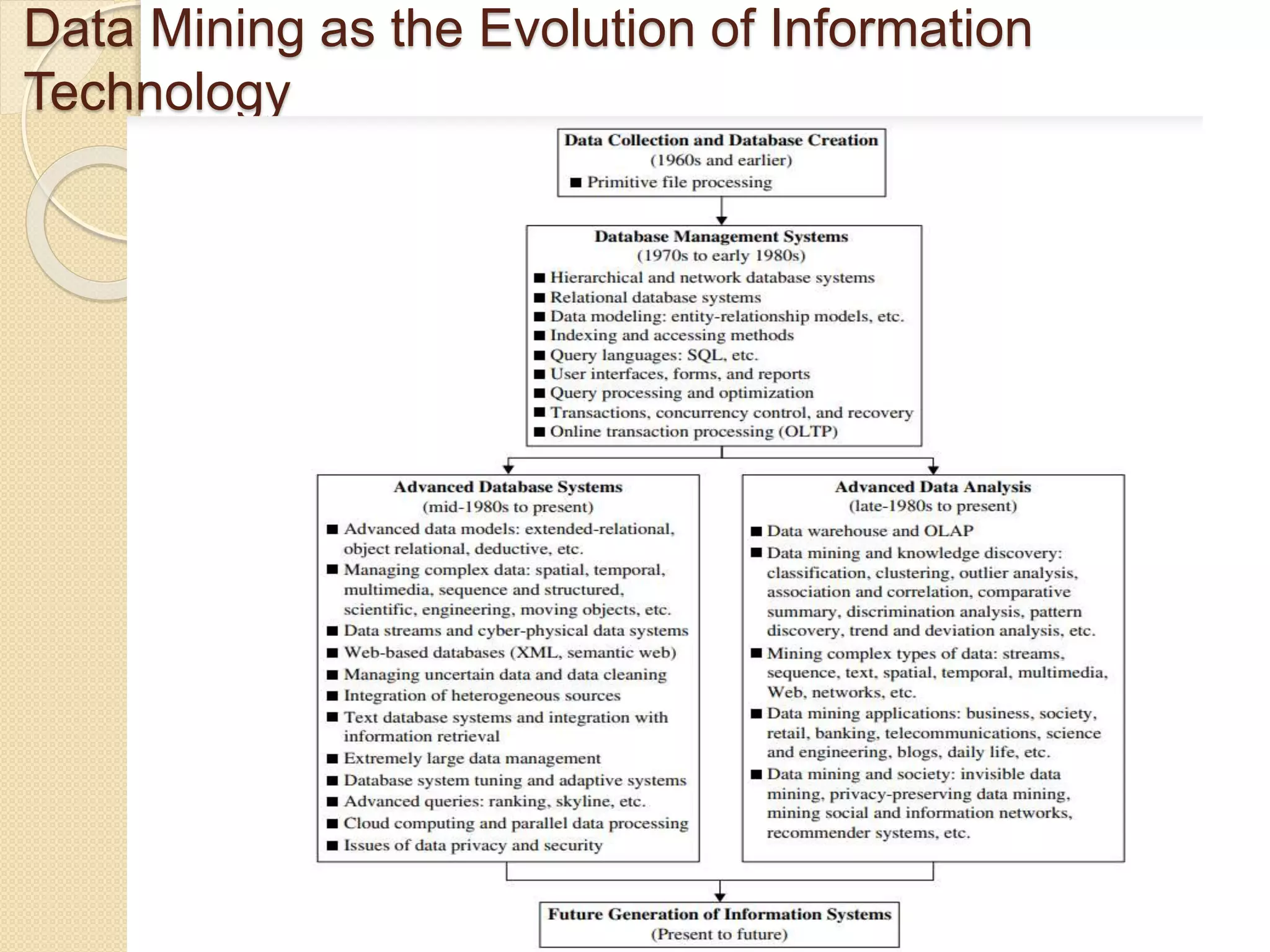
Data mining is a non-trivial process aimed at extracting valid and useful patterns from large datasets. The document outlines a data mining process that includes data cleaning, integration, selection, and pattern evaluation as part of knowledge discovery. It emphasizes the iterative nature of the process and the need for prior knowledge and effective algorithms.