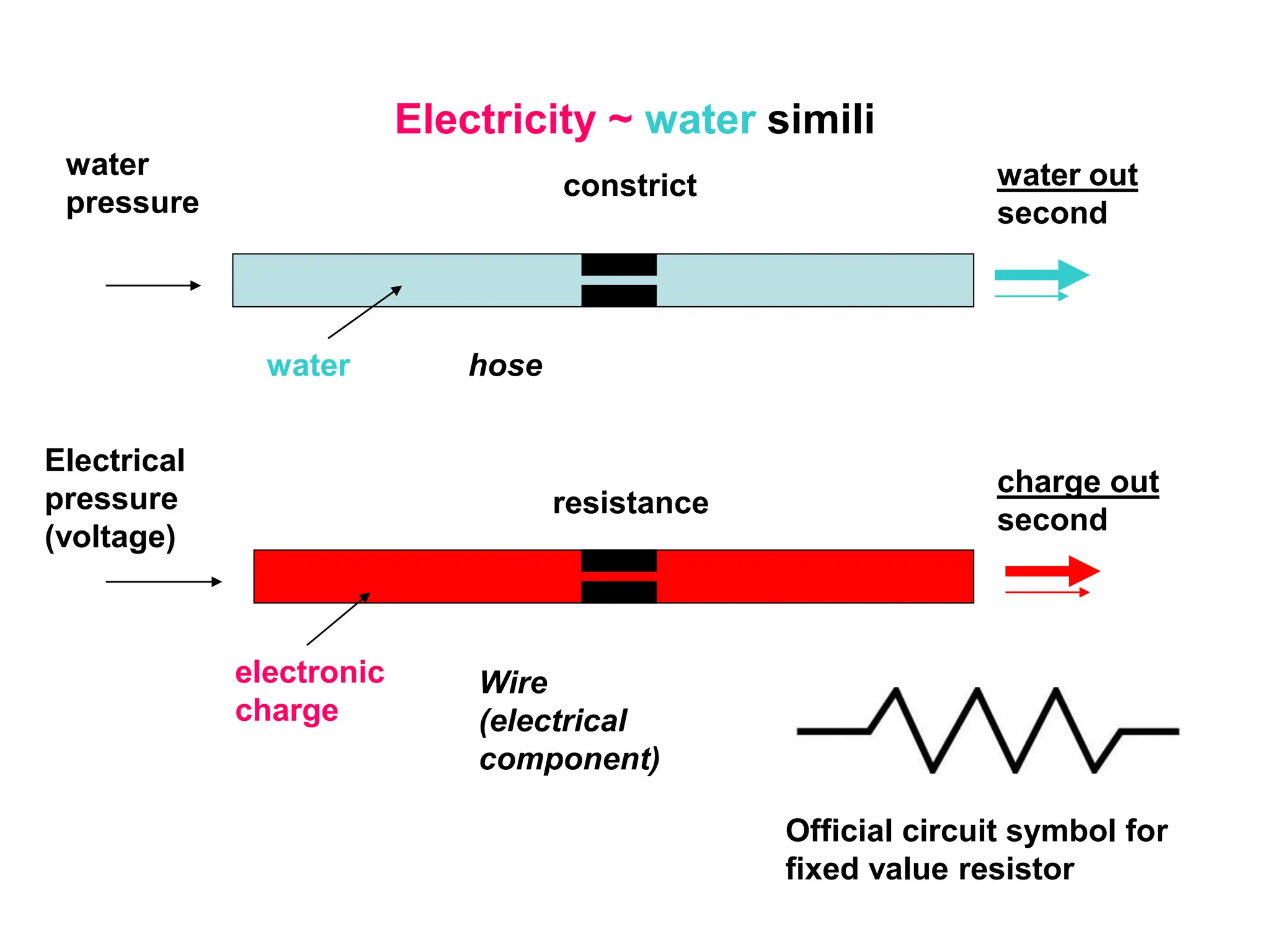
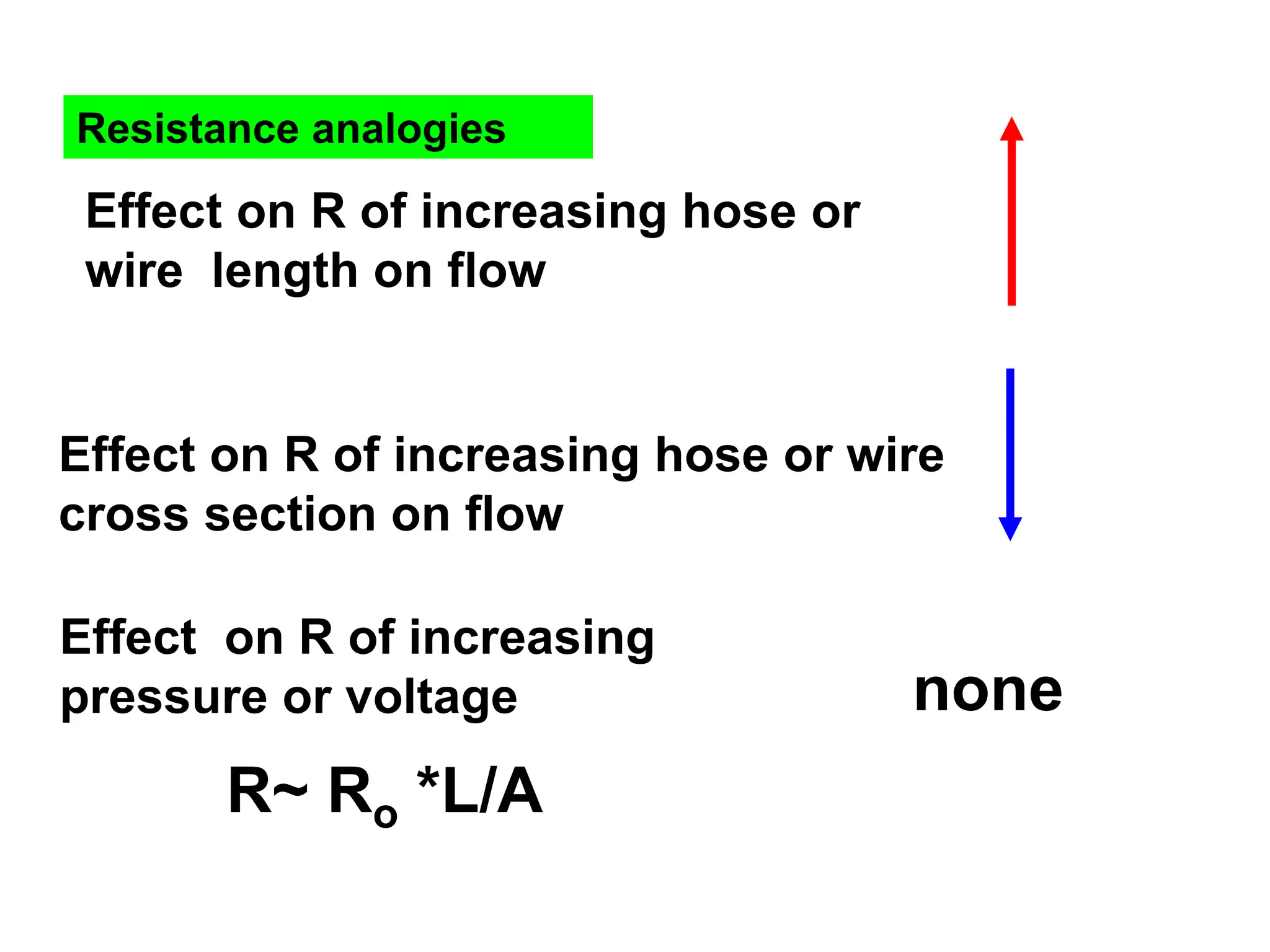
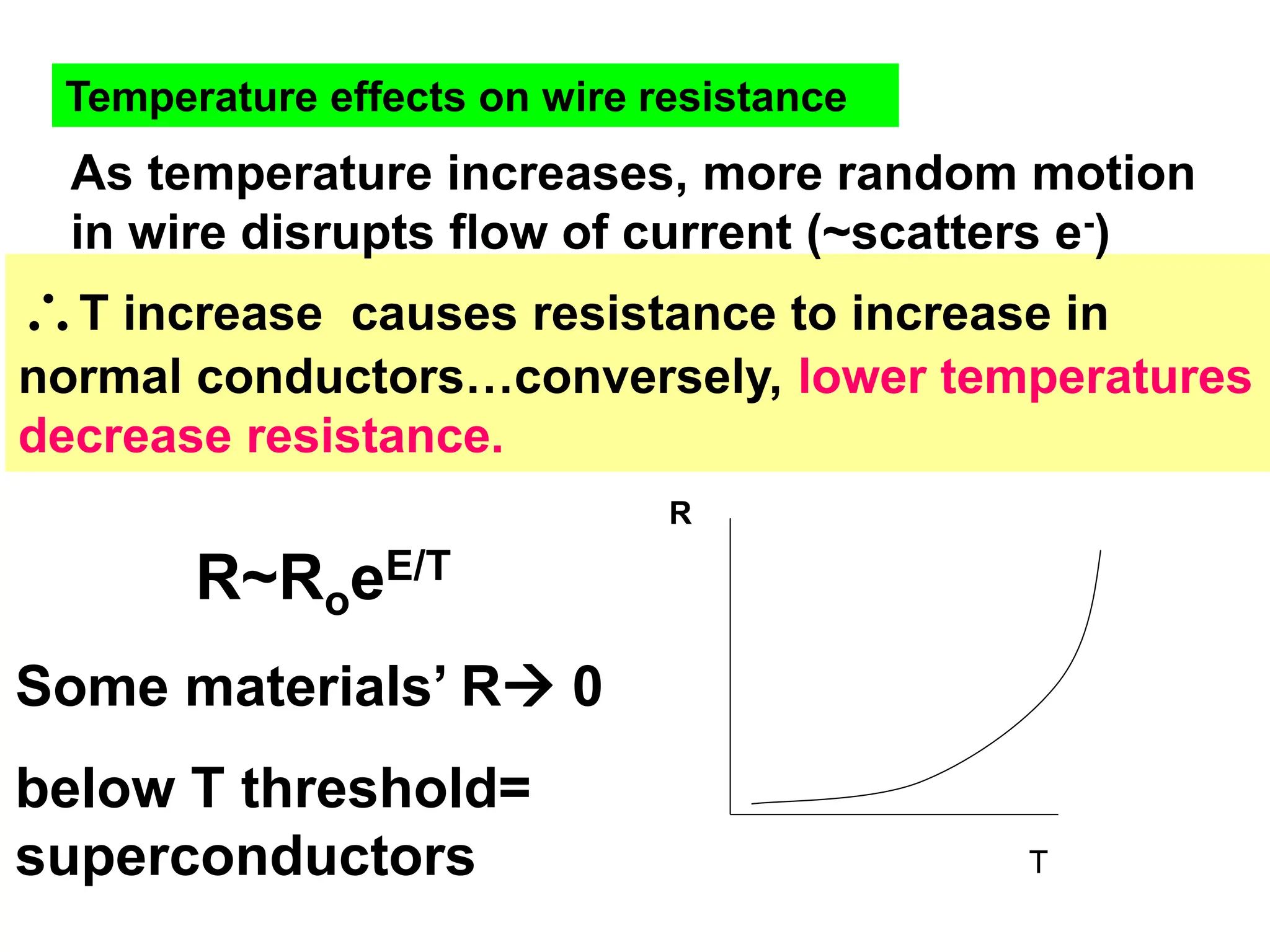
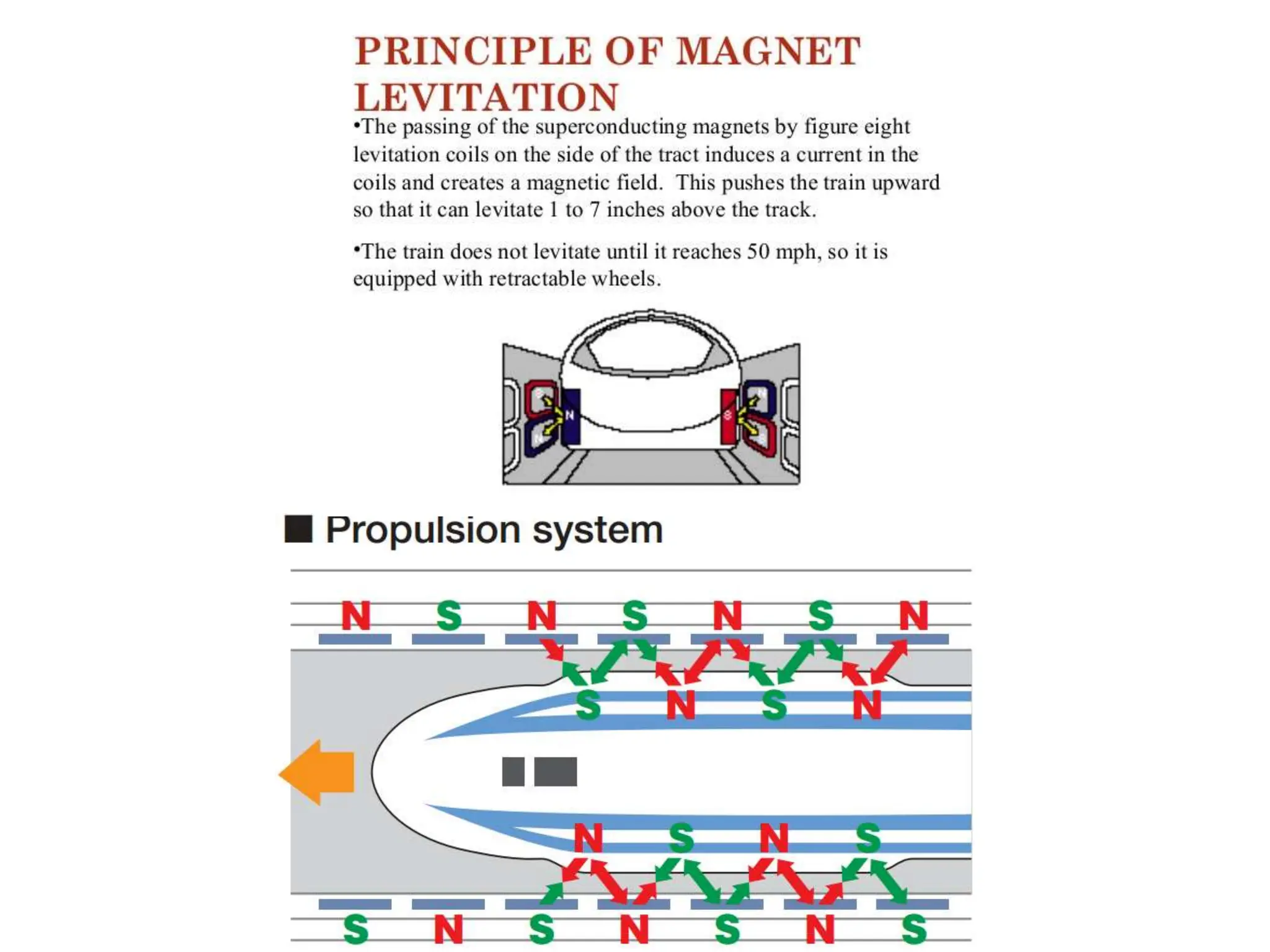
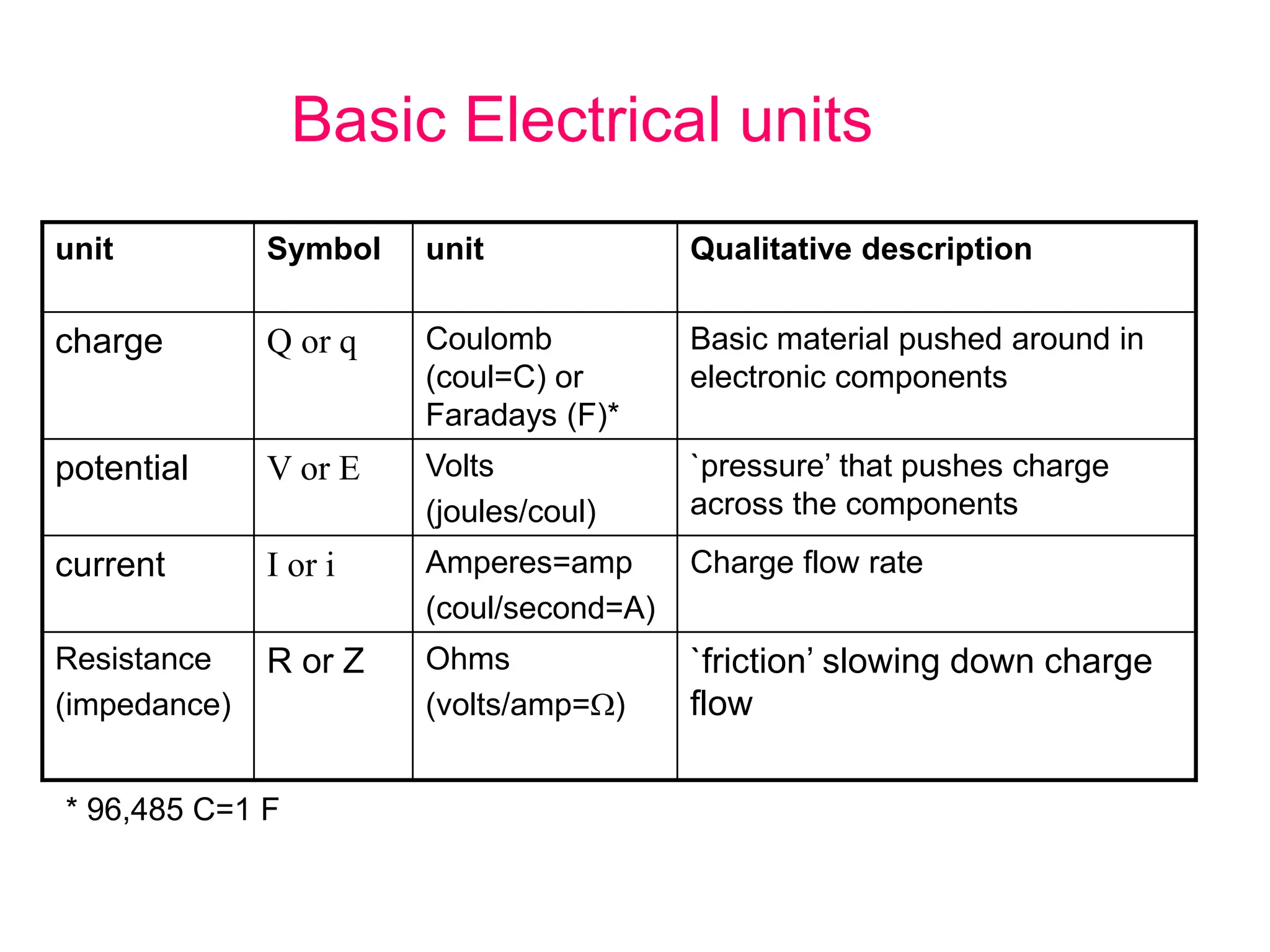
