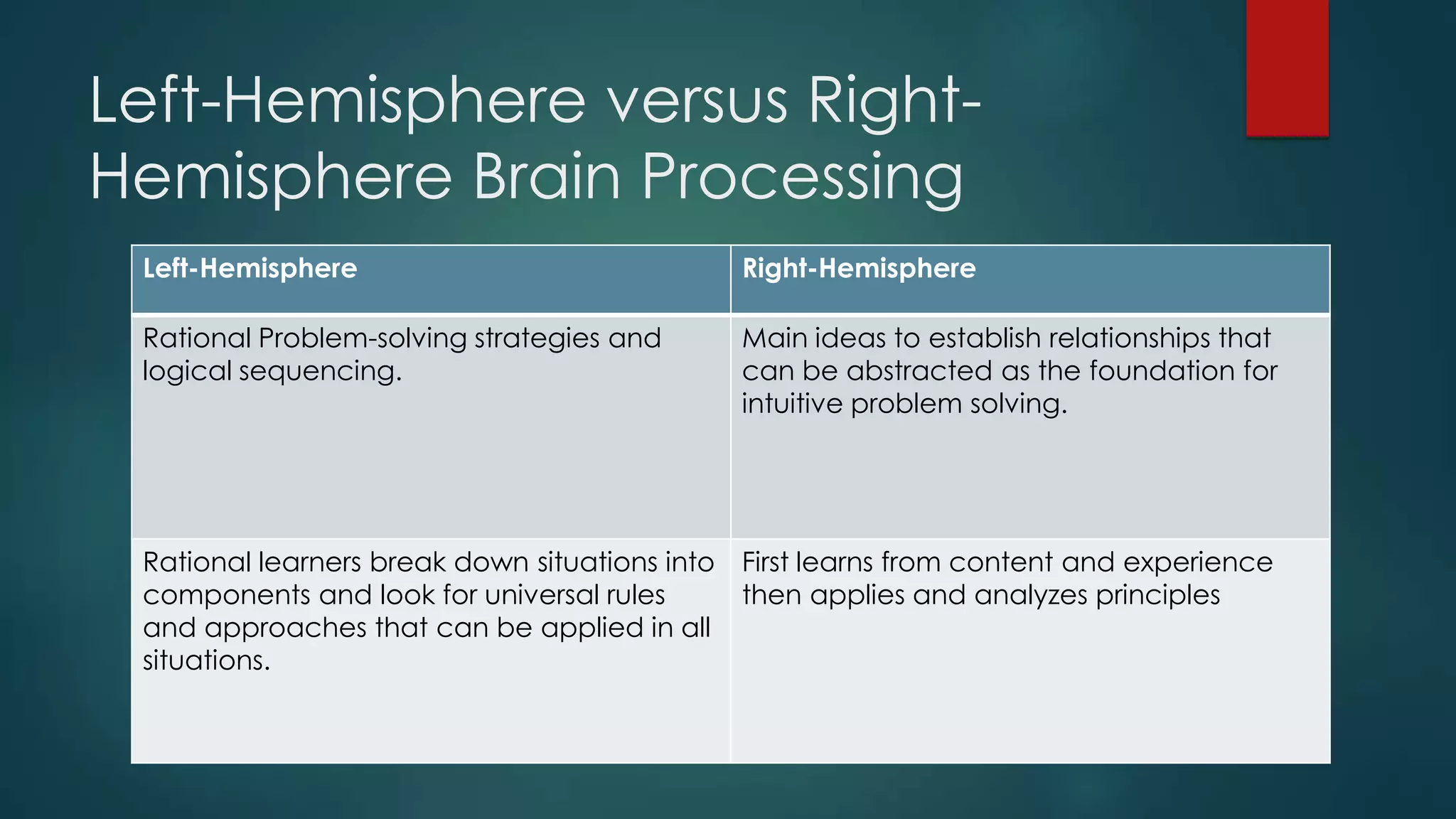
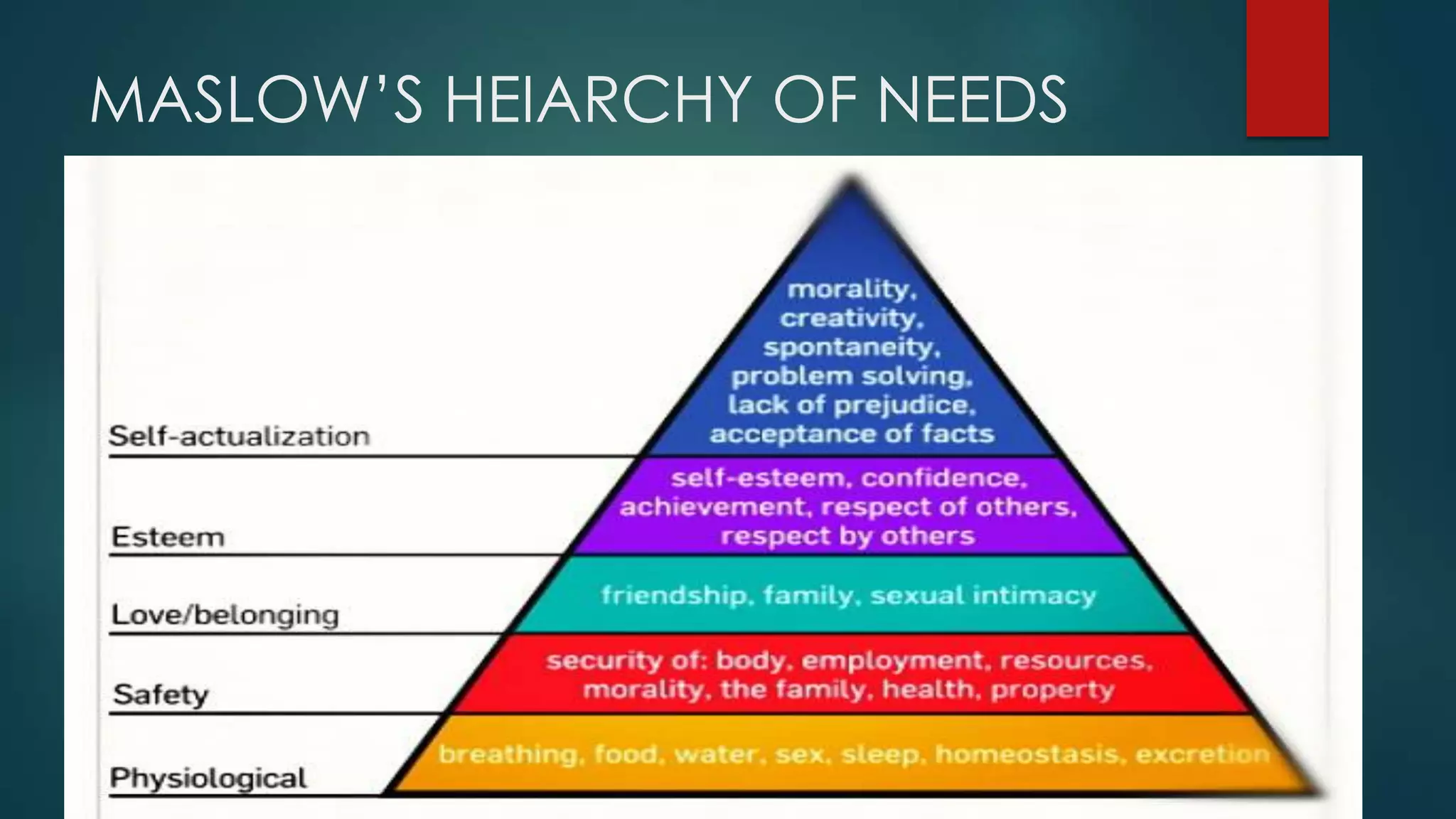
The document provides strategies for effective test taking. It discusses left and right brain processing differences and emphasizes reviewing questions for key concepts before looking at answer choices. The document also discusses exploring consequences of each answer choice and avoiding rewriting the question. It outlines cognitive levels of questions from knowledge to analysis and provides examples. Memorization techniques like acronyms and mnemonics are suggested to increase knowledge. The importance of practice testing to reinforce learning is also highlighted.