The document discusses the evolution of web applications from Web 1.0 to Rich Internet Applications (RIAs), highlighting the impact of AJAX on user experience and client-side processing. It introduces Adobe Flex as a platform for building RIAs, detailing its components, programming languages (MXML and ActionScript 3.0), and the development environment it provides. The document also compares the advantages of RIAs over traditional web and desktop applications, emphasizing their responsiveness and rich media capabilities.































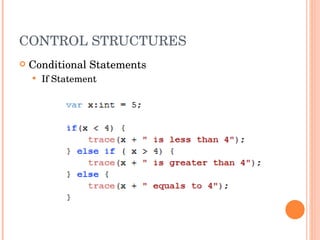

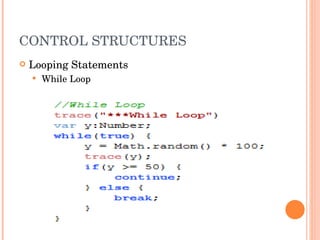
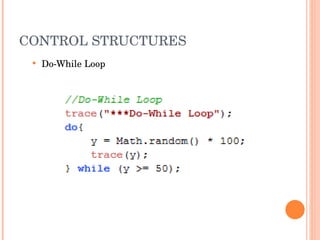










![PARSING XML USING E4X xmlData.employee[2] xmlData..employee All nodes called node xmlData..employee.(firstName==‘Joe’) xmlData..employee.(@id > 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introtorichinternetapplications-12544097432496-phpapp01/85/Introduction-To-Rich-Internet-Applications-47-320.jpg)