Electricity concepts can be understood using analogies to water flow. Voltage is like water pressure, current is like water flow rate, and resistance impedes flow. Resistance increases with length and decreases with cross-sectional area. It also increases with temperature in normal conductors.
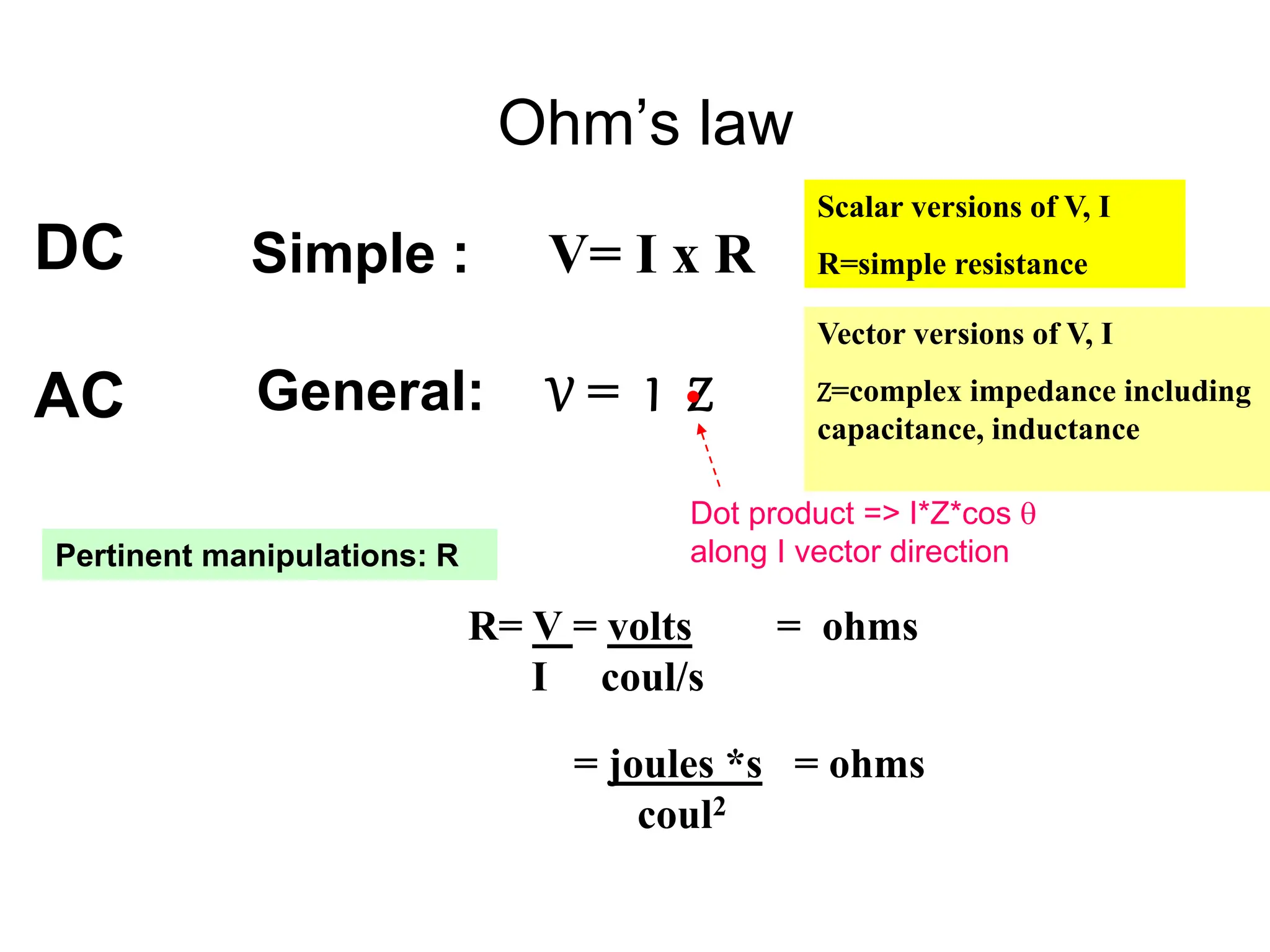
