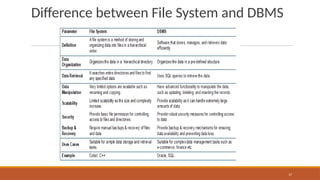
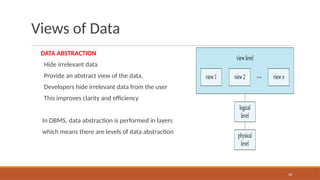
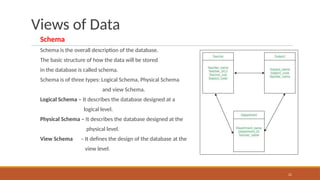
The document outlines the syllabus for a Database Management Systems course, covering topics such as database architecture, SQL, PL/SQL, normalization, indexing, transactions, and NoSQL databases. It emphasizes the advantages of database systems over traditional file processing systems, including reduced data redundancy and improved data integrity. The syllabus also includes references to textbooks and materials for further study.