The document introduces the Python programming language. It discusses Python's interpretor, data types like integers and strings, control structures like if/else statements and for loops, functions, classes, libraries, and input/output. It provides examples of key Python concepts like boolean logic, lists, dictionaries, regular expressions, and socket programming.




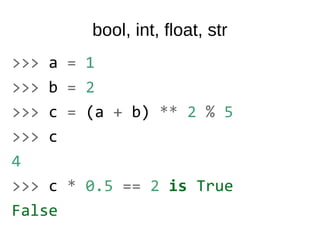
![tuple
>>> a, b = (1, 2, 3), (1,)
>>> a
(1, 2, 3)
>>> b
(1,)
>>> a + b
(1, 2, 3, 1)
>>> a[0]
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-7-320.jpg)
![tuple
>>> a[-1]
3
>>> a[1:2]
(2,)
>>> a[0:10:2]
(1, 3)
>>> a[::-1]
(3, 2, 1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-8-320.jpg)
![list
>>> a = ["text", 1, 0xFF, sum]
>>> a[0] * 3
'texttexttext'
>>> a[3]([a[1], a[1], a[1]])
3
>>> a[2]
255
>>> a.append(True)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-9-320.jpg)
![list
>>> a.insert(0, False)
>>> a
[False, 'text', 1, 255, <built-in
function sum>, True]
>>> dir(a)
[...,
'append', 'count', 'extend', 'index',
'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse',
'sort']
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-10-320.jpg)
![set
>>> a = set([1, 1, 2, 3])
>>> a
set([1, 2, 3])
>>> b = {2, 4, -1, 0}
>>> b
set([0, 2, 4, -1])
>>> help(set.union)
Help on method_descriptor:
union(...)
Return the union of sets as a new set.
(i.e. all elements that are in either set.)
(END)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-11-320.jpg)
![set
>>> a.union(b)
set([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, -1])
>>> a.intersection(b)
set([2])
>>> b.difference(a)
set([0, 4, -1])
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-12-320.jpg)
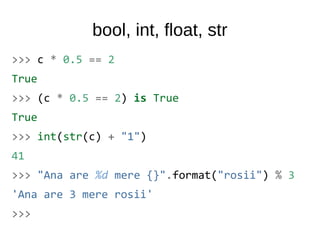
![dict
>>> a = dict()
>>> b = {1: "a", 2: "b"}
>>> b.keys()
[1, 2]
>>> a[_[0]] = b[2]
>>> a
{1: 'b'}
>>> a.update({True: False, False: True})](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-13-320.jpg)

![Referinte
>>> a = [1, 2, 3]
>>> b = a
>>> b.append(4)
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> del b
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> del a
>>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-15-320.jpg)
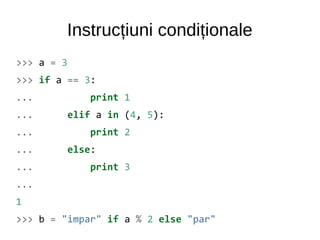
![Instrucțiuni condiționale
>>> print b
impar
>>> if True and (any([False, 0, None, 1]) or 0):
... print all([1, 2, 3, False])
...
False
>>>
* Nu exista switch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-17-320.jpg)
![Instrucțiuni repetitive
>>> a = range(10)
>>> a
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
>>> pare = list()
>>> for i in a:
... if not i % 2:
... pare.append(i)
...
>>> pare
[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-18-320.jpg)
![Instrucțiuni repetitive
>>> total = 0
>>> while pare:
... total += pare.pop()
...
>>> total
20
>>> sum([i for i in a if i % 2 == 0])
20
* Nu exista do-while](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-19-320.jpg)
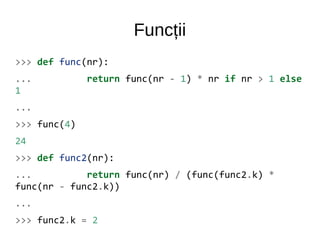





![Biblioteci
>>> import re
>>> text = """
... Abcdef 22 33 45 http://www.site.com/
... }{*| ----
... 11
... """
>>> re.findall("d{2}", text)
['22', '33', '45', '11']
>>> re.findall("(http://.+)", text)
['http://www.site.com/']
>>> re.findall("[a-zA-Z]+", text)
['Abcdef', 'http', 'www', 'site', 'com']
>>> re.findall("[^swd]+", text)
['://', '.', '.', '/', '}{*|', '----']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-27-320.jpg)




![I/O (3)
>>> cl
(<socket._socketobjec
t object at
0x7f09118627c0>,
('127.0.0.1', 58003))
>>>
cl[0].send("Salut!")
6
>>> cl[0].recv(1024)
'Salut!Salut!'
>>> a =
sock.recv(1024)
>>> sock.send(a * 2)
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/intro-140531044418-phpapp02/85/Intro-32-320.jpg)
