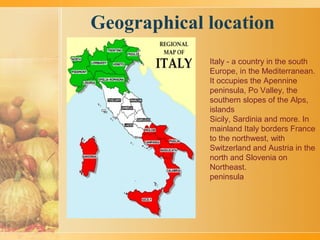
Italy is a country located in southern Europe, occupying the Italian Peninsula, the Po Valley, and the southern slopes of the Alps. It has a parliamentary republic system of government. Italy has a long history dating back to 500 BC with the Roman Empire and became a unified country in 1861. Some key facts are its capital is Rome, its official language is Italian, its currency is the Euro, and its largest cities include Milan, Naples, and Turin. Italy has a highly developed economy with advanced industries and agriculture. It is also known for its significant contributions to world culture, with many UNESCO World Heritage sites showcasing its rich history and arts. Italy has been an important member of the European Union since