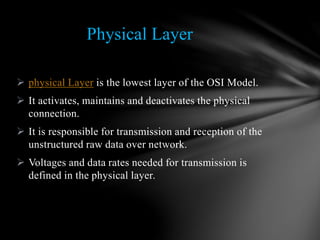
The document describes the seven-layer OSI model for network communication. The seven layers are physical, data link, network, transport, session, presentation, and application layer. The physical layer defines voltages and data rates for transmission. The data link layer ensures error-free transfer of data frames between nodes. The network layer routes signals through different channels and decides the transmission path. The transport layer handles multiplexing, segmenting, and reassembling messages passed between layers.