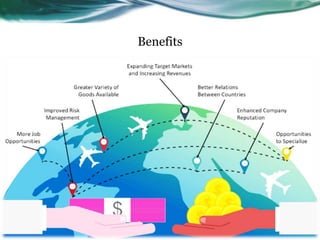
This document discusses international trade. It defines international trade and classifies its types, which include direct business, consignment business, and indent firms. It describes characteristics of international trade such as territorial specialization and government control. The document outlines importance, benefits, and barriers of international trade. It discusses reasons for companies to engage in global trade, as well as problems and advantages/disadvantages. Finally, it explains Adam Smith's theory of absolute advantage in international trade.