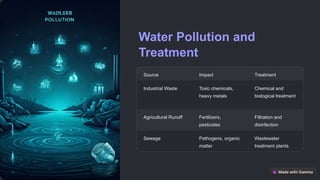
This document provides an overview of the importance, properties, and cycles of water, emphasizing its essential role in life. It discusses the water cycle, water conservation methods, pollution sources, and global water issues like scarcity and conflict. The conclusion highlights the need for responsible management and innovative technologies to secure water resources for the future.