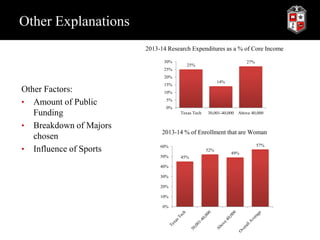
The document presents a case study examining how the size of public universities in Texas, based on enrollment, influences various factors related to enrollment. It finds that the significant factors influencing enrollment vary depending on the size of the institution. For smaller schools with under 10,000 students, location and economic factors are most significant, while for larger schools, measures of quality like acceptance rates, ACT scores, and rankings have a greater impact. The study has implications for Texas Tech University as it works to increase its enrollment to 40,000, suggesting it should focus recruitment within its region and not sacrifice quality for quantity of students.