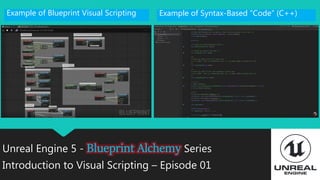
This document introduces visual scripting and Unreal Engine Blueprints. It discusses object-oriented programming concepts like classes, child classes, functions, and variables. It provides examples of visual scripting languages and compares Blueprint visual scripting to C++ syntax. The goal of visual scripting is to represent programming concepts using nodes and connections instead of lines of code. Unreal Engine Blueprints allow complex gameplay to be programmed rapidly without writing code.