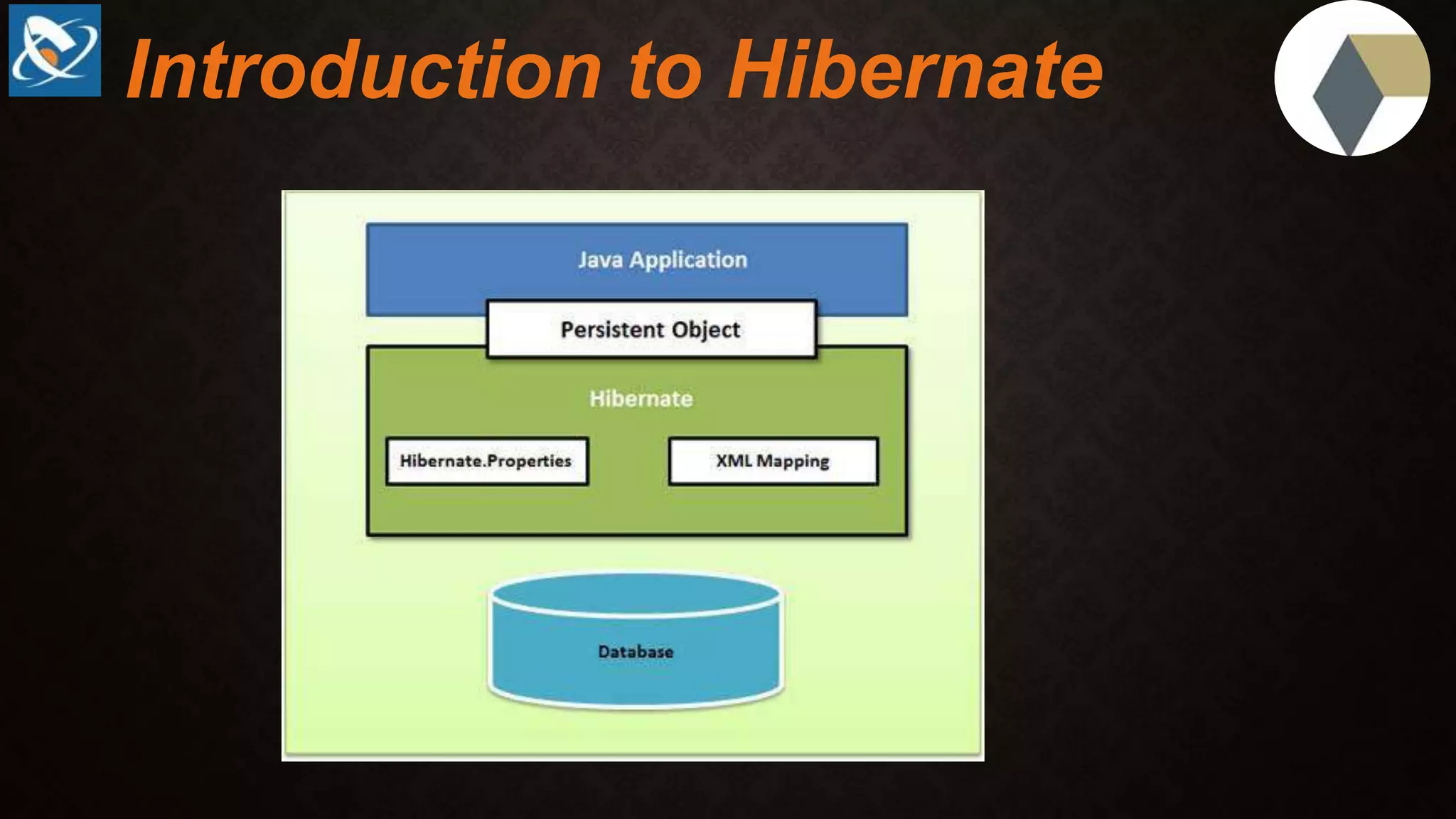
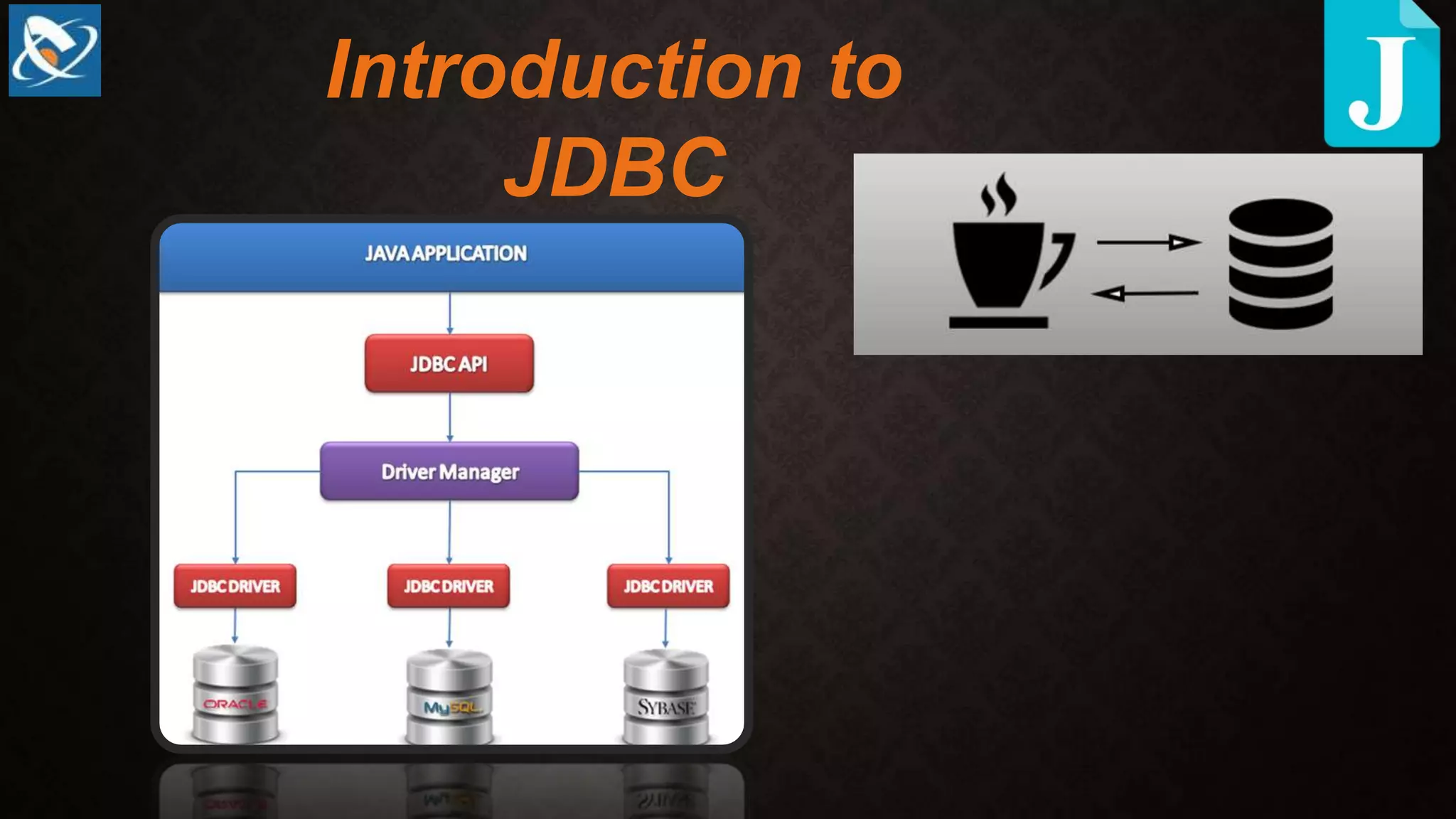
This document compares JDBC and Hibernate for database access from Java applications. It provides reasons to consider Hibernate over JDBC, including that Hibernate solves object-relational impedance mismatches, provides automatic object mapping, supports both HQL and SQL queries, provides database independence and caching for improved performance. It also lists reasons to consider JDBC over Hibernate, such as being easier to learn, supporting some queries not supported by Hibernate, and having better technical support. Overall, the document analyzes key differences between the two approaches and considerations for choosing between them for different situations and types of applications.