This document provides an overview of iOS application development, including the anatomy of an iOS application, the app lifecycle managed by UIKit, and the model-view-controller (MVC) design pattern. Key points covered include:
- An iOS app contains compiled code, nib files defining the user interface and relationships between objects, and resource files like images and sounds.
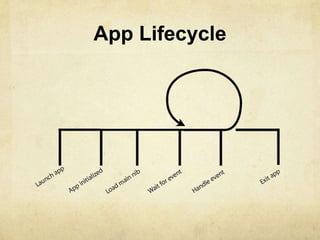
- The UIApplication class orchestrates the app lifecycle by dispatching events and managing the status bar. Delegation is used to avoid subclassing and control is passed to delegate objects.
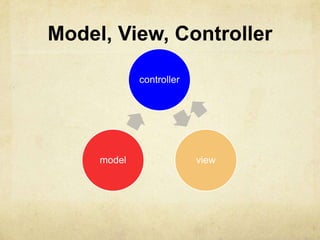
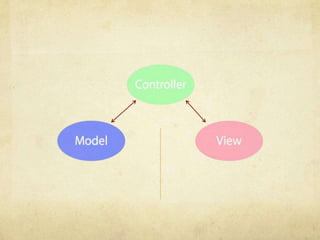
- Nib files help design the view layer and establish connections between controller objects and UI elements at design time. At runtime, objects are unarchived