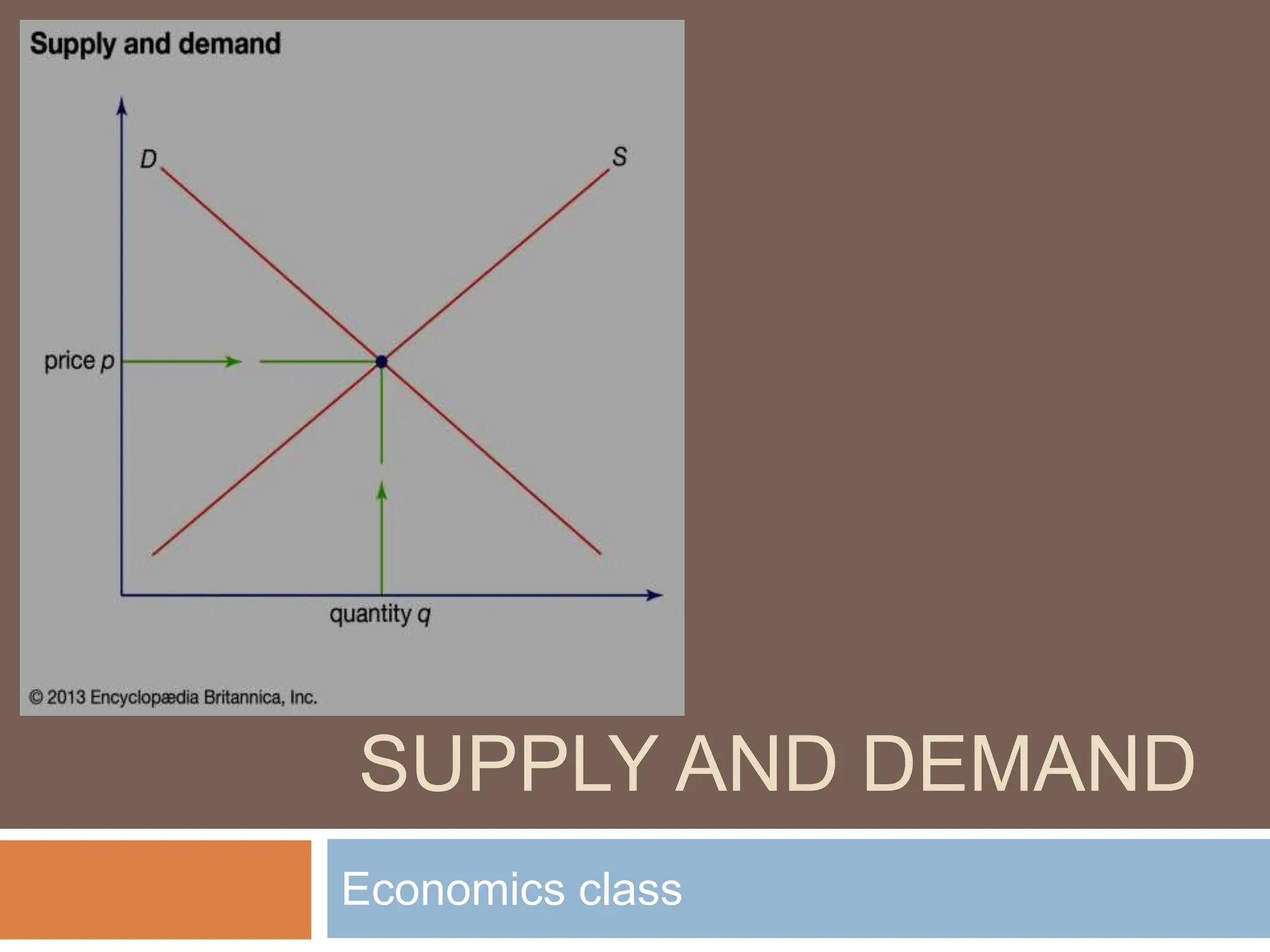
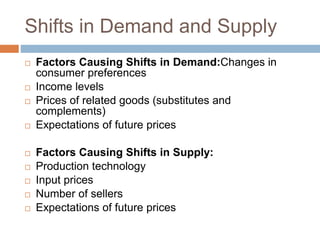
This document introduces the concepts of supply and demand in economics, defining supply as the quantity producers are willing to sell and demand as the quantity consumers are willing to buy at various prices. It explains the laws of demand and supply, illustrating their principles with downward and upward-sloping curves, respectively, and discusses market equilibrium where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Additionally, it highlights factors that can shift supply and demand, along with real-world examples of their applications.