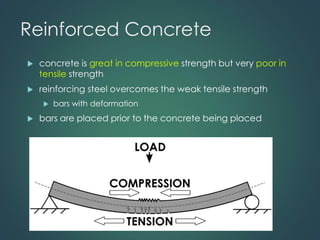
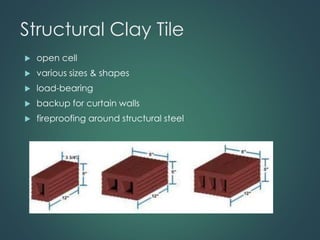
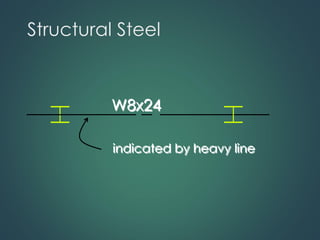
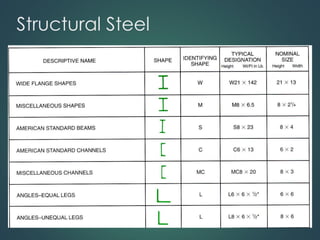
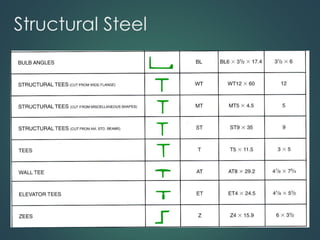
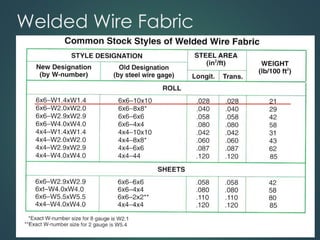
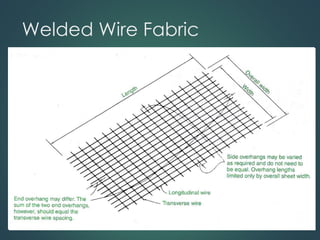
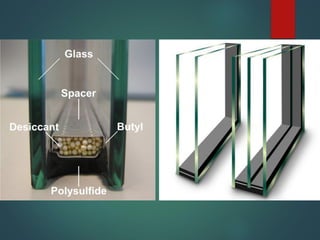
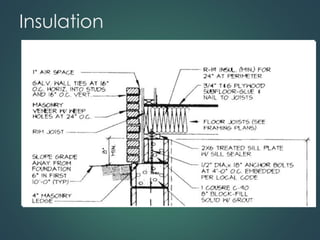
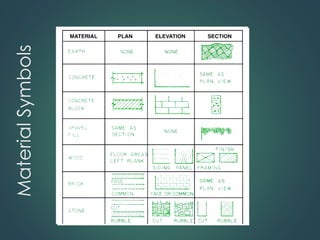
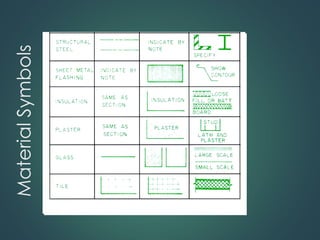
This document provides an overview of common construction materials used in building including concrete, masonry, wood, metals, glass, plastics and insulation. It describes the composition and characteristics of materials like concrete which uses cement, aggregates and water. It also outlines different types of masonry units such as brick, block and stone as well as wood classifications of hardwoods and softwoods. Finally, it discusses metals like structural steel shapes, glass products and plastics used in construction.