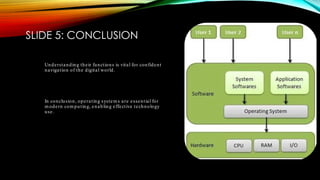
The document discusses the key functions of an operating system (OS) including resource management, user interface, process management, memory management, file system management, and security and access control. It also covers different types of OS like single-user, multi-user, real-time, network, mobile, and server OS. Examples provided are Microsoft Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. The conclusion states that OS are crucial for modern computing as they enable efficient hardware and software coordination and management.