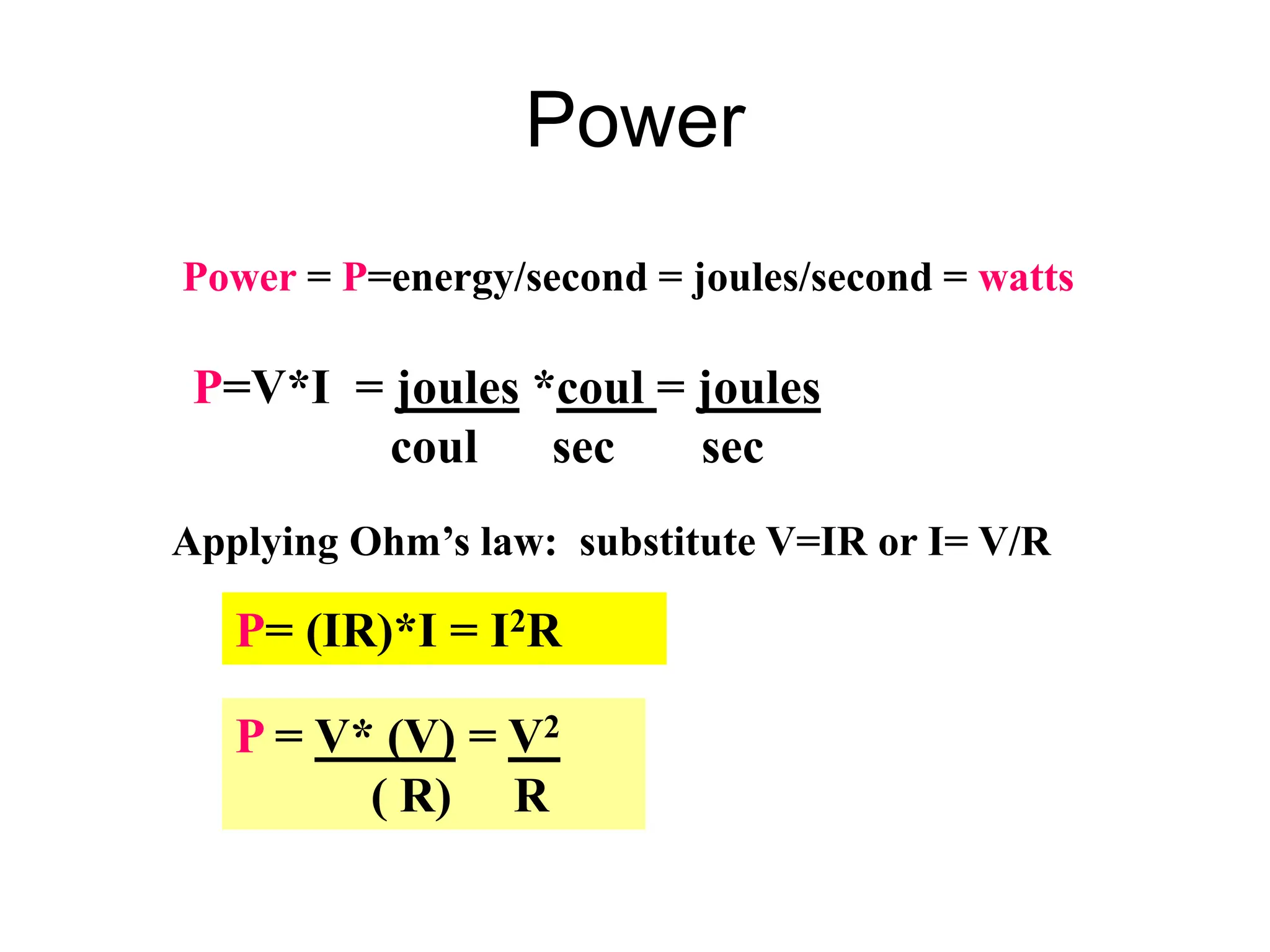
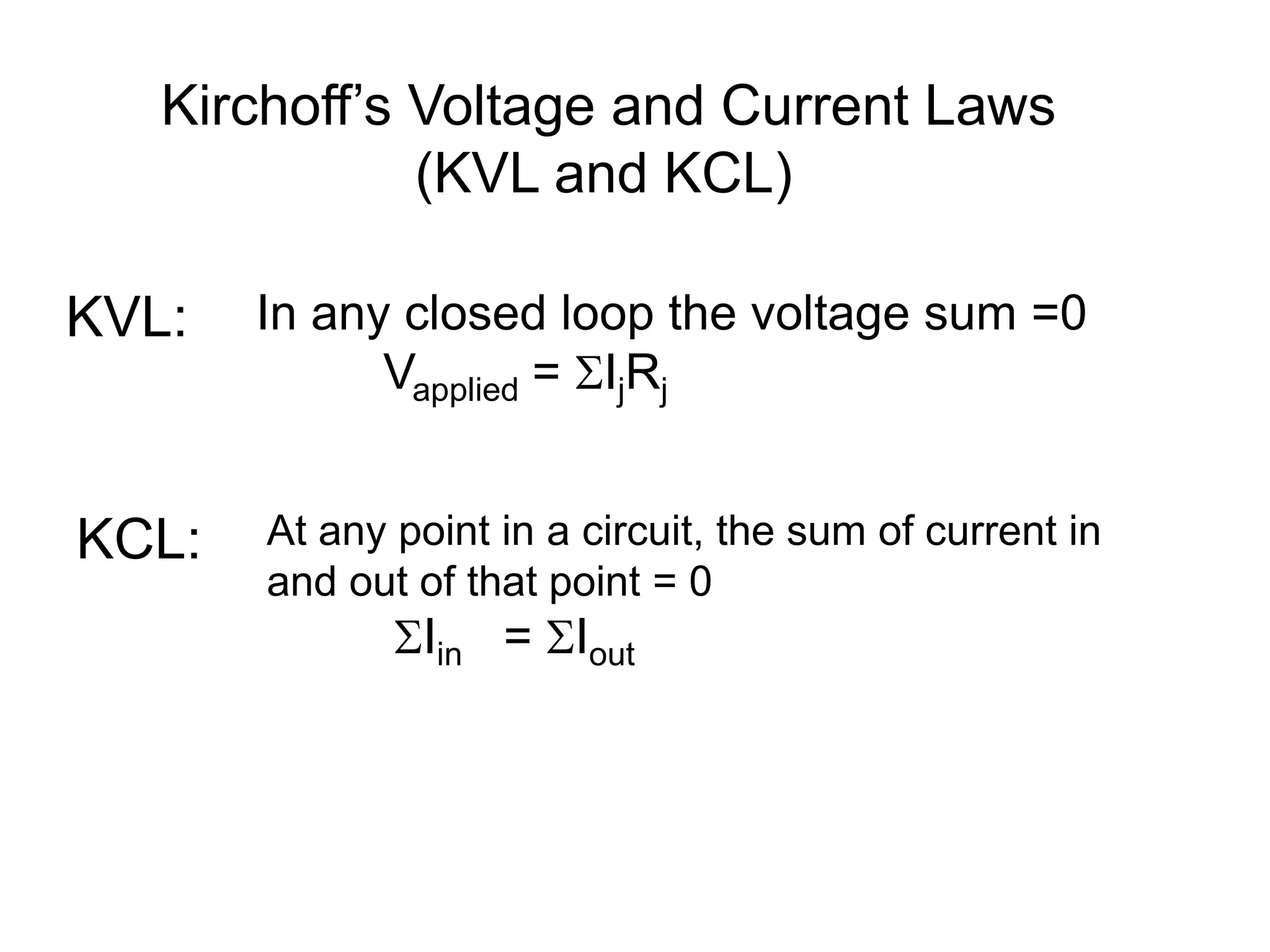
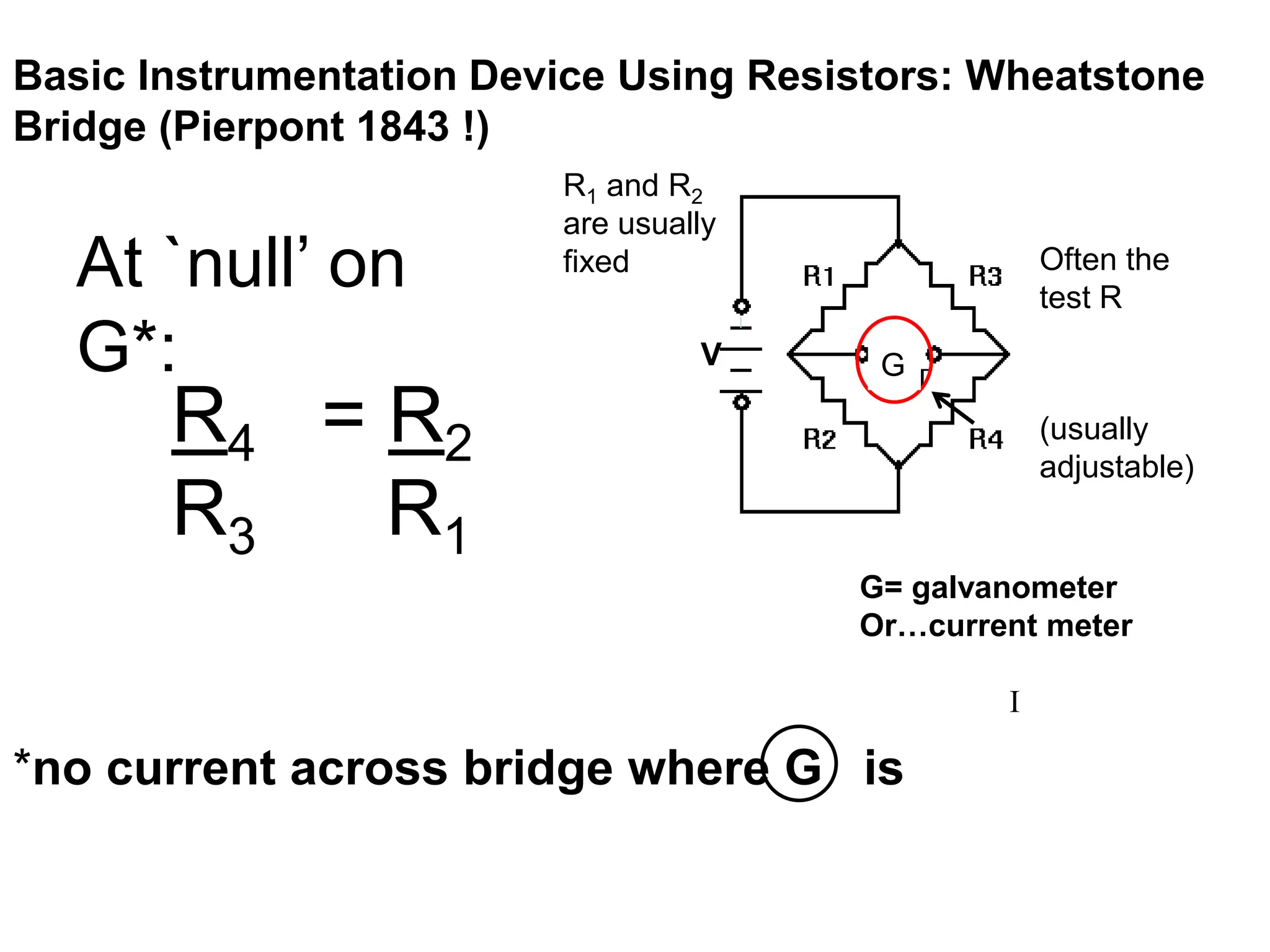
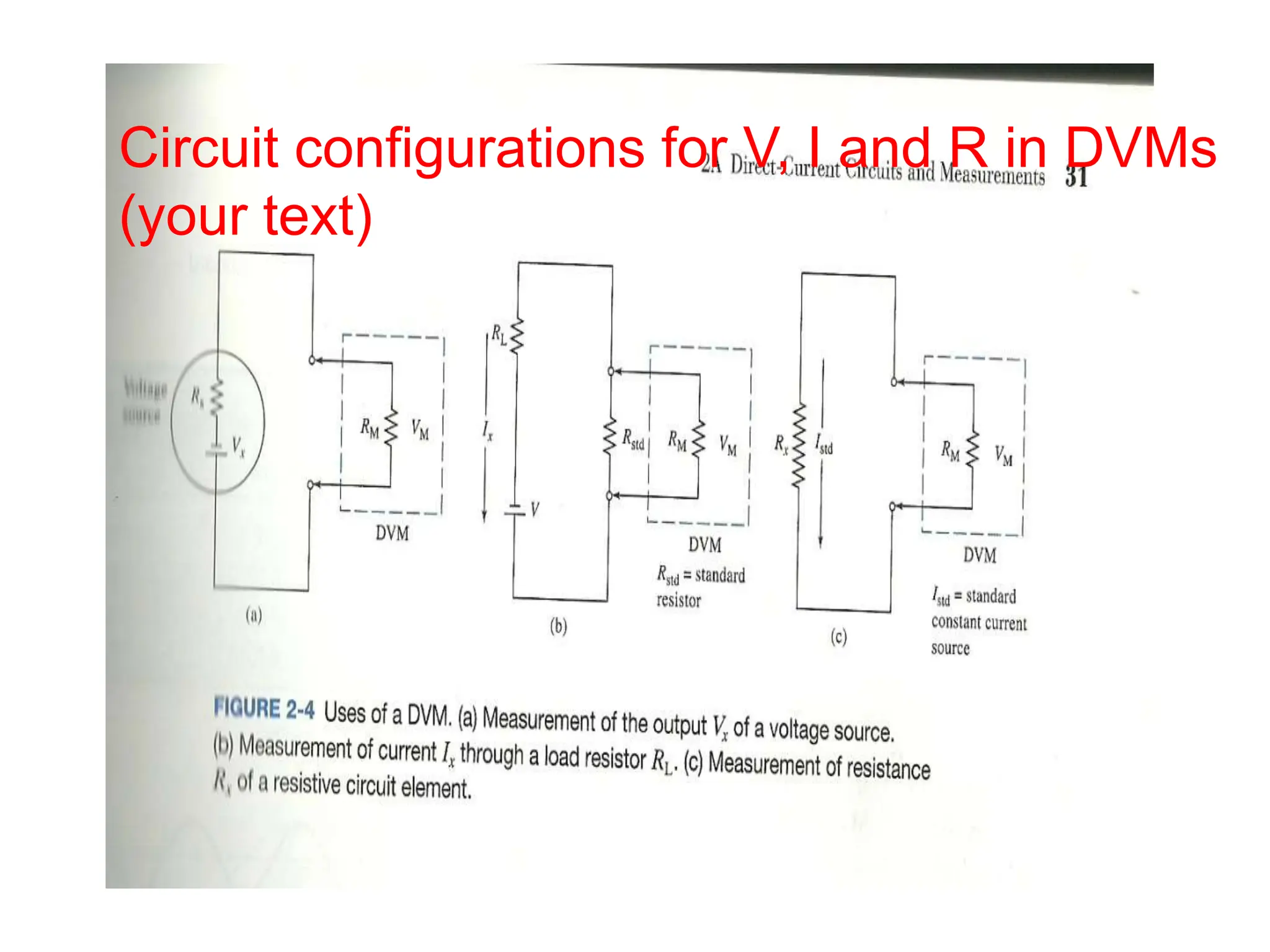
Ohm's law states that voltage equals current times resistance. Kirchoff's laws allow analysis of circuits using voltage and current sums. Meters like multimeters use Wheatstone bridges to measure voltage, current, and resistance.
