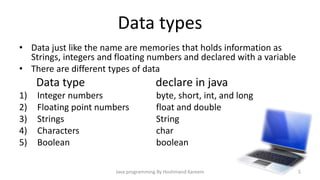
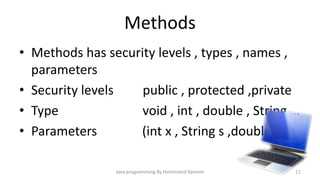
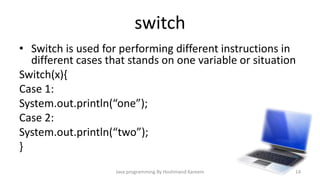
This document provides an introduction to Java programming concepts including writing a first program, using variables, data types, operators, conditional statements, loops, methods, switch statements, and arrays. It explains key Java concepts such as declaring variables to represent data, different primitive data types, using printf to output formatted strings, operator precedence and associativity, conditional if/else statements, for/while loops, defining methods with different access levels and return types, passing parameters to methods, using switch statements with cases, and declaring arrays to store multiple values. The document is intended as an overview of fundamental Java programming topics.


![Writing first program
Public class name {
Public static void main(String args [] ) {
System.out.println(“Welcome to java”);
}
}
Java programming By Hoshmand Kareem 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaprogrammingbyhoshmand-140419093116-phpapp02/85/An-introduction-to-java-programming-3-320.jpg)








![Arrays
• Array is a variable , that could be spitted into a
huge mount of indexes that each index can
hold another data
Int a []=new int [number of indexes];
a[0]=2; a[1]=3 a[2]=6;
Java programming By Hoshmand Kareem 15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javaprogrammingbyhoshmand-140419093116-phpapp02/85/An-introduction-to-java-programming-15-320.jpg)
