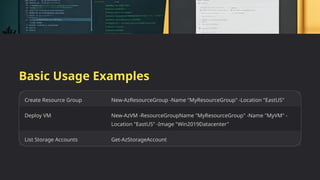
The document provides an overview of the Azure PowerShell module, which allows users to manage Azure resources directly from the command line, making it particularly useful for DevOps engineers and developers. Key features include cross-platform compatibility, a modular design, and a standardized naming convention for cmdlets. The document also outlines the installation process, common commands, and advanced functionalities like filtering and pipelining to automate tasks.