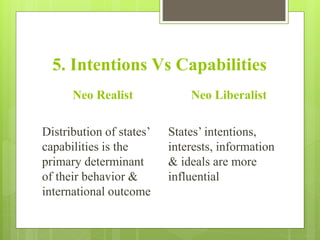
The document discusses several theories and approaches to international relations. It describes explanatory and constitutive theories, with explanatory theories taking a positivist approach to formulating hypotheses to explain phenomena based on assumptions, and constitutive theories adopting a social scientific method and broader scope. Realism and idealism/liberalism are described as traditional approaches, with realism focusing on state power and survival in an anarchic system and idealism advocating for collective security, democracy, and free trade. Neorealism and neoliberalism are system approaches described, with neorealism emphasizing the constraints of the anarchic system and neoliberalism seeing a role for non-state actors and the potential for international cooperation through institutions and inter