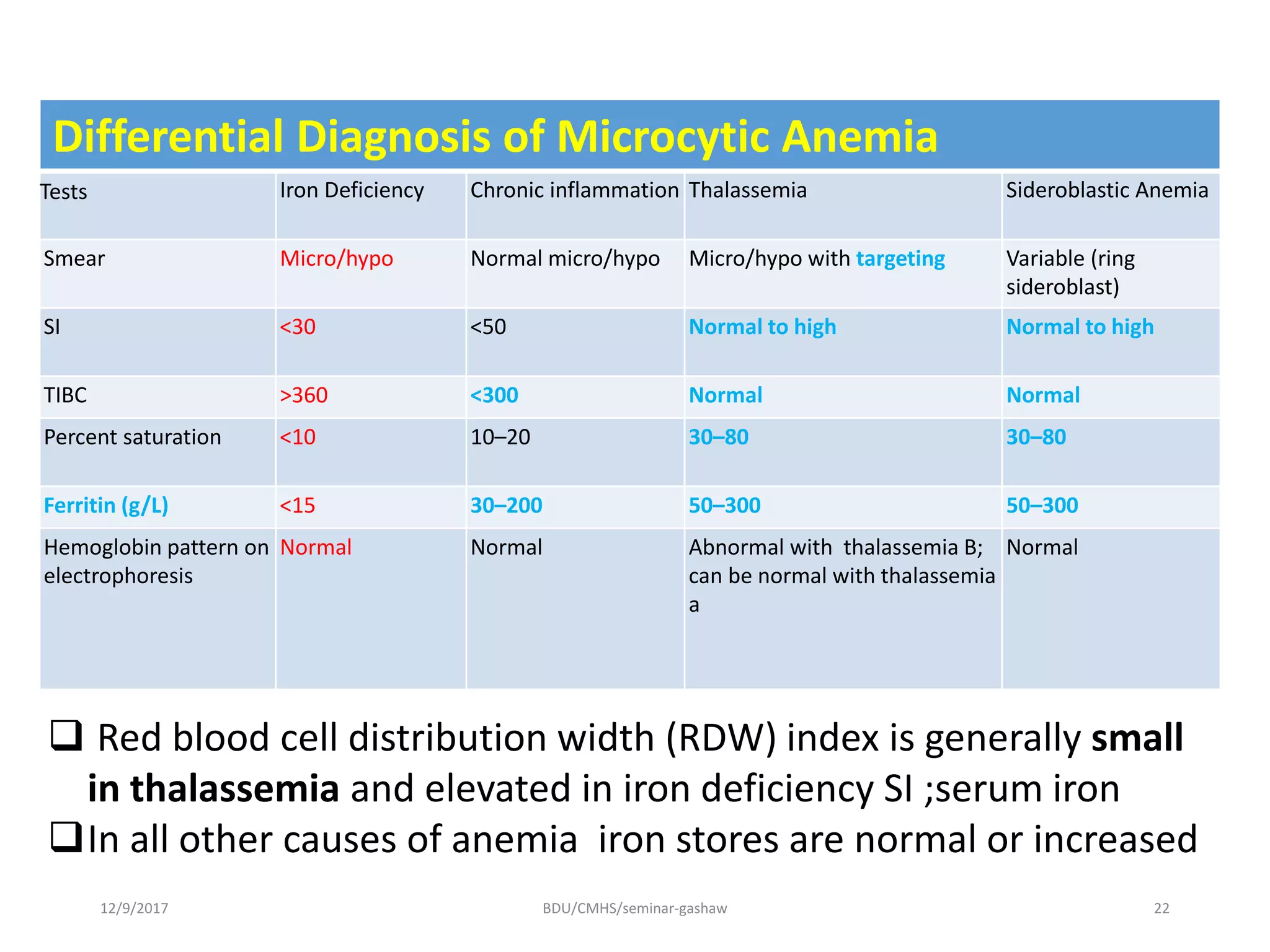
Iron deficiency anemia is a hypoproliferative anemia resulting from insufficient iron intake or absorption to support normal red blood cell production. Globally, iron deficiency affects over 2 billion people and is most prevalent in children, pregnant women, and those from Africa and Asia. Iron is essential for oxygen transport and cellular enzyme functions. Causes of iron deficiency anemia include inadequate dietary iron, malabsorption, blood loss, and increased demands from growth or pregnancy. The condition progresses from depleted iron stores to iron deficient erythropoiesis and finally anemia, with associated clinical features like pallor, fatigue, and glossitis. Diagnosis involves blood tests showing microcytic hypochromic anemia and low iron indicators.