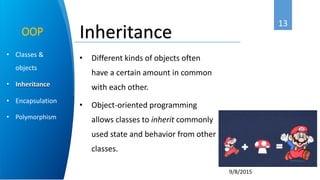
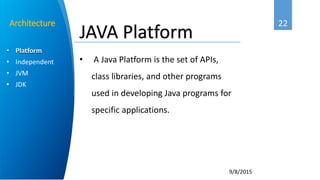
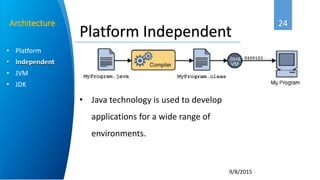
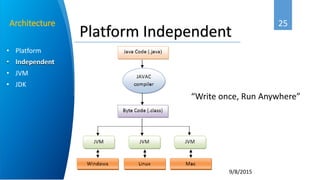
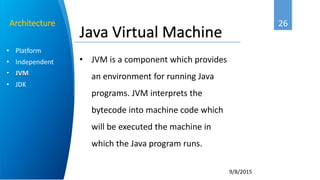
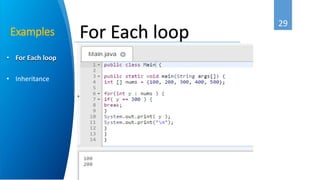
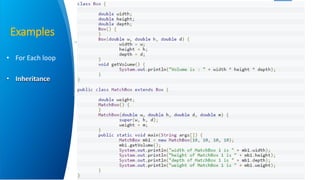
Ahmed Abbadi is an instructor for an introduction to Java course. He has a computer engineering background from Cairo University and is a member of the IEEE professional organization. The course covers what Java is, its object-oriented programming concepts like classes and objects, why Java was developed, its architecture including the Java Virtual Machine, and examples like for each loops and inheritance.