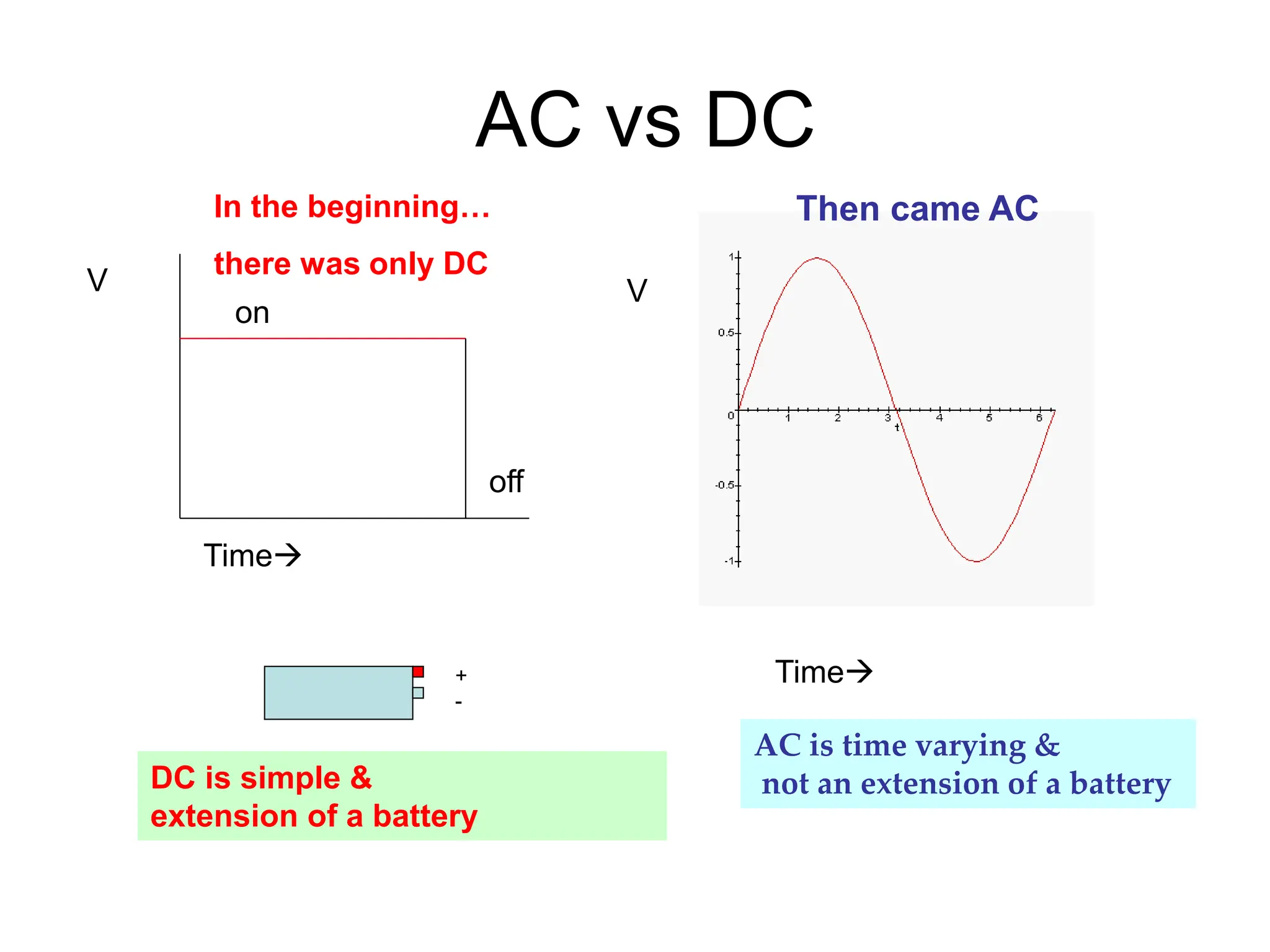
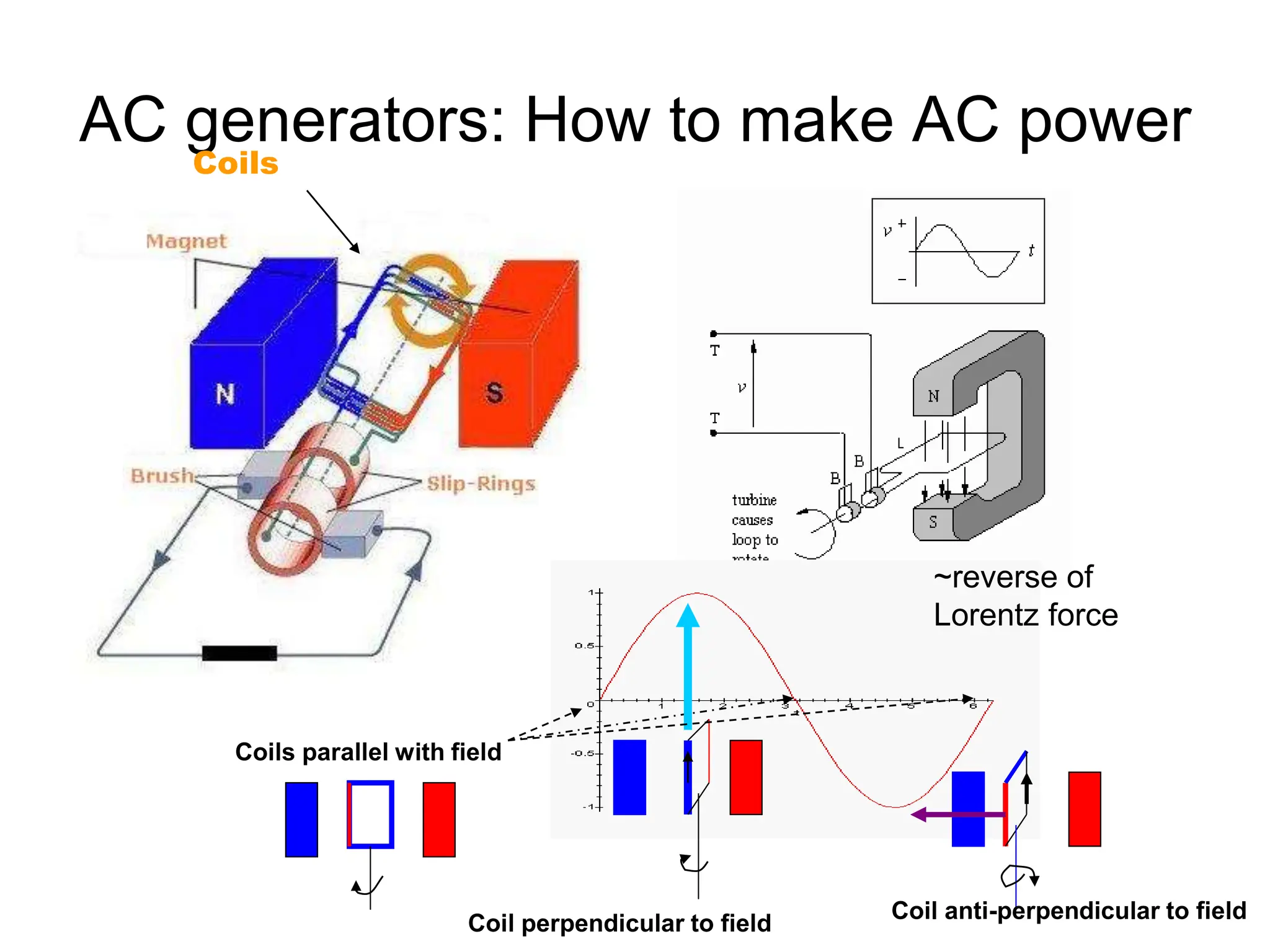
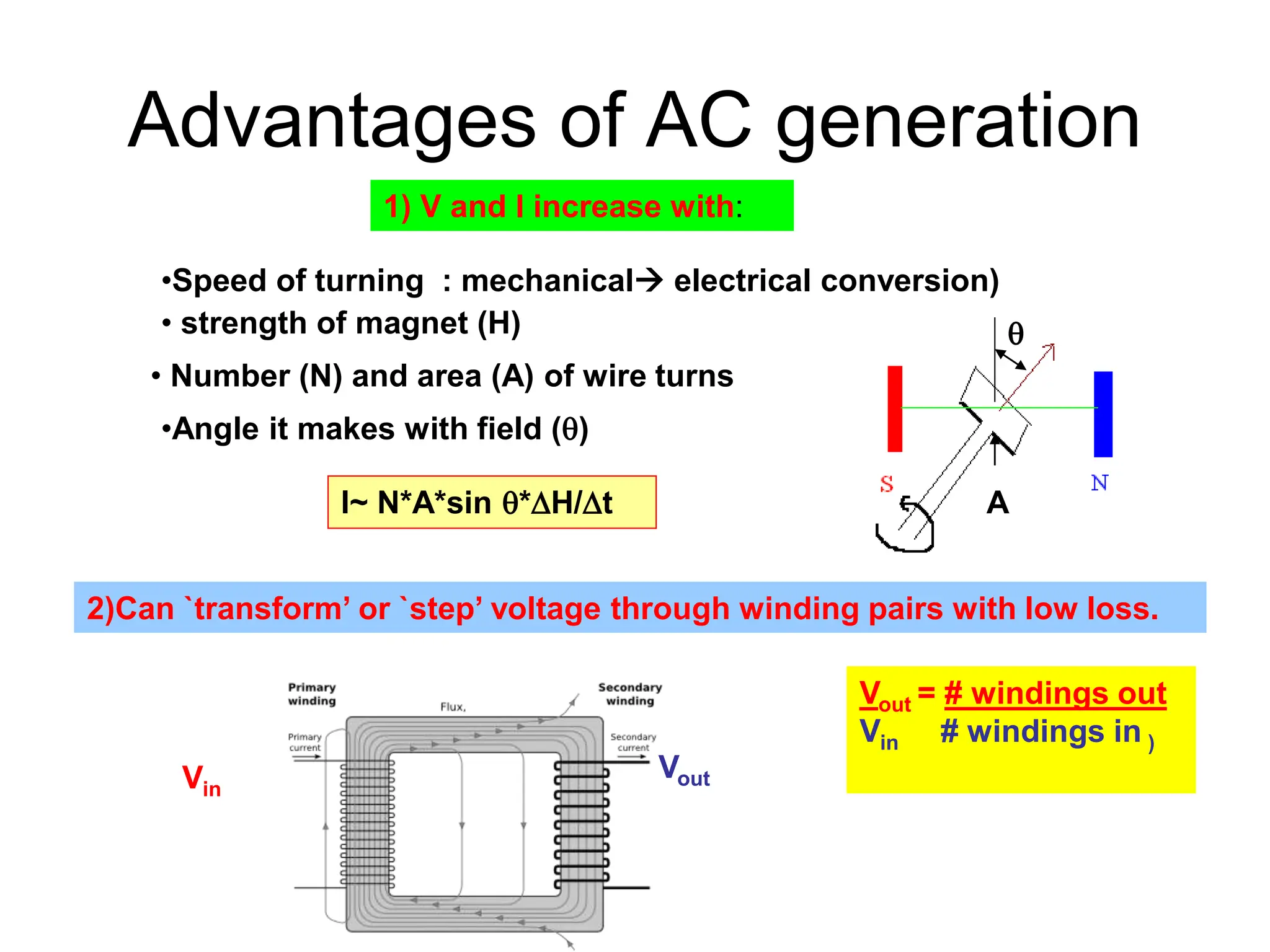
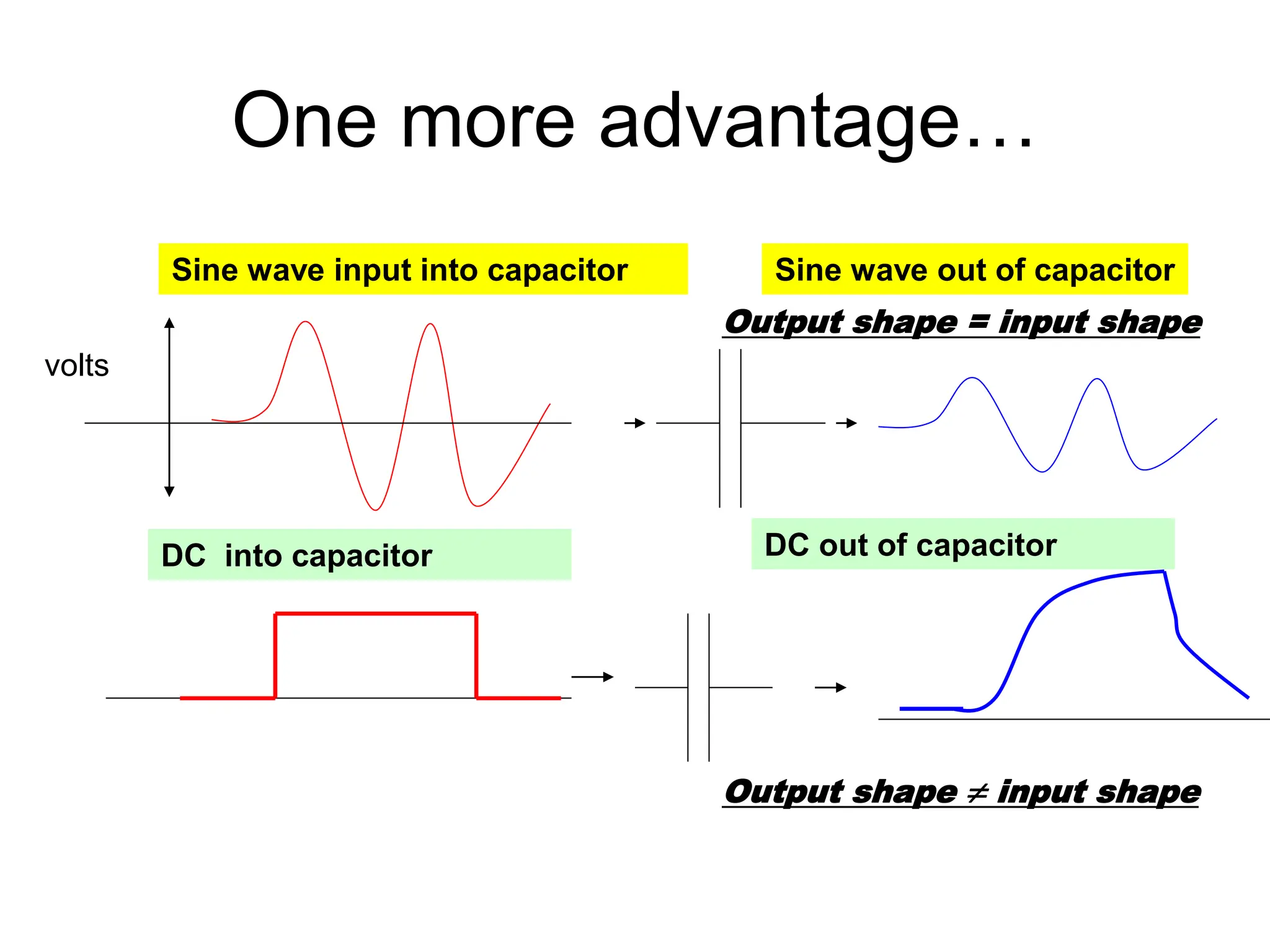
