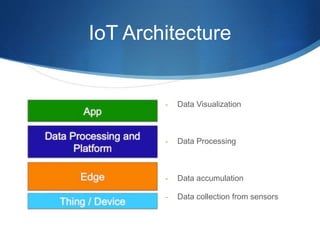
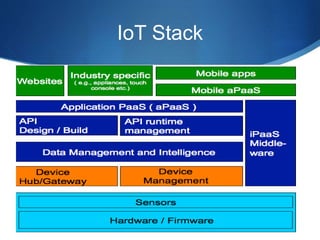
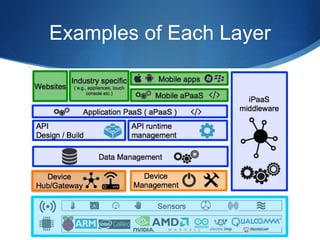
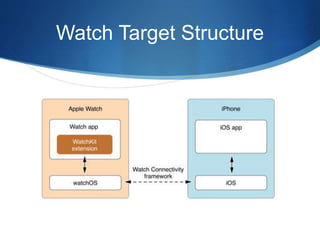
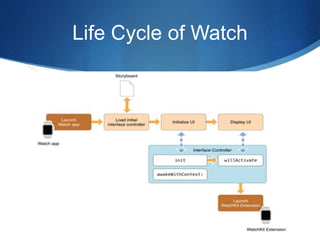
The document discusses the Internet of Things (IoT) and how connected devices, cloud services, and mobile/web applications work together in the IoT ecosystem. It provides examples of IoT applications in various areas like smart homes, cities, manufacturing, and retail. It then discusses challenges like privacy and security. Finally, it uses the example of Apple's ecosystem involving the Apple Watch, iCloud storage, and iPhone to illustrate how these components interact to enable IoT experiences.