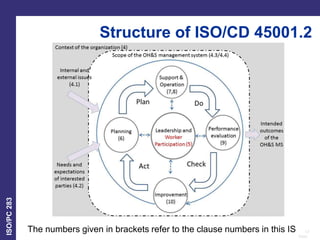
ISO 45001 is a new international standard for occupational health and safety management systems currently under development by ISO/PC 283. It is intended to help organizations minimize risks to workers' health and safety and provide continual improvement in OH&S performance. The draft standard emphasizes top management leadership and accountability for OH&S as well as worker participation. It also focuses on preventing both immediate and long-term health impacts. The standard structure is based on Annex SL for commonality across ISO management system standards.