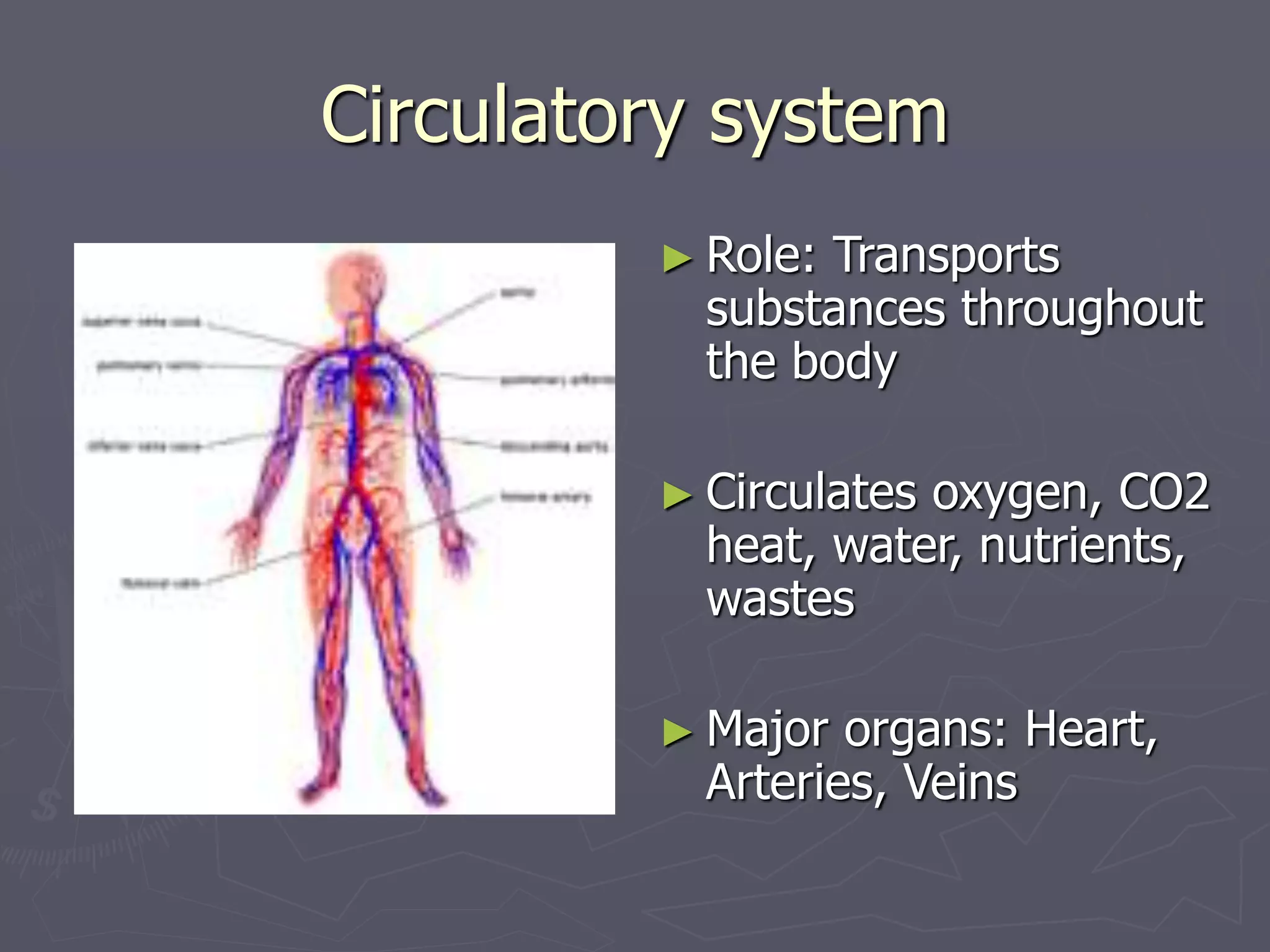
The document outlines the major human body systems, including their roles and main organs. The circulatory system transports substances throughout the body. The excretory system filters wastes from the blood and maintains nutrient balances. The digestive system breaks down macromolecules and absorbs nutrients using organs like the stomach, liver, and intestines. Other systems described are the reproductive, skeletal, muscular, nervous, integumentary, endocrine, lymphatic, and respiratory systems.