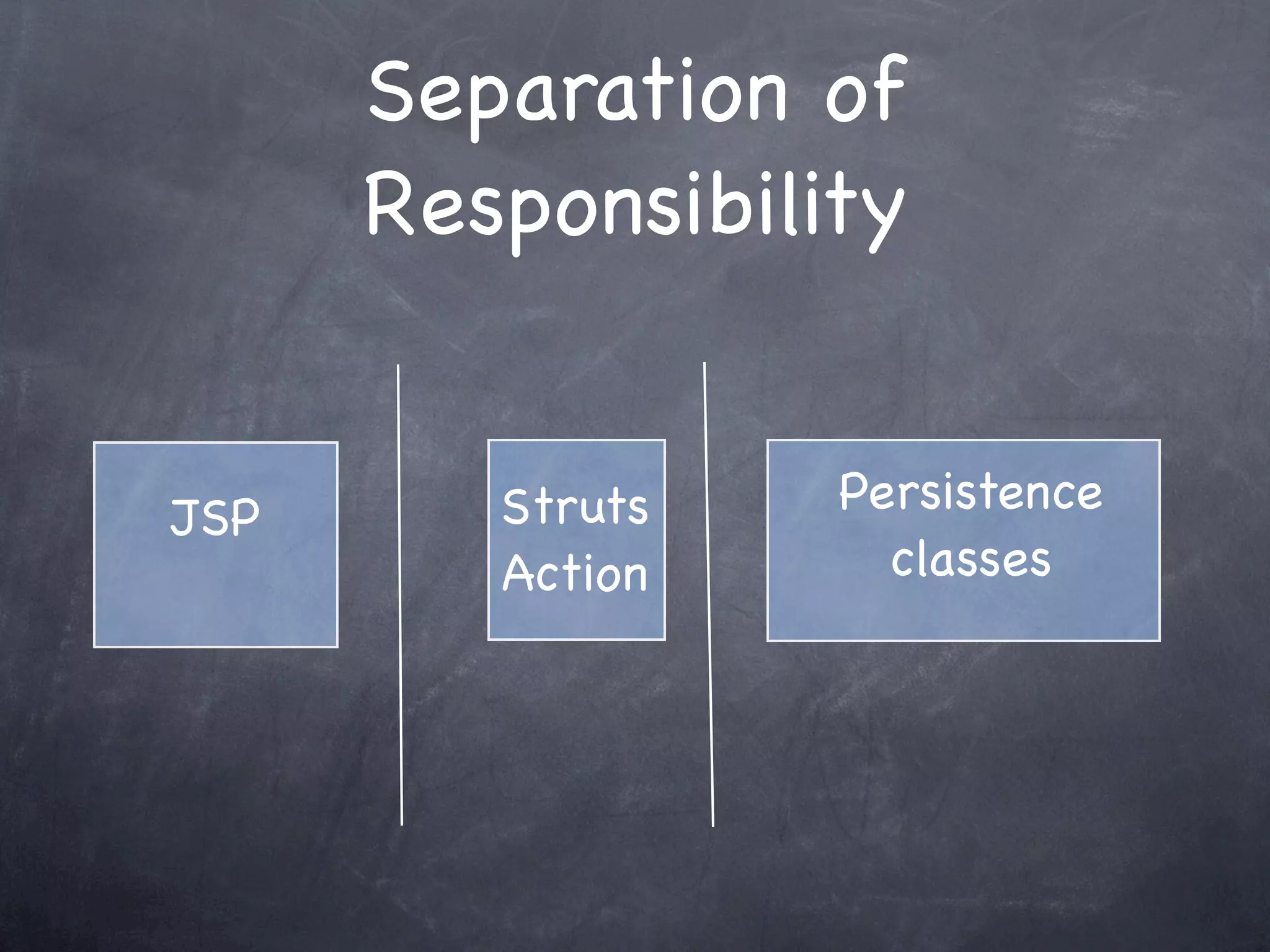
Hibernate is an object-relational mapping tool that allows Java objects to be persisted to a relational database transparently. It provides transparent persistence by mapping Java objects to database tables without requiring developers to write SQL or do object-relational impedance mismatch mapping manually. Hibernate uses an XML configuration file and mapping metadata to define how Java classes are mapped to database tables and columns. This allows Java objects to be treated as persistent domain models while Hibernate handles saving, updating, deleting and querying database data behind the scenes through its API.