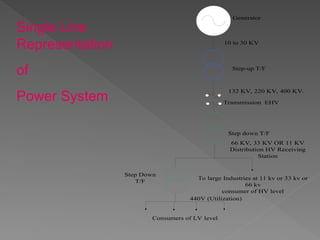
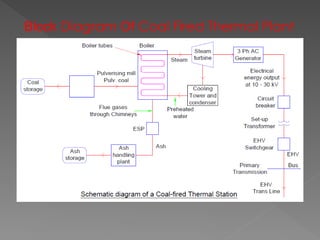
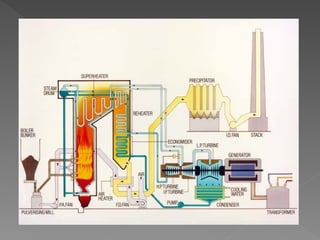
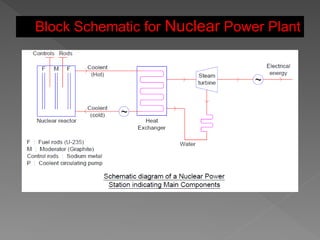
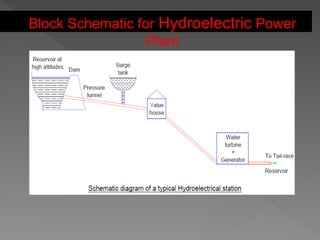
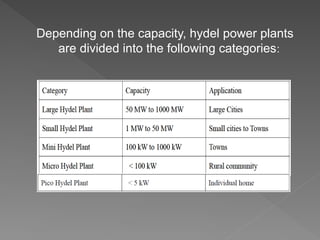
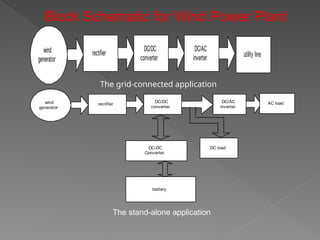
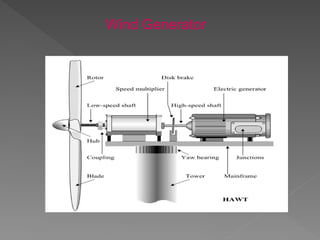
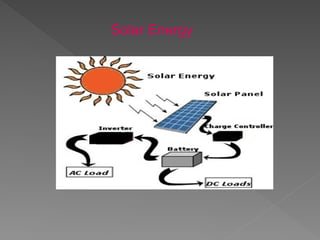
The document provides an overview of electrical power systems, highlighting the significance of electricity for societal growth and various applications. It discusses conventional and non-conventional power generation methods in India, including thermal, hydro, and nuclear energy, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of energy efficiency and environmental considerations in power generation.