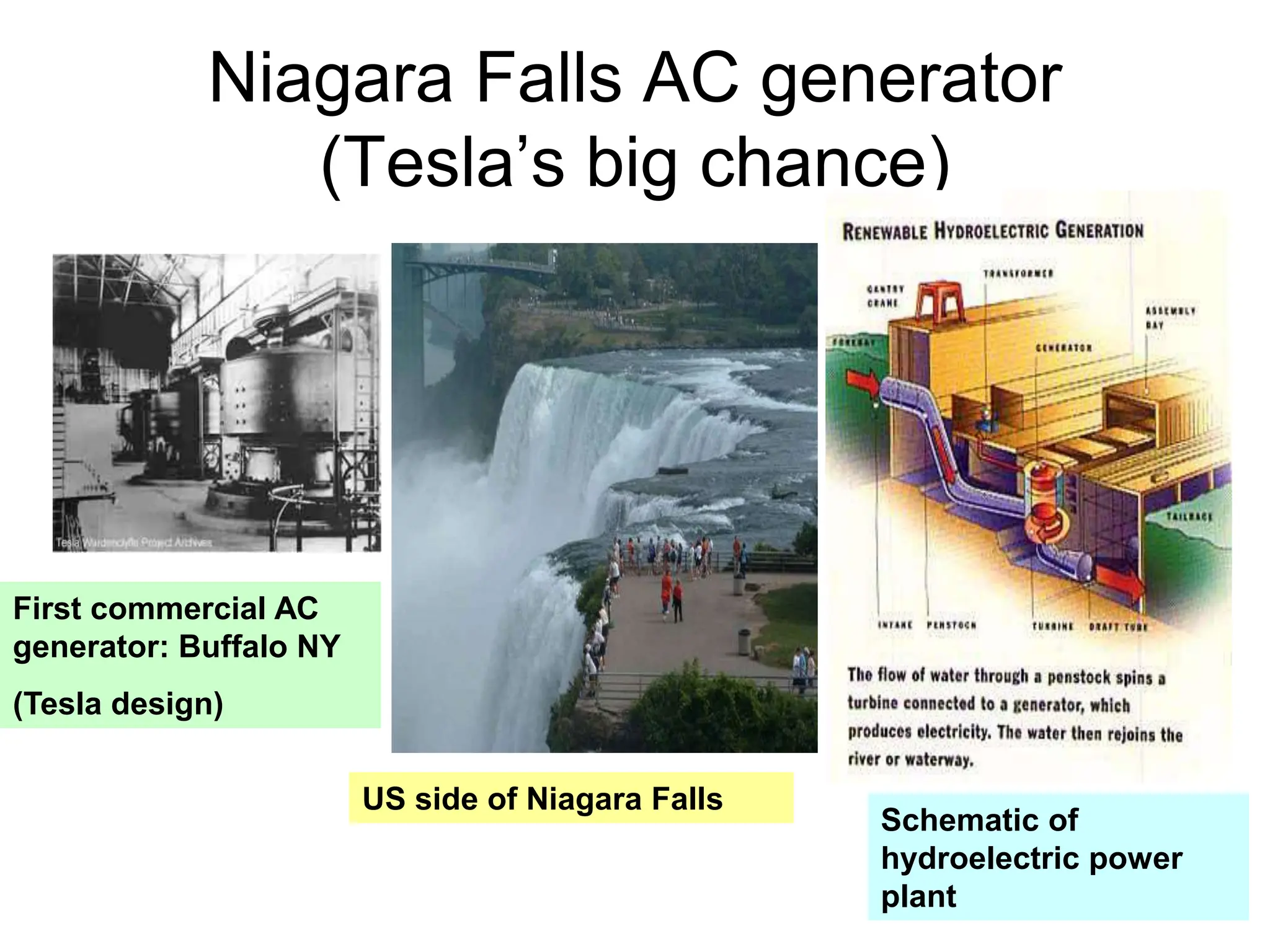
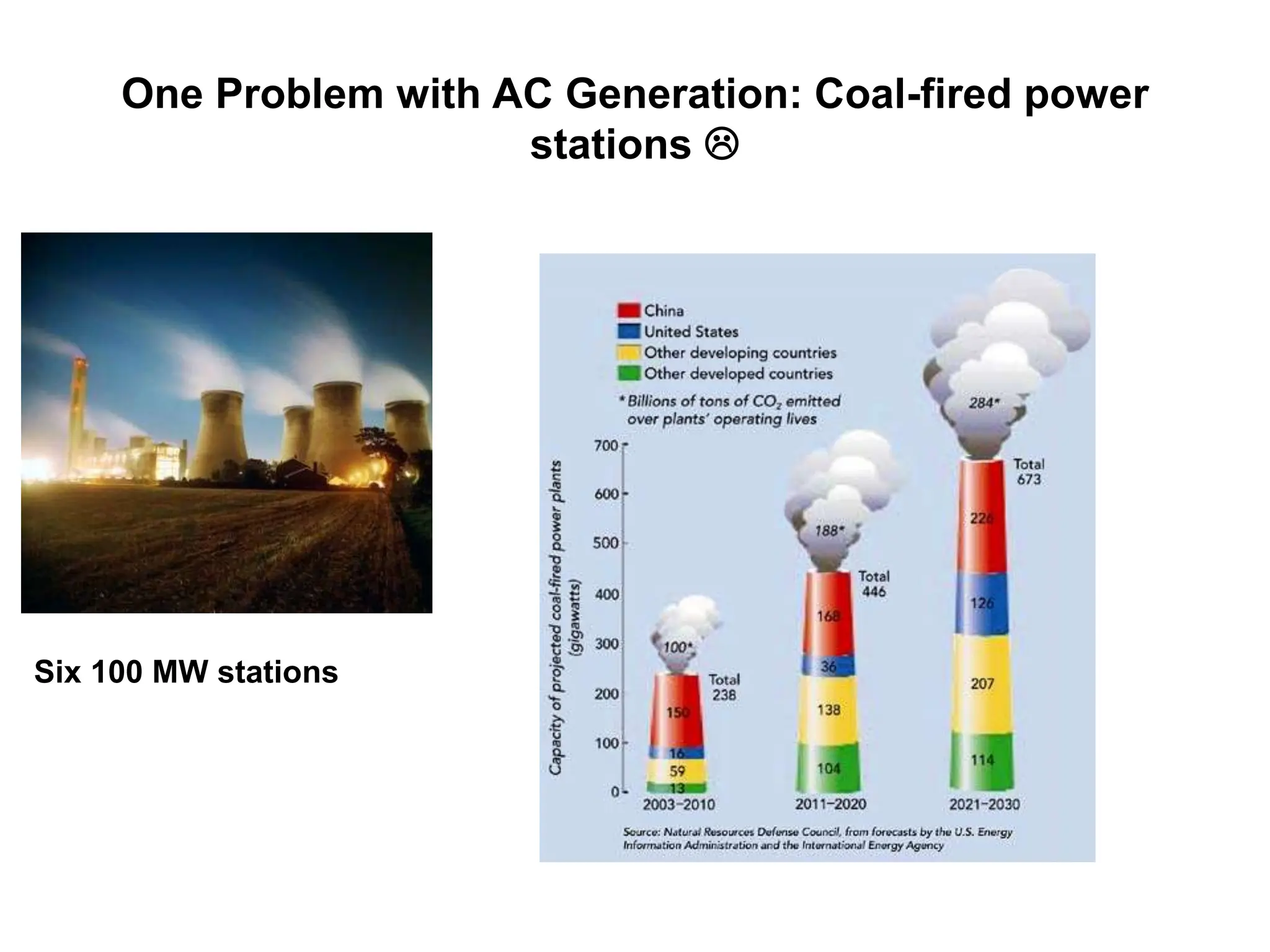
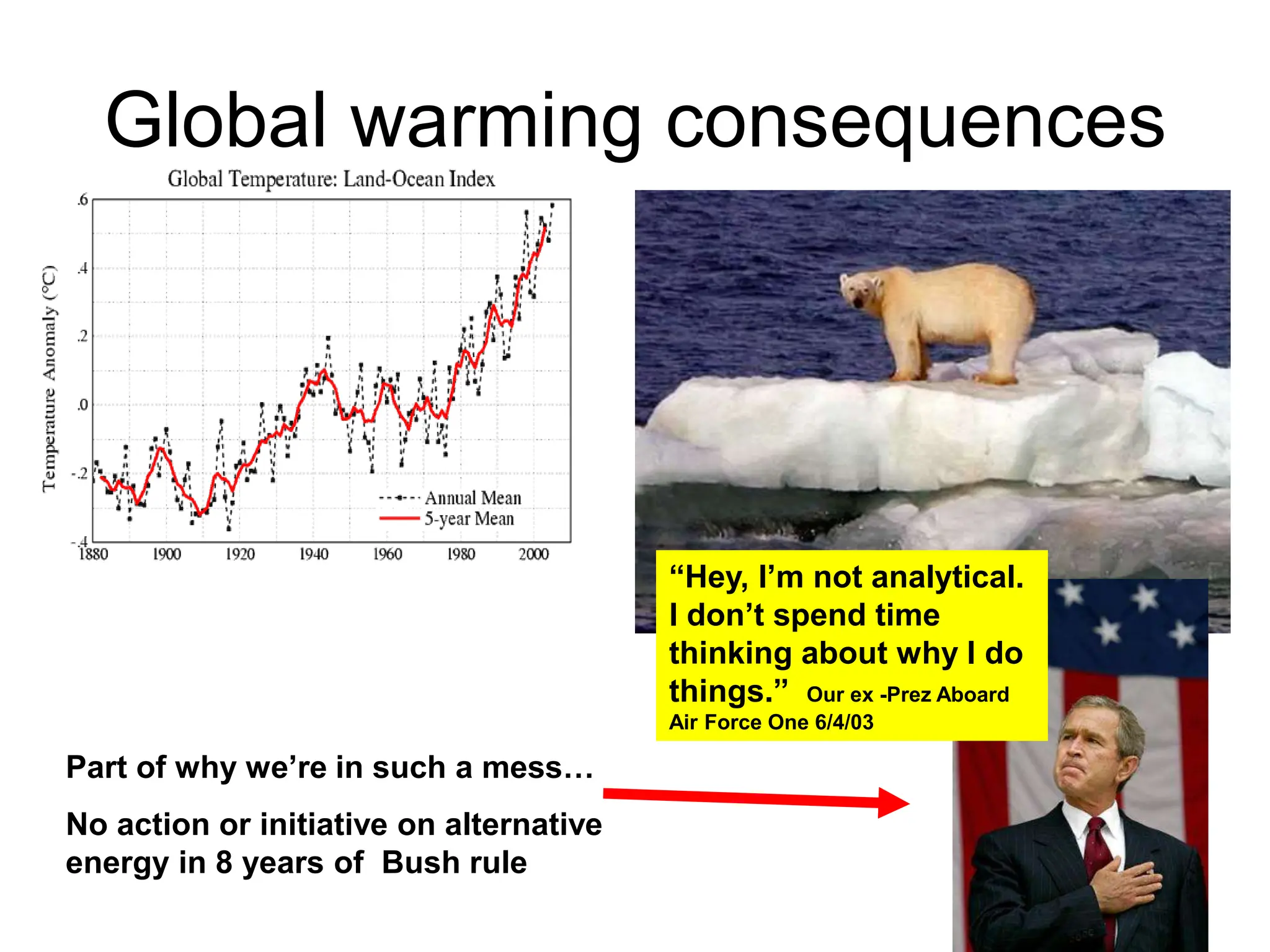
Alternating current has advantages over direct current for power transmission due to easier transformation of voltages. Early battles between Tesla and Edison established AC as the standard for power grids. Large-scale AC