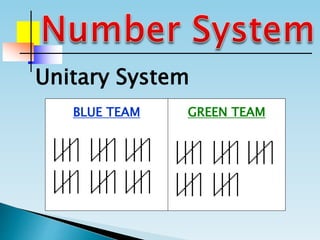
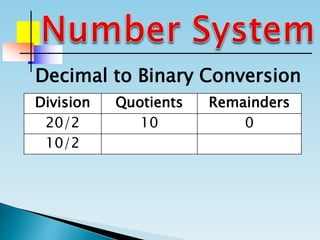
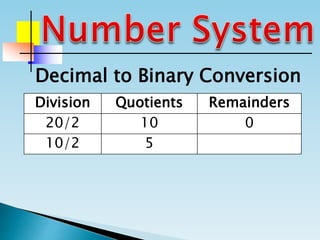
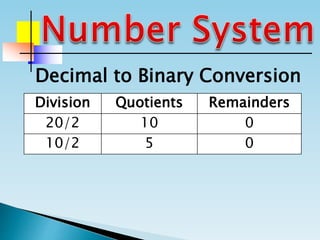
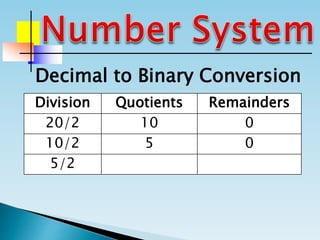
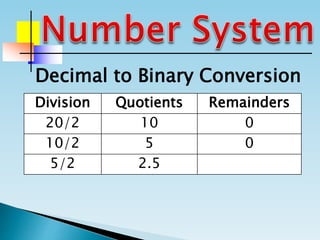
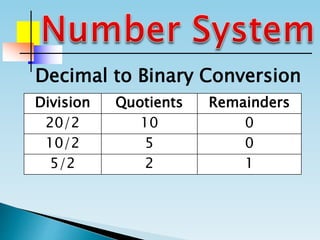
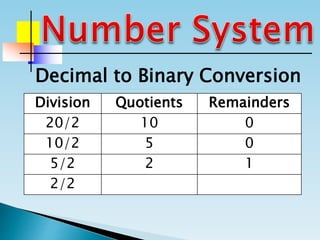
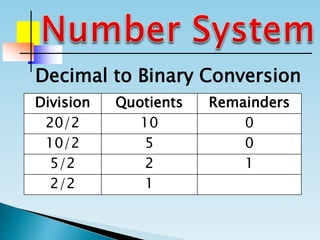
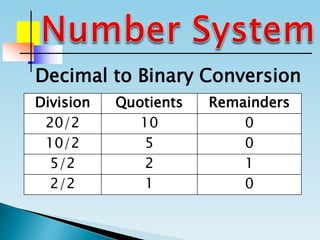
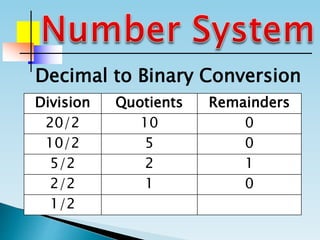
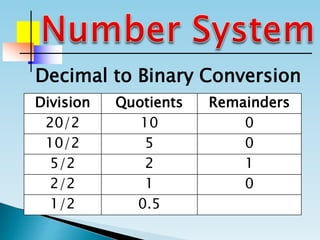
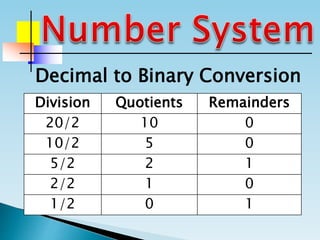
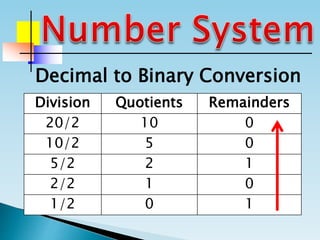
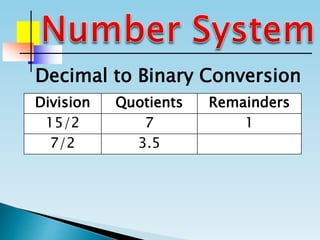
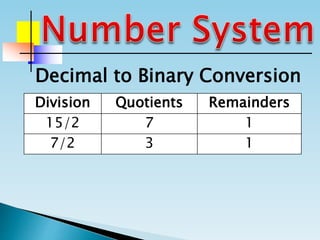
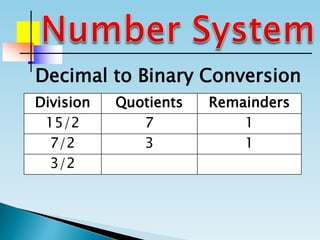
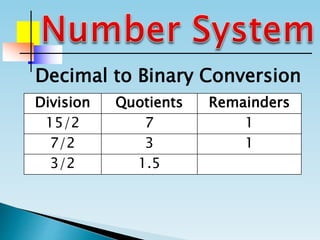
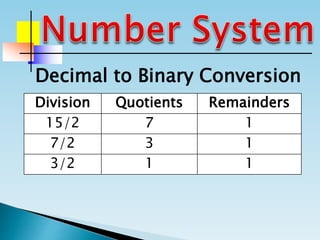
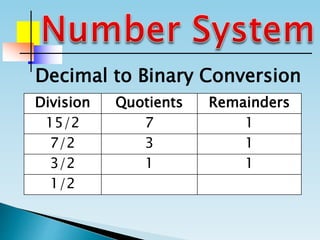
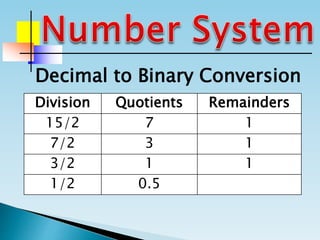
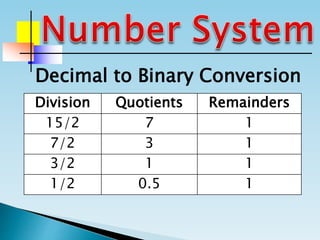
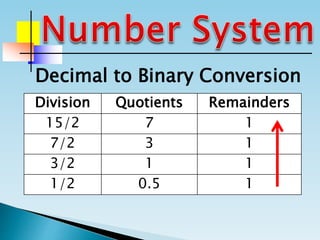
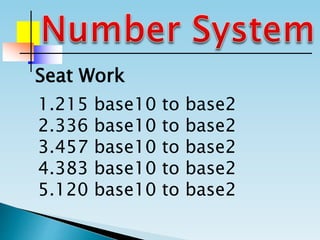
The document discusses the binary number system and how to convert between decimal and binary numbers. It explains that binary uses only the digits 0 and 1 and that each digit has a place value determined by its position. To convert a decimal number to binary, you repeatedly divide the number by 2 and write down the remainders with the rightmost remainder first. Similarly, to convert a binary number to decimal, you multiply each digit by its place value and add the results. Several examples are provided to demonstrate converting specific numbers between decimal and binary representations.