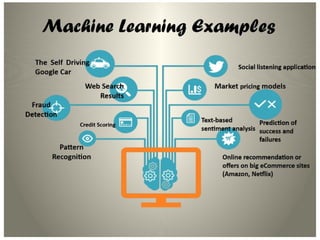
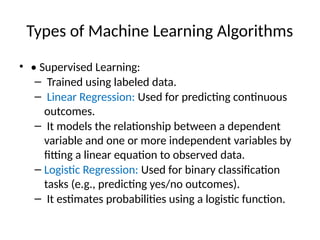
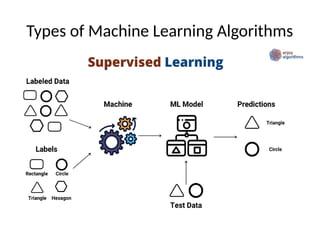
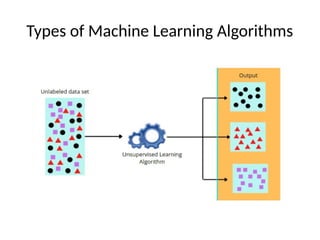
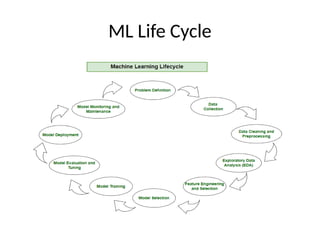
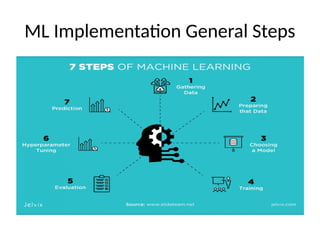
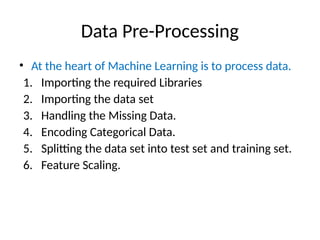
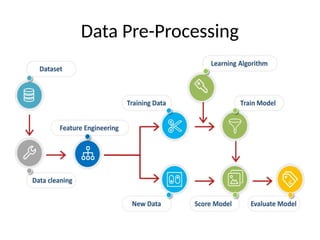
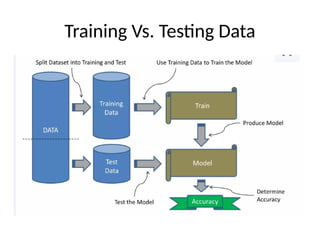
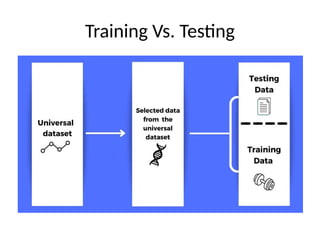
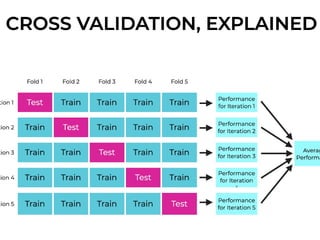
This document introduces key concepts in machine learning, including its definition, types of learning algorithms (supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised), and the machine learning life cycle. It highlights the importance of data and outlines steps for data pre-processing, as well as the distinction between training and testing datasets. Additionally, it discusses cross-validation as a method for assessing model performance.