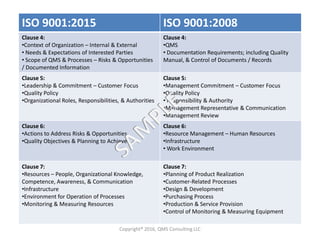
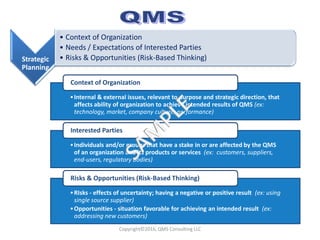
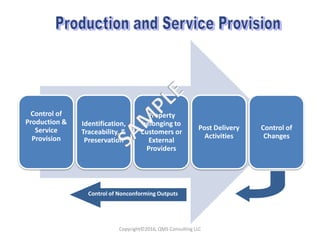
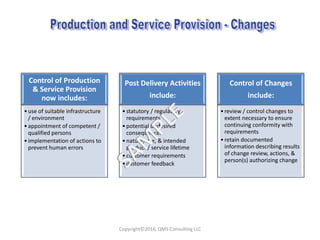
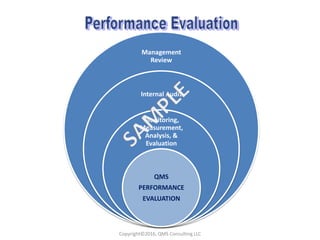
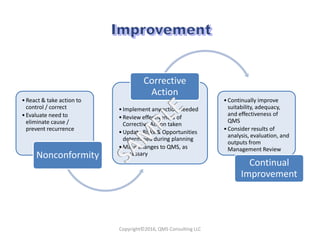
This document compares key changes between ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 9001:2008 quality management standards. Some major changes include a new focus on risk-based thinking and consideration of organizational context and interested parties. Clause structure and terminology were also updated. For example, leadership and planning requirements were strengthened, with an increased emphasis on actions to address risks and opportunities. Overall, the ISO 9001:2015 standard introduced new concepts like risk-based thinking and placed more focus on performance evaluation and continual improvement of the quality management system.