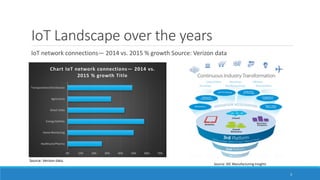
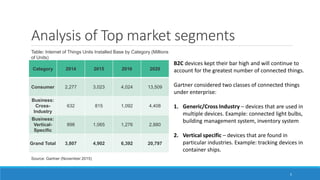
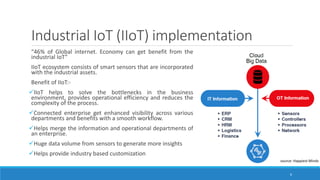
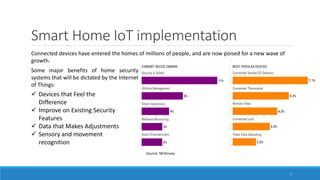
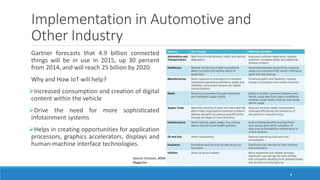
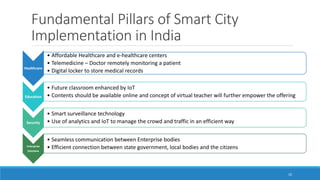
This document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT) landscape in India. It discusses the growth of the IoT market and number of IoT firms in India. Key points include: (1) The Indian IoT market is expected to reach $15 billion by 2020; (2) Nearly 120 firms offer IoT solutions in India, with 60% of startups emerging after 2010; (3) Important applications and use cases driving growth include smart buildings, transportation, logistics, and agriculture. The document also examines technological changes in IoT and implementation across various industries such as industrial IoT, smart homes, automotive, and smart cities in India.