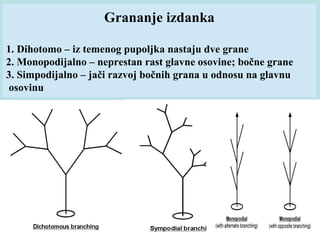
Stems have four main functions: support, conduction, growth, and storage. They support leaves, flowers, and fruits. Stems can be woody or herbaceous, annual or perennial. Stem anatomy includes primary and secondary tissues. Primary tissues include the epidermis, cortex, and central cylinder. Secondary growth occurs via the vascular cambium, adding secondary xylem and phloem. Stems also have specialized structures like rhizomes, tubers, bulbs, photosynthetic stems, stolons, thorns, and tendrils that serve functions like storage, reproduction, and support.