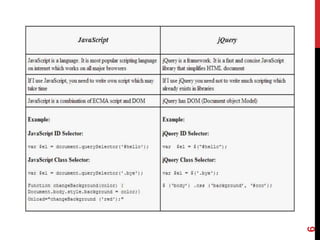
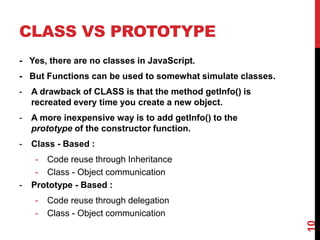
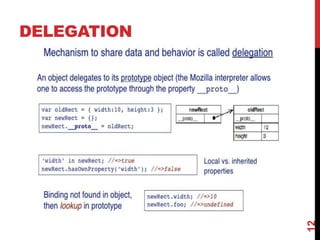
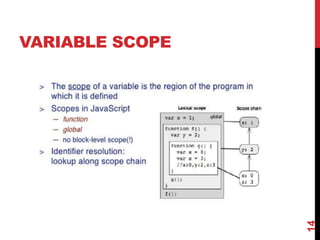
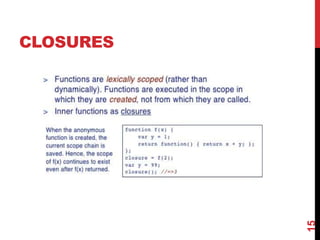
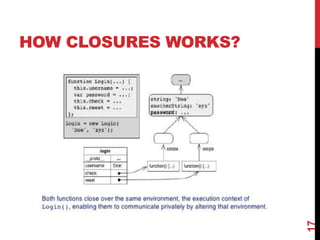
This document provides an overview of jQuery and JavaScript concepts for intermediate learners. It covers: 1) the past, present and future of JavaScript, 2) the difference between JavaScript and jQuery, 3) what a JavaScript engine is and examples of engines used in different browsers, and 4) key JavaScript concepts like values and identity, prototypes vs classes, objects, delegation, closures, and variable scope. The document is intended to expand understanding of JavaScript and jQuery beyond basic usage.